* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download THE COSMIC DANCE
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Fine-tuned Universe wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Abundance of the chemical elements wikipedia , lookup
Expansion of the universe wikipedia , lookup
Flatness problem wikipedia , lookup
Outer space wikipedia , lookup
Lambda-CDM model wikipedia , lookup
Ultimate fate of the universe wikipedia , lookup
Structure formation wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Late Heavy Bombardment wikipedia , lookup
Cosmic microwave background wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Big Bang nucleosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
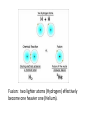
THE COSMIC DANCE with FLYBY, THE ASTRONOMY GUY Take a rocket faster than the speed of light (if that were possible)! • Go all the way back to the Big Bang Or we might enter a parallel universe through a wormhole, and come back through one into the past… 13.7 billion years ago (current theory) -- The Big Bang The Big Bang was not like a bomb going off in a specific place in a pre-existing Universe, it was the explosion of space and time itself from a point. GET THE POINT? The Big Bang makes the Universe like a balloon— it gets bigger as it gets blown up. TINY Microwave ENERGY SWIRLS OF ALL SIZES discovered in 2014 at the south pole by Chau-Lin Kuo and coworkers. They tell us the universe was chaotic early on, and expanded very INFLATION. quickly for a brief fraction of a second— BICEP2 Microwave Telescope at South Pole Chau-Lin Kuo confirms Chaos Theory of Big Bang by Stanford rules! Andre Linde. NEXT: Swirls of Energy make particles: mostly protons and electrons, which come together to make Hydrogen atoms. This coming together creates of electrons and protons to make Hydrogen gives off light we call… MICROWAVES. This is how we know what the lumps of matter look like At 380,000 years after the Big Bang—The Recombination Era. However, for roughly a minute, the Big Bang was hotter than 10 million degrees, and like a star, burned 25% of its Hydrogen into Helium. Fusion: two lighter atoms (Hydrogen) effectively become one heavier one (Helium). 13.5 billion years ago – First Light: First stars ignite, gravity pulling the atoms together and heating them to over 10 million degrees. They ignite to Hydrogen fusion. There is a funny energy in space (usually called dark energy) driving the acceleration like a compressed sponge when released. 12 - 13.5 billion years ago – Birth of the Milky Way galaxy 4.6 billion years – birth of the Solar System and the Earth 4.4 Billion years ago, Mars-sized object hits earth Creates vapor that condenses into our moon. 3.3 Billion years ago an asteroid about 25 miles across hits earth and destroys any life on the surface. Life had to start over? 3 billion years – earliest record of life – Australian bacterial fossils 67 million years – extinction of dinosaurs by asteroid colliding with earth. Asteroid 6 miles wide. Wiped out about 75% of life on the earth. 7 million years ago --’human like’ and walking on 2 legs in Africa 120,000 years ago --our ancestors, the Cro-magnons The Future? 1. Falling into Andromeda Galaxy Impact in about 2 billion years 2. Sun becomes a Red Giant and consumes the Earth in about 4.5 billion years.