* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download GYNECOMASTIA - Dave Palumbo
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
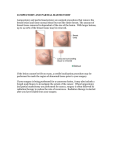
GYNECOMASTIA “Hey, look at Charlie. His breasts are so big you could milk him like a cow!” How many teenage boys have been emotionally traumatized in gym class by a legion of cruel and sadistic kids who take pleasure in seeking out the slightest imperfections among their peers? How many men, young and old, are living with this embarrassing condition for innumerable years not realizing that there is a very simple corrective procedure available? For those of you who are a bit confused, what I’m referring to is a medical condition known professionally as gynecomastia; colloquially as “bitch tits”. Literally translated, gynecomastia means “woman-like breasts” and, believe it or not, gynecomastia affects an estimated 40 to 60 percent of all men in either one or both breasts. Just as woman don't enjoy being teased about having small breasts; men are extremely sensitive when it comes to having a hint of breast tissue hanging from beneath their nipples. I mean, it’s only reasonable to believe that if King Kong doesn't have "bitch tits"; why should I? What causes the overgrowth of breast tissue in men? Commonly, 30-40% of the time, gynecomastia appears in adolescent boys around the age of 12 and lasts about 2-3 years. When boys enter puberty they start producing large quantities of the masculinizing, muscle-building, hormone, testosterone. As testosterone levels rise in the body, a certain percentage converts into the predominately female hormone, estrogen. Boys whose mammary glands (found under the nipple) are particularly sensitive to estrogen seem to exhibit an abnormal overgrowth of their breast tissue. In most, this condition disappears; however, in about 10% of the male population it persists as a stigma throughout life. Another type of gynecomastia that is commonly seen among athletes usually results from the use of synthetic anabolic steroids. When large quantities of exogenous steroids are taken, testosterone levels rise rapidly and the body responds by converting the excess testosterone, via aromatase enzymes, into estrogen. This elevated testosterone level provides significant gains in muscle mass and strength; however, the resulting estrogen often causes long-term changes in the breasts. In some steroid users, gynecomastia may occur after the very first injection. In others it may require many months of repeated use; while in some, they may never see as much as a single lump. When evaluating steroid consumption, gynecomastia is more often than not a doserelated phenomenon. Other causes of gynecomastia include obesity, aging (estrogen levels increase as men age), estrogen-producing tumors, genetic and familial predispositions, chronic liver disease (e.g. chronic alcoholism), and drugs (e.g. antacids, diuretics, cardiac medications, marijuana, and Valium). In rare cases, gynecomastia can transform into cancerous growths. When this occurs, a painless nipple discharge and ulceration may be noted. In some areas of the Middle East and around the Horn of Africa, such incidences of male breast cancers climb to more than 6% of all gynecomastia cases. Presentation 1 The patient with true gynecomastia complains of hard lumps under the nipple that often expand both toward the inside and the outside of the breast. Oftentimes this overgrowth of glandular tissue will even manage to invade the armpit region. The enlarged glands may vary in size and texture, can be painful or tender to the touch, and occasionally present with nipple discharge. Excess fatty tissue sometimes accompanies true gynecomastia and adds to the bulk of the growth. Treatment Modalities While we don’t think of breast reductions as a subject usually associated with men; surgical excision of the overgrown glands remains the treatment of choice in true gynecomastia. Planning Your Procedure The initial consultation with your surgeon will require a complete medical history, examination of the breast and nipple regions, and a full lab workup to ensure that you are medically fit for surgery. If there are any impaired liver functions or other medical problems, you will be referred to a specialist. Breast reduction surgery can be performed on men of any age who are in good physical and emotional health. The best candidates for surgery have firm skin with good elasticity. All surgery, even elective procedures, has elements of risk and uncertainty. Using a board certified plastic surgeon minimizes problems, but complications may still arise. They include infection, skin injury, excessive bleeding, excessive fluid loss or retention, and adverse reaction to the anesthesia. Another inconvenience may be numbness or temporary loss of nipple sensation which may last for several months or more. The Surgical Facility Your gynecomastia surgery will most likely be performed as an outpatient procedure at either your plastic surgeon's office or an ambulatory surgical facility. If there are medical conditions of concern, an overnight hospital stay may be recommended. The procedure typically takes an hour and a half to complete, although that time may increase or increase according to the individual. Pre-Operative Preparation Gynecomastia surgery involves the removal of extremely vascular glandular tissues; therefore, it is imperative that, two weeks prior to surgery, patients refrain from consuming aspirin, NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs), and nutritional supplements. These products significantly increase bleeding times and thus can turn routine surgical procedures into proverbial “blood baths”. While I advise my patients to discontinue all vitamins, meal replacement shakes, and herbals, I’ve found the following products to be the most troubling: • Bilberry (Vaccinium myrtillus) - Bilberry can affect blood cells called platelets and may increase bleeding. 