* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ch. 7, Nutrition
Survey
Document related concepts
Fat acceptance movement wikipedia , lookup
Abdominal obesity wikipedia , lookup
Gastric bypass surgery wikipedia , lookup
Obesity and the environment wikipedia , lookup
Adipose tissue wikipedia , lookup
Vegetarianism wikipedia , lookup
Body fat percentage wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbohydrate diet wikipedia , lookup
Diet-induced obesity model wikipedia , lookup
Food choice wikipedia , lookup
Saturated fat and cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Childhood obesity in Australia wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
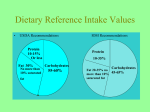
Ch. 7, Nutrition What does food supply? Energy Nutrition Pleasure What is hunger/appetite? Hunger – Physical need to eat – Pangs, weakness, dizziness, nausea. Appetite – Desire to eat - WANNIT What stimulates appetite? Holidays People (i.e. “Gramma”) Places – Movies, mall, etc. What technological changes and societal changes have taken place since 1900 that affect our diets? 1900 – Lots of grain, some fruit//veg, little meat or sweets. 2000 – Lots of meat & sweets, some fruits/veg, less grain. Changes since 1900. Working mothers Convenience – fast food Frozen foods Transportation Canning industry Leisure time spent away from home Cultural differences Key Terms: Nutrition – the science of the way a body uses food. Nutrients – substances that provide energy or build tissues. Metabolism – the chemical process that your body uses to keep you alive and active. Calorie – unit of energy Six Essential Nutrients – Carbohydrates, Fats, Proteins, Vitamins, Minerals, Water Carbohydrates – 4 calories per gram. 50% of diet Simple – Sugar, easily changed to glucose. Complex – Starch, also changed to glucose Glycogen – Carbohydrates that are stored by the body for quick energy. Excess is converted to fat. Fiber – Indigestible fibers necessary for the digestive tract (makes you poo). Fat – 9 calories per gram. 30% or less of diet Uses for fat – stored energy, padding, insulation, ingredient in hormones, storage of vitamins/minerals. Lipids or Triglycerides – another name for fats. Fats are a carbon chain with hydrogen molecules attached. Saturated Fat – As many hydrogen atoms are bonded to the chain as possible. Solid at room temp. Found in animal meats. Unsaturated Fat – Less hydrogen atoms. Mainly found in plant foods. Liquid at room temp. Cholesterol – Another type of Lipid found in animal tissue used to make vitamin D, cell membranes and coverings on nerve fibers. Your body makes all you need. LDL Cholesterol (Low Density Lipid) – Bad. Mixes with fat to create plaque in the blood vessels. Increases risk of heart attack and stroke. Found in red meat. HDL Cholesterol (High Density Lipid) – Good. Carries cholesterol back to the liver to be removed from the blood. Protein – 4 calories per gram. 15% of diet. Protein is used to build tissues, hormones and antibodies. Amino Acids – 20 different amino acids make one protein. 9 of them cannot be made by our body. Complete Protein – A food containing all 9 amino acids. Meat. Incomplete Protein – A food containing less than 9 amino acids. Plants. Vegetarian Diets – This is a healthy way to eat if you plan meals to combine plant foods to create complete proteins. (Vegetarian is an Indian word that means “Lousy Hunter”.) Example: nuts and seeds with grains create a complete protein. A peanut butter sandwich on whole grain bread is a good example. Vitamins – Regulate chemical reactions Fat Soluble – dissolve in fat. Vitamin D is an example. It promotes absorption of Calcium. Water Soluble – dissolves in water. Vitamin C is a good example. Vitamin C is an antioxidant. More examples are on pages 161 and 162. Minerals – Contribute to normal function of body and bone formation. Examples: Calcium – building blocks for bone. Iron – Hemoglobin (red blood cells) Sodium (salt) – Electrolytes More examples on page 163. Water Water is about 60% - 70% of your body weight. Functions of water Medium for chemical reactions Transport nutrients, gasses and waste Regulate body temperature Dehydration – loss of too much water. May cause headache, nausea, disorientation and death. RDA Recommended Daily Allowance as set by the Food and Drug Administration. This is only a guideline for nutrition. Personal body chemistry may vary and require a different diet. Food Labels Serving Size – There may be more than one serving in a package. Everything else on the label will pertain to just one serving relative to a 2000 calorie per day diet. Ingredient List – Largest amount listed first. ABC’s of good health Dietary Guidelines by the American Heart Association. Aim for Fitness Weight and exercise Build a healthy base Use the food pyramid Choose sensibly Foods low in saturated fat and cholesterol Drinks and foods low in processed sugar Low salt foods Avoid alcohol or limit the intake Simple steps to healthful diets Choose foods based on “nutrient density”. A candy bar, for example, may fill you up and have over 200 calories, but they are not useable energy calories. Choose beverages based on nutritional value. Soda pop is a liquid candy bar. Diet pop is high in sodium. Alcohol causes dehydration. Sports drinks, milk and water are better choices for hydration and nutrient intake Snacking – Occasional treats are OK, but moderation is the key. Special Dietary Needs Athletes – Eat and drink to win 24/7. Carbohydrates give you the energy to perform in a game or at practice. Protein builds muscle. Iron builds red blood cells to carry oxygen. Vitamins and minerals keep away cramps and enhance the immune system. Water is needed to transport it all. Pregnancy – Eat and drink to build a healthy baby. Increase caloric intake. Protein is especially important for building the tissues of the fetus. Vitamins B6 and B12 with zinc and iron help avoid birth defects. Alcohol intake goes to the fetus in mass amounts and may cause birth defects. Illness – Force yourself to eat and drink so that the soldiers in your immune system have enough energy to fight. Pop Quiz 1. Carbohydrates provide a. 4 calories per gram b. 9 calories per gram 2. Fat provides a. 4 calories per gram b. 9 calories per gram 3. Protein provides a. 4 calories per gram b. 9 calories per gram 4. A change of 500 calories per day will make a difference of _____ pound(s) at the end of the week. 5. Complex carbohydrates are a. Sugar b. Starch 6. Protein calories are used for a. Immediate energy b. Building tissues c. Insulation/padding 7. Fat is a. Used to make hormones b. Used for storage of calories c. Used for padding d. All of the above 8. Saturated fat is a. Associated with heart disease b. Comes from plant foods 9. The good type of cholesterol is a. LDL b. HDL 10. Protein is made of Amino Acids. Vegetarian diets can provide all the Amino Acids to make a complete protein. a. True b. False 11. Iron is a mineral that is needed in sufficient amounts to a. Prevent Osteoporosis b. Build red blood cells c. Make electrolytes 12. Water is over 50% of your body weight and needed to transport nutrients and waste. a. True b. False 13. Food labels must show all of the following except a. b. c. d. Serving size Calories per serving Calories per ingredient RDA percentages 14. Ingredient lists show what is least in the package first. a. True b. False 15. From bottom to top, the food pyramid shows a. b. c. d. Bread, fruits/vegetables, sweets, meats Bread, meats, fruits/vegetables, sweets Meats, sweets, bread, fruits/vegetables Bread, fruits/vegetables, meats, sweets Answers 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. A B A One B B D A B 10. A 11. B 12. A 13. C 14. B 15. D