* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ambit - Cheminformatics software for data
Serializability wikipedia , lookup
Entity–attribute–value model wikipedia , lookup
Extensible Storage Engine wikipedia , lookup
Oracle Database wikipedia , lookup
Open Database Connectivity wikipedia , lookup
Ingres (database) wikipedia , lookup
Functional Database Model wikipedia , lookup
Microsoft Jet Database Engine wikipedia , lookup
Relational model wikipedia , lookup
Concurrency control wikipedia , lookup
Astrophysics Data System wikipedia , lookup
Database model wikipedia , lookup
AMBIT
Chemoinformatics Software for Data
Management
Joanna Jaworska
P&G Brussels,
Belgium
Nina Jeliazkova
Ideaconsult Ltd.,
Bulgaria
Introduction – why Ambit ?
Limited free, publicly accessible, methodologically transparent software
was identified as one of the roadblocks for broadening use of in-silico
methods (ICCA Workshop in Setubal 2002, OECD)
Realization that efficient use of existing information on chemicals requires
better ways for
• Storage
− standardized formats, computer automated verification of structures,
capability to store large amounts of data
• Taking advantage of rapidly evolving field of data mining and extraction of
relevant information
IT strategy
Ambit - building blocks for Decision Support System
High emphasis on
• interoperability for “plug and play”
• Flexibility modular design
• Transparency
− Open source, relying on open standards. Open source software lowers the
user barrier, facilitates the dissemination activities and enables the
reproducibility of models and results
− The cheminformatics functionality relies on the open source Java library – The
Chemistry Development Kit http://cdk.sourceforge.net/
− The software is based on MySQL database (www.mysql.com), which is the most
popular open source relational database.
− Chemical Markup Language (CML)
• acknowledged method of encoding chemical data in XML
• Is being adopted by a large number of chemical organisations, from government,
through commercial to academia.
• The choice of CML for the internal format makes the database independent of the
software which is able to access it, in contrast to some proprietary solutions.
Ambit - Overview
AMBIT software is a set of libraries and tools, providing various
cheminformatics functionalities for data management.
The AMBIT system consists of a database and functional modules
allowing a variety of flexible searches and mining of the data stored in the
database.
The unique feature of AMBIT is the ability to store multifaceted
information about chemical structures and provide a searchable interface
linking these diverse components.
Ambit overview
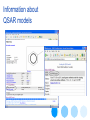
The AMBIT database:
• stores chemical structures, their identifiers such as CAS, INChI numbers; attributes such as molecular descriptors,
experimental data together with test descriptions, and literature references. The database can also store QSAR
models. In addition the software can generate a suite of 2D and 3D molecular descriptors.
• can be searched by identifiers, attribute value or range, experimental data value or range, user defined structure and
substructure, structural similarity
• AMBIT database contains over 450 000 chemical compounds with data imported from over a dozen databases
[http://ambit.acad.bg/ambit/stats/]. The number of compounds is growing all the time and one the of system’s great
strengths is that any dataset can be imported for comparison and analysis. AMBITDatabaseTools 1.10 allows the user
to create a local database and to import his own sets of chemical compounds.
AMBIT Discovery performs chemical grouping and assesses the applicability domain of a QSAR
offering a variety of methods including using different approaches to similarity assessments: statistical
that rely on ‘descriptor space’; approaches based on mechanistic understanding; and approaches based
on structural similarity.
ToxTree ToxTree is a flexible user friendly application which integrates structure based (classification)
schemes. Currently 3 schemes are available: Verhaaar for fish toxicity, Cramer for human acute toxicity,
BfR rules for skin irritation. ToxTree implements a plug-in mechanism, allowing to be extended by modules
developed at a future time, without recompiling the application. ToxTree and AMBIT modules can be
integrated one within another.
Toxmatch – stand alone application for pairwise similarity assessments with intention for read-across.
QSAR database under development. Will store information in QMRF. Large effort on standardization
AMBIT Database Today
Not restricted to these datasets!Any dataset can be imported.
