* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download AIM: What is Astronomy? Do Now:
Astronomy in the medieval Islamic world wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Archaeoastronomy wikipedia , lookup
Equation of time wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Planets in astrology wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Planets beyond Neptune wikipedia , lookup
Satellite system (astronomy) wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
IAU definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Copernican heliocentrism wikipedia , lookup
Definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Planetary habitability wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Hebrew astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek astronomy wikipedia , lookup
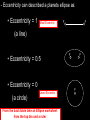
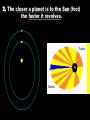
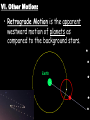
AIM: What is Astronomy? Do Now: Answer the following question in your notebook. Where is the sun in our solar system? What percent of our Solar System’s mass is occupied by the Sun? The sun makes up about 99% of our solar systems mass. I. Astronomy is the science that studies the universe and all objects in it. **Apparent motion= what an object appears to be doing, not what it is actually doing** Why do some objects appear to be moving in space? II. Two Views: • Geocentric: - Earth is motionless at the center of the universe; all planets including the sun revolve around it. • Heliocentric: - Sun is the center of the solar system; all planets revolve around it. (Simple explanation) Which one is true? Heliocentric III. Planetary Motion - Johannes Kepler made observations of objects in the night time sky. In doing this he discovered that: 1. The path of each planet around the sun is an ellipse (oval-shape), with the sun as one focus. - a focus is an object that a planet moves around. - Eccentricity measures the ellipse and describes it’s shape. Eccentricity = Distance between the foci Length of the major axis ESRT Cover Major Axis Focus 1 Focus 2 - Eccentricity can described a planets ellipse as: • Eccentricity = 1 Most Eccentric F F (a line) • Eccentricity = 0.5 • Eccentricity = 0 (a circle) Least Eccentric From the back table take an Ellipse worksheet from the top bin and a ruler F F F 2. The closer a planet is to the Sun (foci) the faster it revolves. Faster Slower IV. Measurement in Space • Astronomical unit (AU) - it is about 150 million kilometers. - is the average distance between Earth and the sun. • Light Year - the distance light travels in one year. V. Gravitational Force • increases as distance between objects decrease. (closer together = stronger force) • increases as mass increases. (more mass = more force) In which diagram does the star have the greatest gravitation force? The greatest mass and least distance VI. Other Motion: • Retrograde Motion is the apparent westward motion of planets as compared to the background stars. Closure: - Obtain an “Intro to Astronomy” worksheet (back top bin) -Using your ESRT and the notes answer the questions. Eccentricity = Distance between the foci Length of the major axis Major Axis Focus 1 Focus 2