* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Sky and the Motions of the Earth
Armillary sphere wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Archaeoastronomy wikipedia , lookup
Copernican heliocentrism wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Chinese astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Lunar theory wikipedia , lookup
Astronomy on Mars wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
Comparative planetary science wikipedia , lookup
Constellation wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial skies wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Axial precession wikipedia , lookup
Hebrew astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
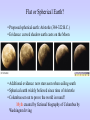
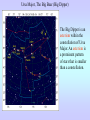
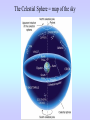
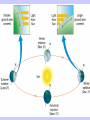
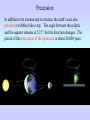
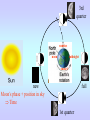
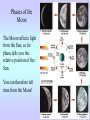
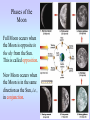
Motions of the Earth and Sky I Outline for Today • • • • • • • History: flat vs. spherical earth Map of the sky Constellations Diurnal and Yearly Motion The seasons Precession Phases of the Moon Flat or Spherical Earth? • Proposed spherical earth: Aristotle (384-322 B.C.) • Evidence: curved shadow earth casts on the Moon • Additional evidence: new stars seen when sailing south • Spherical earth widely believed since time of Aristotle • Columbus set out to prove the world is round? Myth created by fictional biography of Columbus by Washington Irving Constellations • Constellations are patterns of stars that have a historical reference to a mythological figure, animal, or object. • The stars are usually not near each other in space; they just lie in the same direction. 101 LY ~80 LY 124 LY Ursa Major, The Big Bear (Big Dipper) The Big Dipper is an asterism within the constellation of Ursa Major. An asterism is a prominent pattern of stars that is smaller than a constellation. The Celestial Sphere = map of the sky Daily Motion • The earth’s axis of rotation also defines some places on the celestial sphere. • The celestial North pole is over the earth’s north pole. There happens to be a bright star near it, which is called Polaris, or the North Star. • The celestial equator is the extension of the earth’s equator. Daily Motion • Each day, the earth rotates once (west-to-east) on its axis. This causes us to face different directions and see different stars. The stars’ daily (diurnal) motion reflects the earth’s spin. stars appear to rotate about the north & south celestial poles Yearly Motion In addition to rotating, the Earth also revolves about the Sun. As the earth revolves the Sun is projected in front of different constellations at different times of year. The path the Sun takes across heavens is called the ecliptic. The constellations which the Sun passes through are zodiac constellations. Because the Sun is bright, we can only see some constellations at certain times of year. The Seasons • The earth’s spin axis is tilted 23.5° with respect to the plane of the earth’s orbit (the ecliptic). • Because of tilt, the “directness” of sunlight changes during the year. • northern hemisphere tilted toward the Sun summer solstice • southern hemisphere tilted toward the Sun winter solstice • Neither is tilted toward the Sun vernal and autumnal equinox • Seasons not caused by earth changing its distance from the Sun The Seasons During summer, the Sun moves higher in the sky, so sunlight is more direct, and it is visible for a longer period of time. QuickTime™ and a Video Format cvid decompressor are needed to see this picture. Precession In addition to its rotation and revolution, the earth’s axis also precesses (wobbles) like a top. The angle between the ecliptic and the equator remains at 23.5°, but the direction changes. The period of this precession of the equinoxes is about 26,000 years. Precession In addition to its rotation and revolution, the earth’s axis also precesses (wobbles) like a top. The angle between the ecliptic and the equator remains at 23.5°, but the direction changes. The period of this precession of the equinoxes is about 26,000 years. QuickTime™ and a Sorenson Video 3 decompressor are needed to see this picture. Because of precession: • Polaris won’t always be the North Star • The season during which a constellation appears at night changes very slowly over time 3rd quarter sunrise noon midnight sunset new Moon’s phase + position in sky Time full 1st quarter http://www.csulb.edu/~gpickett/ps112_ems.html http://www.astro.psu.edu/users/kluhman/a5/Lunar_Nav.swf Phases of the Moon The Moon reflects light from the Sun, so its phase tells you the relative position of the Sun. You can therefore tell time from the Moon! Phases of the Moon Full Moon occurs when the Moon is opposite in the sky from the Sun. This is called opposition. New Moon occurs when the Moon is in the same direction as the Sun, i.e., in conjunction.