* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Astrophotography wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Perseus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Cygnus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Discovery of Neptune wikipedia , lookup
Circumstellar habitable zone wikipedia , lookup
Space Interferometry Mission wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Star of Bethlehem wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Nebular hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Spitzer Space Telescope wikipedia , lookup
Kepler (spacecraft) wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Directed panspermia wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Planets beyond Neptune wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical naming conventions wikipedia , lookup
Dwarf planet wikipedia , lookup
Comparative planetary science wikipedia , lookup
Planets in astrology wikipedia , lookup
Exoplanetology wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Planetary system wikipedia , lookup
Definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Planetary habitability wikipedia , lookup
IAU definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
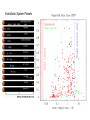
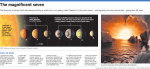
A Census of the Solar System 1 star and 8 major planets Mercury Venus terrestrial giant Earth (1) Mars (2) Jupiter (17) Saturn (18) Uranus (21) Neptune (8) Planetary comparisons The Gas Giants Jupiter -- 1/1000 Msun , 300 Mearth 1/10 Rsun , 11 Rearth Terrestrial Objects 7 largest moons Other members Dwarf Planets – Pluto and the Trans-Neptunian or Kuiper Belt Objects Highly elliptical orbit inclined 170 to ecliptic Brings it inside Neptune’s orbit, 1979 – 1999, Pluto was closer than Neptune Asteroids, Meteors and Comets Formation of Solar System The Condensation Sequence of the elements, minerals and molecules The Heavy Bombardment The Search for ExoSolar Planets Astrometric Detection Method Doppler Detection Method Transit Detection Method The first two methods are based on the fact that a planet orbiting a star will cause the star to "wobble" in space. The first method detects the component of this wobble that is horizontal to our line of site, and is based simply on observing the position of the star over time. ***The second method detects the component of the wobble that is radial to us, (i.e. directly towards or away from us), and is based on the Doppler shift in the star's light as the star moves towards or away from us. *** The third method is based on detecting the small drop in apparent luminosity of a star as a planet transits in front of it, between the star and the Earth. ExtraSolar System Planets Multiple systems As of 1 Feb, 2011 -- 519 planets confirmed Results from Kepler satellite: Press release Feb 2, 2011 A NASA telescope taking a nose count of planets in one small neighborhood of the Milky Way registered more than 1,200 candidates, including 58 residing in life-friendly orbits around their parent stars. The census, collected by NASA's Kepler Space Telescope after just four months of work, shows that small planets like Earth are much more prevalent than Jupiter-sized worlds and that multiple-planet systems are common (about 200).