* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Bellringer - Madison County Schools
Orion (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Dyson sphere wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Constellation wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Star of Bethlehem wikipedia , lookup
Canis Minor wikipedia , lookup
Aries (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Corona Borealis wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Auriga (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Corona Australis wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Future of an expanding universe wikipedia , lookup
Cassiopeia (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
H II region wikipedia , lookup
Stellar classification wikipedia , lookup
Canis Major wikipedia , lookup
Cygnus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Malmquist bias wikipedia , lookup
Star catalogue wikipedia , lookup
Perseus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Cosmic distance ladder wikipedia , lookup
Stellar evolution wikipedia , lookup
Stellar kinematics wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
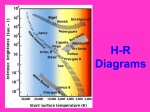
Characteristics of Stars Notes Classifying Stars • • • Characteristics used to classify stars include color, temperature, size, composition, and brightness. Which color has the SHORTEST wavelength? So which color has the MOST energy? Shorter wavelength=More energy. A star’s color gives clues about the star’s temperature. The coolest stars appear red. The hottest stars appear blue. Classifying Stars • Very large stars are called giant stars or supergiants. Our sun is a medium-sized star. MOST stars are small then the sun. • The majority of stars in the universe are red dwarfs. QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. If this video doesn’t play, click below: The Biggest Stars In The Universe.mp4 Classifying Stars • Stars differ in their chemical make-ups. Yes, the majority of chemicals inside a star include hydrogen and helium, but there are other ingredients as well. • Astronomers use spectrographs to find out what elements are in a star. A spectrograph is a device that breaks light into colors (like a prism). Scientists compare a star’s light with the light produced by different elements to find out what elements are in a star. Spectrographs Brightness of Stars • The brightness of a star depends on both its SIZE and TEMPERATURE. • Stars differ in how bright they are. A hot star shines brighter than a cool star. A large star shines brighter than a small star. Brighter Dimmer Is it possible to make the two lights the same brightness without modifying how much light they produce? If so, how? Brightness of Stars • A star’s brightness is described as its magnitude. • A star’s apparent magnitude is the brightness you see from Earth, or what it appears to look like from Earth. A hot, large star that is very far from Earth does not look very bright. But the sun look very bright because it is so close to Earth. Brightness of Stars • A star’s absolute magnitude is the brightness the star would have if all stars were the same distance from Earth. • If the spotlight was placed beside the flashlight, the spotlight would have a greater absolute magnitude. But if the spotlight were placed 10 miles away, then the flashlight would have a greater apparent magnitude. Increasing Distance from Earth Both star A and star B appear to have the same brightness from Earth. Which star has the greater ABSOLUTE MAGNITUDE? Which star has the greater APPARENT Measuring Distances to Stars • A light-year is the distance that light travels in one year. That’s 300,000 km/s for over 31.5 million seconds. That gives us about 9.461 trillion kilometers. • • Our closest star (other than Sol) is Proxima Centauri. It is over 4.5 light-years from us. That’s 9.461 trillion kilometers times 4.5. That number won’t even fit in your calculator without the use of Scientific Notation. A light-year is a unit of DISTANCE, not time. You could also measure distance on Earth in terms of time. For example, if it takes you one hour to ride your bike to the mall, you could say the mall is “one bicycle-hour” Measuring Distances to Stars • Parallax is the change in an object’s position you seem to see when you change your own position. The object does not really move, it only seems to change because you change your position. • To demonstrate this give a thumbs-up at eye level at arms length. Close one eye. Quickly switch eyes by closing the original eye, and opening the other. What appeared to happen to your thumb? Parallax Demos http://sci2.esa.int/interactive/media/flashes/2_1_1.htm http://www.astronexus.com/node/84 Click “Animation” on the right. Measuring Distances to Stars • • • Astronomers use parallax. They measure how far a star seems to move when Earth moves from one side of the sun to the other. The distance the star seems to move tells an astronomer how far the star is from Earth. Notice that the farther away the star is, the smaller the parallax angle. Stars can be too far away to accurately measure their distance using this method. This uses simple geometric math. The HertzprungRussell Diagram • The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram, or the H-R Diagram, shows how the surface temperature of stars is related to their ABSOLUTE magnitude. • The brightest stars are located near the top of the H-R Diagram, and the dimmest stars are located at the bottom. • The hottest (blue) stars are at the left of the diagram, whereas the coolest (red) stars are at the right. The HertzprungRussell Diagram • The points on the H-R Diagram form a pattern. Most stars on the H-R diagram fall into a band that spreads from the top-left corner to the bottom-right corner. This band is called the main sequence. • Stars in the main sequence are called main-sequence stars. About 90% of all stars are main-sequence stars. Betelgeuse is a Red Supergiant located in Orion Rigel is a Blue Supergian t located in Orion