* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Astronomers Learn to Work in Space
Arecibo Observatory wikipedia , lookup
CfA 1.2 m Millimeter-Wave Telescope wikipedia , lookup
Spitzer Space Telescope wikipedia , lookup
Advanced Composition Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Leibniz Institute for Astrophysics Potsdam wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
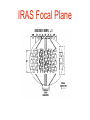
Astronomers Learn to Work in Space Technical Challenges Detectors Pointing and Stability Data Storage Contamination Thermal Control Background radiation First Astronomy from Space V-2 Rocket October 10, 1946 Ultraviolet spectrum of sun 340 nm – 240 nm Bead entrance UV film Aerobee X-ray and Gamma Ray Detectors Geiger counters Proportional counters Solid state detectors Scintillation detectors Explorer 11(1961) X-ray and Gamma Ray Imagers Rotating Grating Spark Chamber Cerenkov counter Grazing Incidence telescope Rotating Grating Spark Chamber Small Astronomical Satellites Three unstabilized survey satellites SAS A (Uhuru) – Rotating Grating SAS B – spark chamber SAS C tandem proportional counters Grazing Incidence Orbiting Solar Observatory 8 launches: 1962-1971 OSO 1 Wheel spun at 30 rpm Solar pointing within 2-3 arc minutes Dry lubricant used when possible; areas that required oils were sealed Passive temperature control using coatings Optical and UV Detectors Film Photomultipliers Vidicons SEC Vidicons IPCS Digicons CCDs Balloons Human Assisted Missions Gemini – hand-held near UV spectrograph Apollo – Spectrometer on moon Skylab – ATM, Small UV spectrograph, various X-ray experiments Spartan Spacelab Airplanes Orbiting Astronomical Observatory OAO Pointing Systems 3 rate gyros + high trust jets to slow tumble at launch <0.75o/s 3 wide-angle solar cells + gyros to orient satellite to sun-line 8 10o solar cells to orient satellite within 0.25o 6 star trackers (f.o.v. =1o) set to pick up at least 3 stars no fainter than magnitude 2 within 15 arc sec of predicted position Bore-sight star tracker to 2arcsec Fine rate gyros counteract drift Electro-magnets interact with terrestrial field to unload fine gyros with gas jets only a backup Data Handling for OAO Magnetic core memory 100 kbits Analog data could be transmitted in real time only 40-foot dishes in Quito and Santiago 85-foot dish in Rosman, NC Commands transmitted to stations and data returned by teletype Microwave link available between control station at Goddard and Rosman Automatic safe mode if commands discrepant OAO Mirrors OAO A: Standard quartz mirrors OAO B: Be mirror OAO C: Egg-crate quartz mirror Infrared Observations Detectors: Bolometer Solid state Heterodyne Survey Satellite: IRAS (1983) IRAS Focal Plane Radio Astronomy Explorer Two V antennas each with 229m arms 37m dipole 1968: Earth orbiter 1973: Lunar orbiter