* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Shapley–Folkman lemma wikipedia , lookup
Rotation formalisms in three dimensions wikipedia , lookup
Technical drawing wikipedia , lookup
Tessellation wikipedia , lookup
Surface (topology) wikipedia , lookup
List of regular polytopes and compounds wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Approximations of π wikipedia , lookup
Complex polytope wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Pythagorean theorem wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
Integer triangle wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
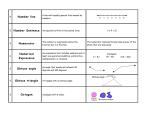
Details of Class: Lesson 4 Date: Time: 50mins Learning Intentions/Topic: Year: 8 Geometry: Polygons To recognise different types of polygons and their properties To be able to draw all different types of polygons, labelling sides and angles correctly To be able to calculate the angles inside different polygons Room: No. of students: Relationship to VELS: Classification of polygons with reference to a definition or key property Using language relevant to the topic Resources Required: Students to each have their own workbook and stationery Maths Quest 8 textbook Whiteboard & Markers Introduction/Housekeeping/Warm-up: Link to last lesson : So far we have learnt how to calculate the interior and exterior angles of a triangle, and last lesson we learnt about different types of quadrilaterals and how to calculate the angles inside a quadrilateral. Today we are learning how to calculate angles inside any polygon. 2 min Content Resources Description: So far we have learnt that the sum of the angles in a triangle is 180˚ and the sum of the angles inside a quadrilateral is 360˚. We will now discover a method of finding the sum of the angles in any polygon. Clarification: What is a polygon? Origin: poly = many Therefore, a polygon is a shape with many sides. This can be anything from 3 sides to 1000 sides, or more. Activity: Complete table provided ‘Sum of Angles in a Polygon’ Time 5 min Sum of Angles in a Polygon table & instructions 10 min Examples of how to find angles in polygons (sheet provided) Write these examples on board, going step-by-step through each example with the class. Example sheet provided 10 min Activity: Students to complete Ex 7F p. 262 – 263, questions 1 - 9 Maths Quest 8 p. 262 - 263 17 min Go through answers to activity. Highlight the patterns evident. Formula: Sum of angles = 180 x (number of sides – 2) 3 min Reinforcement of Ideas/Questioning/Homework: Questions? Homework: Finish any unfinished questions from today’s activities. Overall reflection of lesson: 3 min Sum of Angles in a Polygon Instructions: 1. For every polygon shown in the table, draw as many diagonals as possible from the vertex. Marked X. (This will divide the polygon into a number of triangles.) 2. Complete the table. 3. Can you see a pattern? What would be the sum of the angles in a dodecagon (12 sides)? Can you predict the angle sum of an icosagon (20 sides)? What about a polygon with 100 sides? Polygon Name Number of Sides Triangle 3 Number of Triangles 1 Quadrilateral 4 2 Sum of Angles 180˚ X X Pentagon X Hexagon X Heptagon X Octagon X Decagon X 2 x 180˚ = 360˚ Answers: Sum of Angles in a Polygon Instructions: 4. For every polygon shown in the table, draw as many diagonals as possible from the vertex. Marked X. (This will divide the polygon into a number of triangles.) 5. Complete the table. 6. Can you see a pattern? The number of triangles is 2 less than the number of sides. Sum of angles is 180˚ x number of triangles. Sum of angles = 180˚ x (number of sides – 2) What would be the sum of the angles in a dodecagon (12 sides)? (12 – 2) x 180˚ = 1800˚ Can you predict the angle sum of an icosagon (20 sides)? (20 – 2) x 180˚ = 3240˚ What about a polygon with 100 sides? (100 – 2) x 180˚ = 17 640 Polygon Name Number of Sides Triangle 3 Number of Triangles 1 Quadrilateral 4 2 2 x 180˚ = 360˚ Pentagon 5 3 3 x 180˚ = 540˚ Hexagon 6 4 4 x 180˚ = 720˚ Heptagon 7 5 5 x 180˚ = 900˚ Octagon 8 6 6 x 180˚ = 1080˚ Decagon 10 8 8 x 180˚ = 1440˚ Sum of Angles 180˚ X X X X X X X Examples: 1. Find the sum of the interior angles of the polygon shown: Sum of angles = 180˚ x (n – 2) n = 13 Sum of angles = 180˚ x (13 – 2) = 180˚ x 11 = 1980˚ 2. For the polygon shown, find: a) the sum of its interior angles b) the value of the pronumeral a) Sum of angles = 180˚ x (n – 2) 120˚ 130˚ n=5 Sum of angles = 180˚ x (5 – 2) = 180˚ x 3 = 540˚ 95˚ 95˚ b) p + 120˚ + 130˚ + 95˚ + 95˚ = 540˚ p + 440˚ = 540˚ p = 540˚ – 440˚ p = 100˚ 3. Find the value of the pronumeral in this regular polygon Sum of angles = 180˚ x (n – 2) n=6 Sum of angles = 180˚ x (6 - 2) = 180˚ x 4 = 720˚ a = 720˚ ÷ 6 = 120˚ a p