* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Life Cycle of a Star
Nucleosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Astrophysical X-ray source wikipedia , lookup
Hawking radiation wikipedia , lookup
Planetary nebula wikipedia , lookup
White dwarf wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical spectroscopy wikipedia , lookup
First observation of gravitational waves wikipedia , lookup
Standard solar model wikipedia , lookup
Main sequence wikipedia , lookup
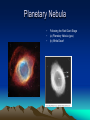
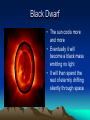
Life Cycle of a Star Waves, Atoms and Space Black Dwarf Stage 1 Protostars Protostars • Huge clouds of gas (hydrogen) in which stars are made. • Many thousands of times bigger than our solar system • As the clouds collapse stars are born in them Stage 2 Main sequence star Main Sequence Star • Burning Hydrogen • E.g. Our sun • Sequence lasts for about 10 000 million years • Our sun is about half way through it’s main sequence Stage 3 Red Giant Red Giant • As the sun runs out of hydrogen the outer layers of the sun will become cooler • They will also expand massively. • The Earth (along with Mercury, Venus and Mars) will be swallowed up. Planetary Nebula • • • Following the Red Giant Stage (a) Planetary Nebula (gas) (b) White Dwarf Stage 4 White Dwarf • The car engine is turned off … • Hood is still hot White Dwarf • Gravity will cause the red giant to collapse • The sun is now much cooler and it collapses into a small white star • **It still has the same mass as the original sun! Stage 5 Black Dwarf Black Dwarf • The sun cools more and more • Eventually it will become a black mass emitting no light • It will then spend the rest of eternity drifting silently through space Stars bigger than our sun! At least four times bigger (you don’t need to know about these for your exams) Stage 4 (for a big star) Red Supergiant Stage 5 (for a big star) Supernova 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. When the core is trying to fuse Fe No more energy can be gained Fusion stops, no more outward pressure Gravity Wins … the collapse starts After the collapse … rebound … material explodes out Heavy elements formed during these final stages Supernova! • The largest and most powerful explosions in the universe. • The red supergiants literally blow themselves apart! Supernova Remnant Supernova • All the heavy atoms made from came originally from these giant supernova explosions. Stage 6 (for a big star … after the rebound) Black hole Black hole • After the supernova a huge mass is left behind. • There is so much mass its gravity prevents even light from leaving it • Black holes can suck in nearby stars and solar systems. Supermassive Black Holes A supermassive black hole (SMBH) is the largest type of black hole, on the order of hundreds of thousands to billions of solar masses. Most—and possibly all—galaxies are inferred to contain a supermassive black hole at their centers. In the case of the Milky Way, the SMBH is believed to correspond with the location of Sagittarius A* Video Clip Neutron Stars A neutron star is a type of stellar remnant that can result from the gravitational collapse of a massive star during a Type (II) event. Such stars are composed almost entirely of neutrons, which are subatomic particles without net electrical charge and with slightly larger mass than protons Neutron Star Formation