* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Gamma-ray burst wikipedia , lookup
Drake equation wikipedia , lookup
Anthropic principle wikipedia , lookup
Fermi paradox wikipedia , lookup
Spitzer Space Telescope wikipedia , lookup
Outer space wikipedia , lookup
Hubble Space Telescope wikipedia , lookup
Dark energy wikipedia , lookup
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Shape of the universe wikipedia , lookup
Cosmic microwave background wikipedia , lookup
Big Bang nucleosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Star formation wikipedia , lookup
Cosmic distance ladder wikipedia , lookup
Andromeda Galaxy wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
H II region wikipedia , lookup
Fine-tuned Universe wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Ultimate fate of the universe wikipedia , lookup
Expansion of the universe wikipedia , lookup
Flatness problem wikipedia , lookup
Lambda-CDM model wikipedia , lookup
Hubble's law wikipedia , lookup
Physical cosmology wikipedia , lookup
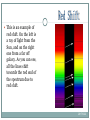
The Discovery of Universe By: Karen Ivy Introduction Of Edwin Hubble Edwin Powell Hubble (November 20, 1889 – September 28, 1953) was an American astronomer. His keen knowledge was combined with a powerful toolHooker Telescope with its 100-inch mirror on top of Mount Wilson in California. Hubble used the telescope resolution and light gathering power to take a series of photograph of the great nebula in Andromeda. An nebula is an interstellar cloud of dust, hydrogen, helium and other ionized gases and Andromeda is a spiral galaxy. For the first time the image revealed faint stars in the nebula. Hubble now knew the Andromeda was a collection of stars. PICTURE 2017/5/22 Discovery Of Galaxy Hubble had a question: How far away is the Andromeda Nebula? He calculated the distance based on the variable stars. In 1923, Hubble found dozens of these variable stars in Andromeda, and determined their distance. Andromeda contains a spiral-shaped galaxy that, at a distance of 2.2 million light-years, is the farthest object visible to the naked eye. He calculated that Andromeda must be at least 10 times farther away than the farthest stars in the Milky Way. The Andromeda nebula was really the Andromeda galaxy. This discovery implies that the other, even fainter, spirals were probably also galaxies even farther away. A nebula is an interstellar cloud of dust, hydrogen, helium and other ionized gases. Astronomers no longer thought our galaxy was the entire universe. Now they knew that the universe was composed of many, many galaxies. PICTURE 2017/5/22 The Big Bang Theory(1) How did our universe begin? How old is our universe? How did it all begin? Everyone was curious about this question. Many once believed that the universe had no beginning or end and the universe was infinite. Through the inception of the Big Bang theory, the universe was no longer considered as infinite. The origin of the Big Bang theory can be credited to Edwin Hubble. Hubble made the observation that the universe is continuously expanding. He discovered that a galaxy’s velocity is proportional to its distance. Galaxies that are twice as far from us move twice as fast. The Big Bang Theory(2) Universe is expanding in every direction. This observation means that it has taken every galaxy the same amount of time to move from a same starting position to its current position. Just like the Big Bang provided for the beginning of the universe, Hubble's observations provided for the beginning of the Big Bang theory. Since the Big Bang, the universe has been continuously expanding and, thus, there has been more and more distance between clusters of galaxies. Galaxies moving farther away from each other is known as the red shift. As light from distant galaxies approach earth there is an increase of space between earth and the galaxy, which makes wavelengths being stretched. The Big Bang Theory (3) The universe began in an extremely hot and dense condition and it was continuously expanding, even today. But the universe is getting cooler as well, scientists believe that universe was approximately 13.8 billion years ago. Scientists base the Big Bang theory on many different observations. The most important is the red shift of very far away galaxies. Red shift is the Doppler Effect occurring in light. 2017/5/22 PICTURE 2017/5/22 PICTURE 2017/5/22 Red Shift In physics, redshift happens when light or other electromagnetic radiation from an object moving away from the observer is increased in wavelength, or shifted to the red end of the spectrum. In general, whether or not the radiation is within the visible spectrum, "redder" means an increase in wavelength – equivalent to a lower frequency and a lower photon energy, in accordance with, respectively, the wave and quantum theories of light. This is an example of red shift. On the left is a ray of light from the Sun, and on the right one from a far off galaxy. As you can see, all the lines shift towards the red end of the spectrum due to red shift. 2017/5/22 Something similar happens to sound waves when a source of sound moves relative to an observer. This is called the Doppler effect. As the train moves towards a person, the sound it makes as it comes towards them sounds like it has a higher tone, since the frequency of the sound is squeezed together a little bit. As the train speeds away, the sound gets stretched out, and sounds lower in tone. The same happens with light when an object that emits light moves very fast. An object, like a star or a galaxy that is far away and moving toward us, will look more blue than it normally does. This is called blue shift. A star or galaxy moving farther away from us will look more red than it should, that's where red shift got its name. 2017/5/22 Thanks For Watching! 2017/5/22