* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Section 16.4
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
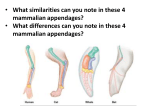
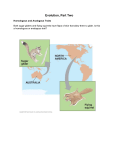
Lesson Overview Evidence of Evolution Lesson Overview 16.4 Evidence of Evolution Lesson Overview Evidence of Evolution Biogeography – study of where organisms live now and where they and their ancestors lived in the past. – Two biogeographical patterns are significant to Darwin’s theory. 1. a pattern in which closely related species differentiate in slightly different climates. Ex. variation in shell shape among the giant land tortoises that inhabit the Galápagos islands. Lesson Overview Evidence of Evolution Species Vary Globally 2. a pattern in which very distantly related species develop similarities in similar environments. Ex. similar ground-dwelling birds (rheas, ostriches, and emus) inhabit similar grasslands in Europe, Australia, and Africa. emu. Rheas ostriches Lesson Overview Evidence of Evolution Homologous Structures – Structures shared by related species and that have been inherited from a common ancestor are called homologous structures. – Darwin proposed that animals with similar structures evolved from a common ancestor – Biologists test whether structures are homologous by (1)studying anatomical details the way structures develop in embryos, (2)the pattern in which they appeared over evolutionary history. Lesson Overview Evidence of Evolution Homologous Structures –Ex. the front limbs of reptiles and birds are more similar to each other to than either is to the front limb of an amphibian or mammal. –Scientists say that this similarity is used to show that the common ancestor of reptiles and birds lived more recently than the common ancestor of reptiles, birds, and mammals. Lesson Overview Evidence of Evolution Analogous Structures –Another example used by scientists are analogous structures body parts that share a common function, but not structure. –Ex. The wing of a bee and the wing of a bird are analogous structures. Lesson Overview Evidence of Evolution Vestigial Structures –inherited from ancestors, but have lost much or all of their original function due to different selection pressures acting on the descendant. –Ex. The hipbones of bottlenose dolphins Pelvic bone of a whale Lesson Overview Evidence of Evolution Other Examples of Vestigial Structures –The wings of a flightless cormorant –The legs of an Italian three-toed skink cormorant three-toed skink Lesson Overview Evidence of Evolution Embryology –Some scientists use the similar patterns of embryological development as evidence that organisms have descended from a common ancestor. Lesson Overview Evidence of Evolution Life’s Common Genetic Code – Some scientists believe that the strongest evidence supporting evolutionary theory comes from genetics. Lesson Overview Evidence of Evolution Life’s Common Genetic Code – This genetic code is nearly similar in almost all organisms, including bacteria, yeasts, plants, fungi, and animals – This compares a small portion of the DNA for the same gene in three animals—a mouse, a whale, and a chicken.