* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download What is the difference? - StaticControl.com
Fault tolerance wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Printed circuit board wikipedia , lookup
Distribution management system wikipedia , lookup
Electrostatic loudspeaker wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
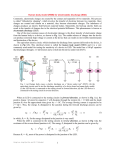
ESD Control Experts HBM vs. CDM vs. CBE What is the difference? © 2015 Desco Industries Inc. StaticControl.com Agenda • ESD Basics • Different ESD Models • Applications ESD Basics ESD Fig 1: ESD damage/short between Emitter/Collector regions on a device. What is Electrostatic Discharge (ESD)? • ESD is a rapid, spontaneous transfer of electrostatic charge induced by a high electrostatic field through a spark between two bodies at different electrostatic potentials as they approach or are separated from one another. • There are three different ESD models identified by the standards presently: − Charge Device Model (CDM) − Machine Model (MM) − Human Body Model (HBM). Fig 2: ESD damage to a bipolar transistor Formula Q=V*C Q – Charge/Potential V – Voltage C – Capacitance Mechanism of ESD generation Product 1 vs. Product 2 C1 * V =Q1 = Q2= V * C2 No ESD Event generated C1 * V= Q1 ≠ Q2= V * C2 ESD Event generated ESD Models Real-life Situation • Different discharges reflect different situations • Real-life discharges may differ from specified ESD models • Models considered for component qualification test • Important to analyze your process and define most relevant model HBM – Human Body Model • Best understood model to date • Dominant discharge on manual operation electronic assembly • Operation handling devices by hand is a must • Poorly grounded charged operator touching a component is source of HBM Event • Processes automation eliminates HBM • Better attention to grounding eliminate HBM • Better in-component protection against slow rise (2-10ns) events eliminates HBM What is ESD? • Charged Human Body • Discharge from a fingertip to a grounded component • 100 pF capacitor discharged through a switching component and 1,500 ohm series resistor into the device under test By ESDA Example CDM – Charge Device Model • Most relevant in today’s electronic production • Rapidly discharge of energy from a charged device to ground • Dominant discharge on automated operation electronic assembly • Voltage induction to component and tribocharging is a must • Faster processes automation - problematic • Very fast discharge – high energy, trace overheating – craters or blown-up traces • RF high frequency components have little protection CDM – What is it? • Device depended • CDM event has less than 2.0 nanoseconds duration • Rise time of CDM event could be as short as 65 picoseconds By ESDA Example CBE – Charge Board Event • Rapidly discharge of energy from a charged PCB to component • High capacitance board (>125pF) holds much more voltage • Voltage induction to the board and component becomes important • Very fast discharge – high energy/high current • CBE an extension of CDM • Components on the board go through EOS CBE – What is it? • PCB potential depended – rapid discharge • Higher Peak Current than CDM Event • Influences component in the path of the discharge By Analog Devices Detecting ESD Events in Your Production • Identify component sensitivity and measure ESD events • Instrumentation insures compliance • Products used: − SCS EM Aware TNG ESD Event Monitor Starter Kit − SCS EM Eye Meter − SCS ESD Pro Event Indicator Applications Finding the Root Causes of ESD • Identify the Application Where ESD Events are Being Created • For Example… − − − − − − SMT Line Soldering Printer Repair Functional Test (Manual or Automatic Testing) Manual Applications Must Know Where to Look… SCS Expertise and Technology Can Help