* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 11.3 Measuring Distances in Space
Reflecting instrument wikipedia , lookup
Gamma-ray burst wikipedia , lookup
Fine-tuned Universe wikipedia , lookup
Drake equation wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Aries (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Fermi paradox wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Hubble Deep Field wikipedia , lookup
Cassiopeia (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Cygnus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Perseus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Star formation wikipedia , lookup
High-velocity cloud wikipedia , lookup
Proxima Centauri wikipedia , lookup
Stellar kinematics wikipedia , lookup
Andromeda Galaxy wikipedia , lookup
Expansion of the universe wikipedia , lookup
Chronology of the universe wikipedia , lookup
Malmquist bias wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
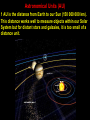
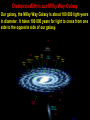
Measuring Distances in Space Sizes of Objects in the Universe Quarks (parts of neutrons and protons) are the smallest objects at 10-18 m while our universe is estimated to be 1026 m. This is a total difference of 1044 from smallest to largest things in our universe. Astronomical Units (AU) 1 AU is the distance from Earth to our Sun (150 000 000 km). This distance works well to measure objects within our Solar System but for distant stars and galaxies, it is too small of a distance unit. The Light-Year One light-year is the distance that light will travel in one year. It is 9 500 000 000 000 km or 9.5 trillion km. One light-year is about 63 000 AU. Distances to other stars and galaxies are measured in light-years. Distance to Proxima Centauri Proxima Centauri, a dim red dwarf, is the nearest star from our sun. It is 4.2 light-years away which means that the light we see from Proxima Centauri today started on its way 4.2 years ago (is 4.2 years old). This star is so dim it can only be seen through a telescope. It is the red object in the centre of the picture. Distances Within our Milky Way Galaxy Our galaxy, the Milky Way Galaxy is about 100 000 light-years in diameter. It takes 100 000 years for light to cross from one side to the opposite side of our galaxy. Andromeda Galaxy The distance to Andromeda galaxy, the nearest spiral galaxy to our Milky Way galaxy is 3.5 million light-years. The light we see today from Andromeda took 3.5 million years to get here, it is 3.5 million years old! Milky Way Andromeda Determining Distances by Triangulation The distance to a far away object can be determined by measuring two angles and the distance between those two angles. A line (called a baseline) is laid out and angle measurements are taken at the baseline endpoints to the distant object. Geometry and Trigonometry are then used to determine the perpendicular distance from the far away object to the baseline. Parallax Parallax is the apparent difference in position of an object against a distant background due to a change in position of the observer. Stellar Parallax If a star is viewed against a distant background at one “side” point in the earth’s orbit around the sun and then six months (1/2 an orbit) later, the star will appear to have moved slightly against the distant background. This is Stellar Parallax. More Distant Objects Show Less Parallax The Parallax Angle Astronomers measure angle p as the parallax angle. The distance in parsecs is computed by the formula, d = 1/p (in arcseconds). One parsec is 3.26 lightyears (about 31 trillion km) and one arc second is an angle of 1/3600 th of a degree. For example, Proxima Centauri has a parallax angle of .7687 arc seconds. It’s distance is 1/.7687 = 1.3009 parsecs. 1.3009 parsecs X 3.26 light-years/parsec = 4.243 light-years. The Parallax Method has Its Limits Parallax can now be used for star distances up to 1,600 lightyears using the Hipparcos satellite. In 2012, a new satellite (Gaia Mission) will measure star distances up to 10,000 light years. Hipparcos Gaia Measuring Distances Over 2000 Light-Years Astronomers use Cepheid Variable Stars, Supernovae and degree of Red Shift for measuring stars at great distances (beyond 10 000 Light-Years). Summary of Methods for Measuring Distances God is Beyond Measure. Man is Insignificant, Yet Cared For “When I consider your heavens, the work of your fingers, the moon and the stars, which you have set in place, what are mere mortals that you are mindful of them, human beings that you care for them?” Psalm 8: 3-4 In the Immense Universe, Humans Have Dominion Here “You have made them a little lower than the heavenly beings and crowned them with glory and honour. You have made them rulers over the works of your hands.” Psalm8: 5-6 God Redeems and Forgives Us “God does not treat us as our sins deserve or repay us according to our iniquities…As far as the east is from the west so far has he removed our transgressions from Him.” Psalm 103: 10, 12. How far is our sin removed? What Does the Vastness of the Universe Teach? Despite our smallness, the universe declares the greatness of God’s love. His love removes our sins beyond the ends of our universe for each one of us! “For as high as the heavens are above the earth, so great is His love for those who fear him. Psalm 103: 11 End of Presentation A A