* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Universal Motor
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
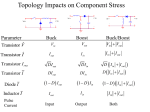
Electricity & Magnetism • An electric current in a wire creates a magnetic field. [http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/nova/magnetic/images/reve-current.gif] Click here to view demonstration videos. [http://demoroom.physics.ncsu.edu/multimedia/images/ demos/797Solenoid_and_iron_filings.jpg] Electricity & Magnetism • Conversely, a moving magnet can create an electric current in a wire. Click Here for a Demo Electric Generators • Motion is turned into Electricity • A “force” spins a loop of wire inside a magnet producing electric current • This occurs because of electromagnetic induction [http://www.nhn.ou.edu/~jeffery/course/c_energy/energyl/lec0 05/turbine_001_diagram.jpg] Electric Generators • Generators normally produce Alternating Current (AC) which changes the direction that electrons move. (120 times per second) • Batteries produce Direct Current (DC) where electrons always move the same direction. Click Here for an Interactive Example Electromagnets • Piece of iron placed inside a loop of copper wire. • Magnetic field is present only when current is flowing in the wire. [http://media.fwbell.com/images/electromagnet.gif] Magnetic poles reverse when current is switched. S N N S [http://www.speakercity.ca/images/diagram.gif] Click Here for Speaker Demo Electric Motors • Electricity is turned into motion. • Current is passed through an electromagnet so it turns inside a “normal” magnet to produce motion. Click Here for Demos http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/0/04/Electri c_motor_cycle_2.png/300px-Electric_motor_cycle_2.png Electric Motors • For DC motors, the commutator switches the current in the electromagnet. Transformers • These change the voltage of alternating current. Click Here for an Interactive Demo [http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/en/thumb/1/1c/Polemount-singlephase-closeup.jpg/397px-Polemount-singlephase-closeup.jpg] Voltage is controlled by the coils of wire at the ends. Vout Vin Power is the same [http://www.worsleyschool.net/science/files/transformers/stepdown.gif] Vout Vin [http://www.worsleyschool.net/science/files/transformers/stepdown.gif] Transformers • Example: • What does the voltage change to in the transformer below? Vin = 50 V Vout = ? Iin = 10 A Iout = 2.5 A [http://www.worsleyschool.net/science/files/transformers/stepdown.gif] First, calculate the power on the primary side… Vin = 50 V Vout = ? Iin = 10 A Iout = 2.5 A [http://www.worsleyschool.net/science/files/transformers/stepdown.gif] P=VxI P = 50 V x 10 A P = 500 W Power is equal on both sides, so use the power to calculate Vout… Vin = 50 V Vout = ? Iin = 10 A Iout = 2.5 A [http://www.worsleyschool.net/science/files/transformers/stepdown.gif] 500 W = V x 2.5 A 2.5 A 2.5 A V = 200 V