* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Neritic Zone
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
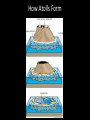
Neritic Zone Ms. Bridgeland Where is the Neritic Zone? • Extends from the low-tide line out to the edge of the continental shelf • Why is the neritic zone home to so many living things? The Neritic Zone is home to so many living things because: • The shallow water over the continental shelf receives: – Sunlight – Steady supply of nutrients washed from the land into the ocean – The light and nutrients enable large plantlike algae to grow – Large quantities of algae is a food source and shelter for other organisms Neritic Zone • Of the three ocean zones, it has the most constant conditions and is easiest for organisms to live in Upwelling • In the Neritic Zone, upwelling currents bring nutrients from the bottom to the surface. – These nutrients support plankton (the base of food webs) – Major fisheries in upwelling areas include: • Monterey Canyon (off the California coast) • Newfoundland’s Grand Banks • Georges Ban (off the New England coast) Coral Reefs Coral Reef • A diverse habitat found in the Neritic Zone • Looks like it is made of rock, but is actually made of living things • Created by colonies of tiny coral animals • Coral animals: each produce a hard structure that surrounds its soft body – When the coral dies, the empty structure remains Coral Reefs can only form in shallow, tropical ocean waters because: – Microscopic algae live in the bodies of the coral animals – Provide food for the corals – Algae need warm temperatures and sunlight – Reefs grow above the continental shelves or around volcanic islands where the water is shallow Atolls • A ring-shaped reef surrounding a shallow lagoon • An atoll begins as a reef that closely surrounds the edges of a volcanic island • As the sea-floor sinks, the island sinks with it, and the reef continues to grow upward • The island sinks until it is completely underwater, and you can only see the atoll Atoll How Atolls Form Types of Coral • Elkhorn • Brain • Plate • Star Elkhorn Coral Brain Coral Plate Coral Star Coral Coral Reef Animals • Octopus • Spiny lobsters • Shrimp • Fish Animals in the Coral Reef What produces the fine, soft sand around the reef? • The Parrotfish grinds up the broken coral inside their bodies, which produces the sand Benefits of the Coral Reef • Protect the coastline from violent storms • The reefs prevent waves from severely eroding the land Harm to Coral Reefs • Coral grows only a few millimeters per year, so if a boat anchor drags across it, reefs cannot easily recover • Changes in water temperature and clearness endanger the reefs • Cloudy water harms the algae because it reduces the amount of light reaching them • Coral animals need to eat the algae to live































![Planet Earth - Shallow Seas[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/005018245_1-ccc70e34b50477455ce86a81f666ba9f-150x150.png)

