* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Our Solar System The Sun
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
Impact event wikipedia , lookup
Circumstellar habitable zone wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial atmosphere wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
Planets beyond Neptune wikipedia , lookup
Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Dwarf planet wikipedia , lookup
Planets in astrology wikipedia , lookup
Definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
IAU definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Naming of moons wikipedia , lookup
Planetary habitability wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial skies wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
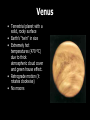
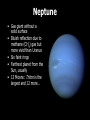
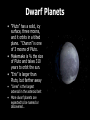
Our Solar System The Sun • It is a medium-sized yellow star in the middle of its life cycle. • Its the center of our Solar System and holds objects in orbit by gravity • More than 1,000,000 Earths can fit inside the Sun • The only source of energy, it’s fueled by nuclear fusion of small atoms to form larger ones • Has sun spots, solar flares, and prominences Mercury • Terrestrial planet with a solid rocky surface • Covered with craters • Extreme temperatures (from -170 ºC up to 467 ºC) • Thin atmosphere so its temperatures vary by day and night • Fastest planet to revolve around the Sun, thus named “Mercury” • No moons Venus • Terrestrial planet with a solid, rocky surface • Earth’s “twin” in size • Extremely hot temperatures (470 ºC) due to thick atmospheric cloud cover and green house effect. • Retrograde motion (it rotates clockwise) • No moons Earth • Terrestrial planet with a solid, rocky surface • Frozen caps at North & South Poles • Capable of supporting life due to [C], 70% water, and protective atmosphere • Seasons due to axis tilt • 1 Moon: “Luna” where we have landed multiple times and sent more than 70 spacecraft Earth’s Moon “Luna” • The moon acts like a mirror; it reflects sunlight to Earth • Phases of the moon occur as the moon revolves around Earth and reflects sunlight. • Tides -- high tide and low tide -- are caused by the moon’s gravitational pull Mars • Terrestrial planet with a solid, rocky surface • Red surface due to [Fe] • Enormous active volcanoes and dust storms • Thin atmosphere • Frozen polar caps like Earth • Liquid water once? • 2 Moons: Phobos and Deimos Asteroids • Made of rock, minerals, and rare elements • More than 100,000 orbit in the “Asteroid Belt” between Mars and Jupiter • Could collide with Earth, but probably won’t • One asteroid named “Ceres” is a dwarf planet • Moons: a few asteroids have moons Meteors or “Shooting Stars” • Pieces of rock that are falling toward Earth are meteors • They glow brightly as they are burning up due to fluid friction • Called “meteoroids” if they are far away, “meteors” if they have a bright tail, and “meteorites” once they hit Earth Answer this… • What is a solar system? • Where does energy come from in our solar system? • Name one characteristic of each planet we’ve talked about so far. • What do the first few planets in our solar system have in common? • What are “shooting stars?” Jupiter • The largest “gas giant” with no solid surface • Faint rings • Made of elements [H] and [He] with a hot, solid core of [Fe] -almost a star! • “Red Spot” is a massive storm • 62 Moons: the four largest are named Io, Europa, Ganymede, Callisto, but there are more… Saturn • Second largest gas giant without a solid surface • Famous for bright, icy rings that we can see from Earth with a telescope. The rings have large divisions. • Mostly made of elements [H] and [He] • Less dense than water! • 60 Moons: Titan and Pheobe and more, some orbit in the gaps of the rings Uranus • Gas giant without a solid surface • Made of elements (H) and (He) and water, ammonia and methane • Bluish reflection due to methane (CH4) gas • Faint rings, but the brightest clouds • Axis is turned “sideways” so it has wild seasons • Retrograde motion • 27 Moons: Ariel and more… Neptune • Gas giant without a solid surface • Bluish reflection due to methane (CH4) gas but more vivid than Uranus • Six faint rings • Farthest planet from the Sun, usually • 13 Moons: Triton is the largest and 12 more… Dwarf Planets • “Pluto” has a solid, icy surface, three moons, and it orbits in a tilted plane. “Charon” is one of 3 moons of Pluto. • Makemake is ¾ the size of Pluto and takes 310 years to orbit the sun. • “Eris” is larger than Pluto, but farther away • “Ceres” is the largest asteroid in the asteroid belt • More dwarf planets are expected to be named or discovered… Comets • Made of rock, ice and dust • Comets consist of a head, coma, and two tails that point away from the Sun • Short-period comets come from the “Kuiper Belt” and orbit the Sun every 200 years or less • Long-period comets come from the “Oort Cloud” and take longer to orbit the Sun Think About this… • What do the last of the planets in our solar system have in common? • Name one characteristic of each of the outer planets. • What is the relationship between the size of a planet and the number of moons it has? • What makes a planet a “dwarf planet?” Name the dwarf planets.