(e.g. DSSTox, AQUIRE, LLNA …)
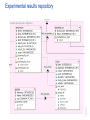
AMBIT Database Schema
Experimental results repository
Ambit database
Two user interfaces to the database
• Online
• Standalone
Online
• a more restricted interface
Standalone
• Full interface
• Can be used for storing & managing confidential data
Common
• Can link with other databases and pull information via webservices
AMBIT database functionalities
Storage: information about chemicals name and structure, descriptors, experimental data and
QSAR models
• Example with a tailored template : BCF golden database LRI project ( EURAS) Q2 2007
• QSAR database with QMRF ( ECB funded)
Conversion:
• Different computer formats of structure, CAS-structure
Calculation
• Variety of descriptors
• The available list is growing thanks to contributions to CDK
Search
• identification search
(CAS, SMILES, chemical name)
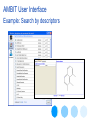
• Descriptor search
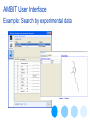
• Experimental data search
• Substructure and similarity search
Complex searches with multiple criteria (standalone)
What kind of searches are desired ?
•Detailed analyses for pairwise similarity
•Similarity of a compound to compounds in the database
•Similarity of a compounds to a reference set
•Similarity of a set of compounds to compounds in the
database
•Grouping based on chemical class
Ambit online
Searching for basic information
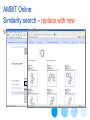
AMBIT Online:
Similarity search – replace with new
search results !!!
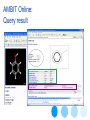
AMBIT Online:
Query result
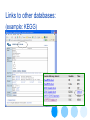
Links to other databases:
(example: KEGG)
Link to Aquire
Information about
QSAR models
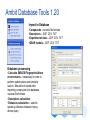
Ambit Database Tools 1.20
Standalone application
available at http://ambit.acad.bg/downloads
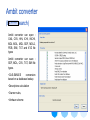
Ambit converter
(Batch search)
Ambit converter can open :
CML, CSV, HIN, ICHI, INCHI,
MDL MOL, MDL SDF, MOL2,
PDB, SMI, TXT and XYZ file
types
Ambit converter can save :
SDF, MOL, CSV, TXT, SMI file
types.
•CAS-SMILES
conversion
based on a database lookup
•Descriptors calculation
•Cramer rules,
•Verhaar scheme
Ambit Database Tools 1.20
Import to Database
•Compounds – several file formats
•Descriptors – SDF, CSV, TXT
•Experimental data – SDF, CSV, TXT
•QSAR models – SDF, CSV, TXT
Database processing
•Calculate SMILES/Fingerprints/Atom
environments – necessary in order to
perform substructure and similarity
search. Should be invoked after
importing compounds into database
•several file formats
•Descriptors calculation
•Distances calculation – used to
speed up distance between heavy
atoms query
Ambit Database Tools 1.20
•perform a CAS RN search in the database (submenu "Search ->
CAS RN search");
•perform a SMILES search in the database (submenu "Search ->
SMILES");
•perform a molecular formula search in the database (submenu
("Search -> Molecular formula");
•define structure,descriptor,distance-based and experimental
data criteria and perform searches in the database database
•Output:
•On screen
•To file
The user can select between the different datasets
existing in the AMBIT database.
Subsequent searches will be performed only
within the selected dataset
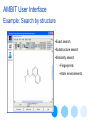
AMBIT User Interface
Example: Search by structure
•Exact search
•Substructure search
•Similarity search
•Fingerprints
•Atom environments
AMBIT User Interface
Example: Search by descriptors
AMBIT User Interface
Example: Search by experimental data
Similarity based on toxicity mechanism
Verhaar scheme
Verhaar H.J.M., Van Leeuven C., Hermens J.L.M.,Classifying Environmental Pollutants. 1: Structure-Activity Relationships for
Prediction of Aquatic Toxicity, Chemosphere, Vol.25, No.4, pp.471-491, 1992
34 rules
5 classes
• Class 1. Narcosis or baseline toxicity
• Class 2 Less inert compounds
• Class 3 Unspecific reactivity
• Class 4 Compounds and groups of
compounds acting by a specific
mechanism
• Class 5 Not possible to classify
according to these rules
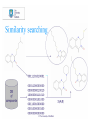
Chemical similarity assessment using the
database
Exact substructure search based on 2D
Structural Similarity search (various methods)
Criteria on descriptors
Based on mechanistic understanding ( Verhaar scheme)
Another view on Similarity assessments
with Toxmatch and Discovery
Discovery
• similarity to a set (summary representation)
Toxmatch
• pairwise similarities
• Similarity to a set (nearest neighbours)
Thank you
Questions?