2 • • • • • • • • • • • • Cayenne (Capsicum frutescens) - Also known as red pepper, cayenne may affect platelets. Dong Quai (Angelica sinensis) - An active constituent in Dong quai is a coumarin-like compound, which may increase existing anticoagulant (blood-thinning) medications. Echinacea (Echinacea augustfolia) - Used to boost the immune system and for infections of the respiratory tract, Echinacea may negatively affect the liver when general anesthetics or certain other medications are used. Feverfew (Tanacetum parthenium) - Feverfew may increase bleeding, especially in patients taking certain blood-thinning medications. Fish Oil - The Omega-3 essential fatty acids found in fish oil have blood-thinning properties which can be problematic during surgery. Garlic (Allium sativum) - Garlic may augment the effects of blood-thinners like Coumadin (warfarin) and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) causing abnormal bleeding time. Ginger (Zingiber officinale) - Use of ginger may alter bleeding time and interfere with cardiac and anticoagulant medications. Ginkgo Biloba (Ginkgo biloba) - Ginkgo biloba improves blood circulation by strengthening the vascular system and inhibiting platelet aggregation. Ginkgo has significant blood-thinning activity which is three times stronger than Vitamin E. Ginseng (Panax quinquefolium/Panax ginseng) - Ginseng acts as an anticoagulant and may interact with cardiac, high-blood pressure medications and blood-glucose lowering medications. Red Clover (Trifolium pratense) - An active constituent in Red Clover includes coumarin derivatives, which may potentiate existing anticoagulant medications. Vitamin E - Vitamin E has strong anti-clotting activity can prolong bleeding time during surgery. Yohimbe (Corynanthe yohimbe) - Yohimbe can raise the heart rate and blood pressure, and increase the potency of anesthetics. Surgical Procedure Your surgeon will choose either general anesthesia or local anesthesia (with sedation); and he will explain the basis for the particular option that is recommended. In a typical gynecomastia surgery, an incision is made in an inconspicuous location-- either on the edge of the dark skin around the nipple, or in the underarm area. Through the incision, the surgeon cuts away the excess glandular tissue, fat, and skin from around the areola and from the sides and bottom of the breast. If your surgeon has determined that liposuction will be used in conjunction with excision, the liposuction cannula can be inserted directly through the same incisions. In breast reductions involving greater amounts of breast tissue, larger incisions may be necessary and more noticeable scars can result. If your surgeon has determined that your gynecomastia consists primarily of excessive fatty tissue, liposuction would be an appropriate surgical technique for removal of this tissue. At the edge of the areola, in the dark skin that surrounds the nipple, a very small incision (less than a half inch in length) is made. Depending on patient-specific factors and preferences, the incision 3 may be placed in the underarm area, as well. A cannula, (a slim, hollow, tube attached to a vacuum pump) is inserted through the incision. Your surgeon uses the cannula to break up the fat and suction it out. In cases where large amounts of tissue have been removed, it may be necessary for excess skin to be trimmed so that the remaining skin will adjust to fit the new breast contour. Post-Operative Experience It is normal to feel some discomfort for a few days after your procedure. This can be controlled with pain medication prescribed by your surgeon. You should arrange to be driven home after the surgery and you should have someone to help you manage for a day or two after the surgery. Bruising and swelling may cause it to appear that there has been little improvement in your gynecomastia. Although extreme swelling usually resolves itself within the first few weeks, it may take three months or longer before the true results are visible. In over two thousand cases, I have rarely used drains or compression garments. Routine follow-ups include a suture removal visit 5 to 7 days post surgery. Sexual activity should be avoided for at least a week post surgery and heavy exercise for at least three weeks. All activities that risk blows to the chest area should be avoided for at least a month. Avoid exposing scars to the sun for at least six months. Sunlight can cause the scar to darken permanently. If sun exposure is unavoidable, use a strong sun screen (SPF 15 or greater). Most conventional surgeons use a textbook procedure that results in the need for additional surgeries since they don’t remove all the underlying breast tissue. I have developed a technique that safely and effectively removes all the glandular tissue and produces an athletically contoured chest. I get it right the first time so that there is no need for additional surgeries. DR MORDCAI BLAU, M.D., P.C. Dr. Blau has operated on over 1000 top amateur and professional bodybuilders alone. He is, without a doubt, the most experienced gynecomastia surgeon in the country. Located in White Plains New York, Dr. Blau’s office can be reached at (914)-428-4700. His email is: [email protected] and his website can be seen at http://www.cosmetic-md.com/. Feel free to contact him. 4