* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 07 May: Omnis In Exitu Eius Pulchrima
Astrophotography wikipedia , lookup
Circumstellar habitable zone wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Cygnus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Advanced Composition Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Dyson sphere wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Planets beyond Neptune wikipedia , lookup
Star of Bethlehem wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Star formation wikipedia , lookup
Spitzer Space Telescope wikipedia , lookup
Directed panspermia wikipedia , lookup
Satellite system (astronomy) wikipedia , lookup
Late Heavy Bombardment wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical naming conventions wikipedia , lookup
Beta Pictoris wikipedia , lookup
Definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
IAU definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Nebular hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Exoplanetology wikipedia , lookup
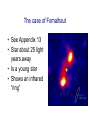
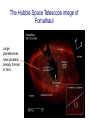
Other planetary systems Are there other “solar systems” out there? Can we see the processes of planetary formation going on in other star systems? When small particles condense, they are heated by the starlight, and radiate in the infrared. A star at the beginning of the planetesimal formation process will be bright at infrared wavelengths as well as in visible light The case of Fomalhaut • See Appendix 13 • Star about 25 light years away • Is a young star • Shows an infrared “ring” The Hubble Space Telescope image of Fomalhaut Large planetesimals have probably already formed in here Fomalhaut…a replica of the early solar system happening right now A final question: where can we see evidence that the planets “swept up” the planetesimals 4 - 4.5 Gyr ago? A final question: where can we see evidence that the planets “swept up” the planetesimals 4 - 4.5 Gyr ago? Can we find other star systems with a set of planets? Beta CVn Prior to 1995, it seemed impossible. The reflected light from a planet is tiny compared with the light emitted by a star In 1995, the discovery was announced of a Jupiter-sized planet around the solar type star 51 Pegasi How was the discovery made? Radial velocity measurements We detect the planet by measuring the star moving around the center of mass of the star-planet system The surprise came because to produce radial velocity variations as large as observed, a planet would have to be as large as Jupiter, but much, much closer to the star than Mercury is to the Sun HOT JUPITERS! Let’s do an example: 55 Cancri B • 55 Cancri: G8V star • Distance: 41 light years • 5 planets! • Planet b: >= 0.84 Jupiters • A=0.116 au • P=14.65 days • E=0.016 What we know now…the exoplanet catalog http://exoplanets.org The status of exoplanets • In 1995, none known • As of today, 453 planets known outside the solar system • Most are very different from planets in our solar system (hot Jupiters) • Developments in astronomical observations will discover many more, including ones like in the solar system • Stay tuned

















![SolarsystemPP[2]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008081776_2-3f379d3255cd7d8ae2efa11c9f8449dc-150x150.png)






