* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Seasonal Motion
Antikythera mechanism wikipedia , lookup
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Copernican heliocentrism wikipedia , lookup
Constellation wikipedia , lookup
Archaeoastronomy wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Chinese astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Epoch (astronomy) wikipedia , lookup
Equation of time wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial skies wikipedia , lookup
Armillary sphere wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Stellar kinematics wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Standard solar model wikipedia , lookup
Hebrew astronomy wikipedia , lookup
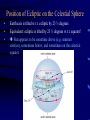
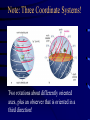
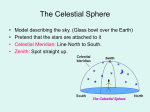
Seasonal Motion The Zodiac throughout the Year Example: In Winter sun in Sagittarius, Gemini at night sky; in summer sun in Gemini, Sagittarius at night sky How do we “see” that the earth is moving around the sun or v.v.? • Small discrepancy between sun’s motion and motion of stars • Sidereal vs solar day • At noon, say, the sun is not exactly in front of the same stars on the next day. – It is exactly in the south – The stars are faster, so a little west of south Position of Ecliptic on the Celestial Sphere • • • Earth axis is tilted w.r.t. ecliptic by 23 ½ degrees Equivalent: ecliptic is tilted by 23 ½ degrees w.r.t. equator! Sun appears to be sometime above (e.g. summer solstice), sometimes below, and sometimes on the celestial equator Note: Three Coordinate Systems! Two rotations about differently oriented axes, plus an observer that is oriented in a third direction! Homework: Starmaps 1& 2, March 1, 2006 & April 1, 2006 Homework: Star Maps 3 & 4, March 2, 2006 & March 1, 2007 Homework: Use Proportions • Angle traveled compared to full 360 degrees = time elapsed while traveling the angle compared to total time to complete a 360 degree, full rotation • angle/360 = time elapsed / x • x is the period we are looking for, will come out in same units as we put in “time elapsed”