* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download CONTINENTAL DRIFT THEORY PANGAEA PANTHALASSA
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
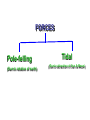
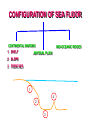
CONTINENTAL DRIFT THEORY •ABRAHAM ORTELIUS- 1596 1st Proposed the movement of continent •ANTONIO PELLEGRINI – Drew a map showing Europe, America and Africa together •ALFRED WEGENER -1912 Proposed ‘Continental Drift theory. PANGAEA PANTHALASSA DRIFTING OF CONTINENTS LAURASIA TETHYS SEA GONDWANA EVIDENCE IN SUPPORT OF THE CONTINENTAL DRIFT • The Matching of Continents (Jig-Saw-Fit) Bullard in 1964. • Rock of Same Age Across the Oceans- Radiometric dating. • Tillite: Sedimentary rock formed out of deposits of glaciers. • Placer Deposite: Deposits of gold in Ghana coast and veins in Brazil. • Distribution of Fossils: Lemur occur in India, Madagascar and Africa. Mesosaurus a small reptile’s skeletons are found in southern cape province of south Africa and Iraver formation of Brazil. FORCES Pole-felling (Due to rotation of earth) Tidal (Due to attraction of Sun & Moon) Post-Drift Studies • Convectional Current Theory- Arthur Holmes in 1930. • Mapping of the Ocean Floor: CONFIGURATION OF SEA FLOOR CONFIGURATION OF SEA FLOOR CONTINENTAL MARGINS 1. SHELF MID-OCEANIC RIDGES ABYSSAL PLAIN 2. SLOPE 3. TRENCHES 1 4 2 3 DISTRIBUTION OF EARTHQUAKES AND VOLCANOES •Mid-Atlantic ridges •It bifurcates a little south of Indian subcontinent with one branch moving into East Africa and other meeting Myanmar to New Guiana. •Alpine Himalaya system. •Rim of Pacific called Ring of Fire. SEA FLOOR SPREADING SEA FLOOR SPREADING • The theory proposed by Hess in 1961. • Volcanic eruptions are common along Midoceanic ridges. • Rocks equidistant on either sides of crest of midoceanic ridges shows remarkable similarities. • The Ocean crust rocks are much younger then continental crust. • Sediments on the ocean floor are unexpectedly very thin. • The deep trenches have deep-sheeted earthquakes. PLATE TECTONICS • Theory proposed by McKenzie and Parker and Morgan in 1967. • Tectonic Plate ore Lithosphere Plate is massive, irregularly-shaped slab of solid rock, generally composed of both continental and oceanic lithosphere. • Thickness 5-100km in ocean and upto 200km in continental areas. MAJOR PLATES 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Antarctica plate North American Plate South American Plate Pacific Plate India-Australia-New Zealand Plate Africa Plate Eurasia Plate Minor Plates 1. Cocos Plate: Between Central America and Pacific Plate 2. Nazca Plate: South America and Pacific Plate. 3. Arabian Plate: South Arabian landmass. 4. Philippine Plate: Asiatic and Pacific Plate 5. Caroline Plate: Philippine and Indian Plate. 6. Fuji Plate: North-east of Australia. PLATE BOUNDARIES • DIVERGENT BOUNDARIES: When two plates move away from each other. • CONVERGENT BOUNDARIES: When two plate move towards each other. • TRANSFORM BOUNDARIES: When two plates slide horizontally each other. RATE OF MOVEMENT • Artic ridge has the slowest rate 2.5cm/year • East Pacific Rise near Easter Island in the South Pacific fastest rate of movement 15cm/ year. FORCE OF MOVEMENT • Arthur Homes and Herry Hess convectional current