* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Circumstellar habitable zone wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
Cygnus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Nebular hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Spitzer Space Telescope wikipedia , lookup
Astronomical unit wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Planets beyond Neptune wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
IAU definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Planets in astrology wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Stellar kinematics wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
Space Interferometry Mission wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Exoplanetology wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Definition of planet wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Planetary system wikipedia , lookup
Kepler (spacecraft) wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
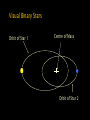
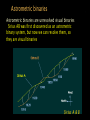
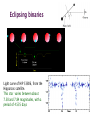
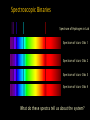
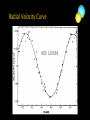
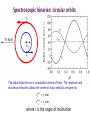
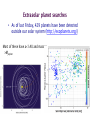
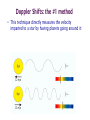
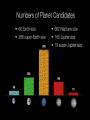
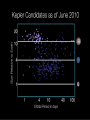
Somak Raychaudhury Lecture 7 www.sr.bham.ac.uk/~somak/Y2SiU/ Guest Lecturer: Dr W. J. Chaplin Two-body problem Binary stars Visual Eclipsing Spectroscopic How to find extrasolar planets Two-body problem: centre of mass The two bodies must have the same angular speed ω, otherwise one body will catch up with another and the force will no longer be directed towards the common centre of the circles. Two-body problem: centre of mass But Types of binary stars Visual Binary Stars Orbit of Star 1 Centre of Mass Orbit of Star 2 Astrometric binaries Astrometric binaries are unresolved visual binaries Sirius AB was first discovered as an astrometric binary system, but now we can resolve them, so they are visual binaries Sirius A & B Eclipsing binaries In these stars, inclination is close to 90 deg Eclipsing binaries Light curve of HIP 53806, from the Hipparcos satellite. This star varies between about 7.58 and 7.84 magnitudes, with a period of 4.535 days Spectroscopic Binaries Spectrum of Hydrogen in Lab Spectrum of stars- Obs 1 Spectrum of stars- Obs 2 Spectrum of stars- Obs 3 Spectrum of stars- Obs 4 What do these spectra tell us about the system? Spectroscopic binaries The absorption lines are redshifted or blueshifted as the star moves in its orbit Radial Velocity Curve HDE 226868 Spectroscopic binaries: circular orbits • The radial velocities are a sinusoidal function of time. The minimum and maximum velocities (about the centre of mass velocity) are given by v1max v1 sin i r v2max v2 sin i r where i is the angle of inclination Measuring masses in a binary Kepler 3: Observed speeds We know the value of i only if the binary has eclipses Methods of finding exoplanets Pulsar timing 1992 (PSR 1257+12) Doppler shift Astrometry Microlensing Direct obs. Transit 1995 2002 ? 2003 2004 (51 Peg b) (Gl 876 b) (O235/M53) (2M1207) 2000 and 2004 Exoplanets are extreme cases of binaries, where one member is much less massive than the other. So we can use some of the same techniques as binaries for detection, and mass measurement. We’ll discuss some of these methods. (HD209458b) Extrasolar planet searches • As of last Friday, 429 planets have been detected outside our solar system (http://exoplanets.org/) Most of these have a<1 AU and masses >MJupiter Direct Detection: very hard The albedo of the Earth is about AV=0.4. Issues to think about: How bright is it in visible (reflected) light, relative to the Sun? How do they compare at infrared wavelengths, where Earth emits thermal radiation? A picture of Earth, from the surface of Mars, just before sunrise. Doppler Shifts: the #1 method • This technique directly measures the velocity imparted to a star by having planets going around it: All gravitationally bound systems orbit their Centre of Mass (CM). Here index 1 refers to the Sun, and 2 to the planet C.M. outside the surface of the Sun! Sun’s wobble due to Jupiter Here index 1 refers to the Sun, and 2 to the planet Period of Jupiter’s orbit=13.86 years Speed of Jupiter around Sun= We expect Speed of Sun around c.m.= Transits • Imagine viewing the Earth-Sun system from a distant star. By how much will the Sun fade during a transit of the Earth? How about during a transit of Jupiter? Planetary transits • This is a fairly direct technique that relies on the correct orientation of the solar system to give rise to the transit of a planet across the face of its star. Transits • Detects a planet's shadow when it transits in front of its host star. • Can be used to measure the radius of a planet. Transit method Space Interferometry mission • NASA: Would have searched for terrestrial planets around the nearest ~250 stars, with astrometry accurate to 1mas. Cancelled in 2010 Kepler • NASA mission launched in 2009 • Searching for large numbers of stars for Earth-sized terrestrial planets using the transit method. Field of view Cygnus-Lyra regions along the Orion arm NASA Kepler Mission • Finding Earth-like planets • Formal seismology component: Kepler Asteroseismology Investigation (KAI) • KAI has an international consortium of ~400 scientists called the Kepler Asteroseismology Science Consortium (KASC) http://kepler.asteroseismology.org NASA Kepler Mission • Nominal mission 3.5 yr (up to 10 yr) • Will observe Sun-like and classical pulsators: – Survey Phase: 1-month data on ~1500 Sun-like stars! – Long-Term Phase: data for several years on 100 Sun-like stars Kepler Results Chaplin et al. (2010)