* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Eight Worlds wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Earth's rotation wikipedia , lookup
Space: 1889 wikipedia , lookup
Giant-impact hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Planets in astrology wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
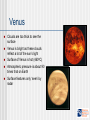
Foundations of Astronomy Science and Religion in Schools Project - Unit 4a The Scientific Account of the Beginning The Sun Ball of super-hot gas Core temperature 16 million degrees ºC Roughly 4.5 billion years old Will last another 4.5 billion years A very typical star The Solar System In this image, the planets are in the correct order The relative sizes of the planets is about right, but the distances are not The Sun is the arc on the far left! Mercury 0.4 times Earth’s diameter No atmosphere worth mentioning Surface temperature 1700C on average Mercury rotates two times for every three orbits round the Sun Takes 88 days to orbit the Sun Distance from the Sun is about 0.4 times that of Earth Venus Clouds are too thick to see the surface Venus is bright as these clouds reflect a lot of the sun’s light Surface of Venus is hot (4600C) Atmospheric pressure is about 90 times that on Earth Surface features only ‘seen’ by radar Guess where? Meteorites Lumps of rock from space that generally burn up in the atmosphere Some large ones make it to the surface and can cause damage The Moon Orbits the Earth No atmosphere Some water, as ice Craters due to being hit by meteorites Probably made when a giant meteor hit the Earth and blasted part of the crust into space Phases of the Moon Moon keeps the same face to the Earth Time it takes to turn on its axis, same as the time taken to orbit Earth Phases dependent on how much of the Moon visible from Earth is lit by the Sun Mars Atmosphere is carbon dioxide Atmospheric pressure is 0.75% of Earth’s Smaller than Earth, but about the same size of land area Being well explored by unmanned probes Martian Surface Olympus Mons Olympus Mons is the large volcano in the top left The pale features are clouds drifting over the region Jupiter Largest planet in the solar system Composed entirely of gas Black dot is the shadow of Europa Large red dot is a hurricane - bigger than Earth 11 times the diameter of Earth and a thousand times more massive Saturn Beautiful gas giant Nearly as big as Jupiter Ring system can clearly be seen from Earth with even a small telescope Saturn’s rings Complex structure of rings Large gap is the Cassini division The F ring contains shepherd moons The Moons lap each other every 25 days Can cause the rings to be ‘braided’ Uranus True colour image from Voyager 2 makes Uranus seem bland Infra-red image from the Hubble Space telescope shows more activity and the thin ring system Hubble image shows cloud structure Also that Uranus rotates on it side so it ‘rolls’ around the Sun, unlike the other plants Neptune Final gas giant Similar in size to Uranus Great dark spot was thought to be a storm system, but could be a ‘hole’ like the hole in Earth’s ozone layer High altitude ‘wispy’ clouds can also be seen Pluto Pluto’s orbit crosses that of Neptune Also highly angled with respect to the other planets Pluto’s moon Charon was discovered in 1978 New planet? Discovered on 14 November 2003 Far beyond Pluto Orbit yet to be worked out Status as a planet to be determined (is it big enough?) Provisionally called Sedna, the Inuit goddess of the sea, who was believed to live in the cold depths of the Arctic Ocean The Milky Way Andromeda Galaxy Nearest galaxy to the Milky Way Still about 2 million light years away In about 3 billion years, Andromeda will collide with our galaxy Can be seen with the naked eye on a dark night Deep Field One of the most important pictures ever taken Hubble space telescope Try to count the number of galaxies! This patch of sky could easily be covered by the end of your finger at arm’s length