* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Types of Community Interactions
Habitat conservation wikipedia , lookup
Molecular ecology wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity action plan wikipedia , lookup
Overexploitation wikipedia , lookup
Latitudinal gradients in species diversity wikipedia , lookup
Introduced species wikipedia , lookup
Island restoration wikipedia , lookup
Storage effect wikipedia , lookup
Coevolution wikipedia , lookup
Renewable resource wikipedia , lookup
Occupancy–abundance relationship wikipedia , lookup
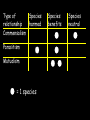
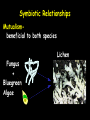
Habitat vs. Niche Habitat- the place in which an organism lives out its life Niche - the role a species plays in a community; its total way of life A niche is determined by the tolerance limitations of an organism, or a limiting factor. Competitive Exclusion Principle • No two species can occupy the same niche in the same place at the same time. • One species will be eliminated from a community because of competition for the same limited resource. Limiting Factors • Limiting factor- any biotic or abiotic factor that restricts the existence of organisms in a specific environment or causes population growth to decrease. • Most of the time the limiting factor is a resource in insufficient supply. Limiting Factors Examples of limiting factors •Amount of water •Amount of food •Temperature •Amount of space •Availability of mates Limiting Factors • Density-dependent limiting factor — factor that only limits growth of a population when the population density reaches a certain level (overcrowding). • Examples: food, water, shelter, competition, predation, parasitism, and disease Limiting Factors • Density-independent limiting factors — these limit growth regardless of the population size. • Examples: unusual weather, natural disasters, seasonal cycles, and human activities Resources • Renewable Resources—a resource that can regenerate quickly and that is replaceable. – Examples: sunlight, trees, etc… Resources Nonrenewable Resources—a resource that cannot be replenished by natural processes. Example: fossil fuels Competition—interaction in which organisms of the same or different Competition species attempt to use the same ecological resource in the same place at the same time. Predator/Prey—interaction in which one organism captures, Predation KILLS, and feeds on another organism. Symbiotic Relationships Symbiosis- two species living together http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zSmL2F1t81Q 3 Types of symbiosis: 1. Commensalism 2. Parasitism 3. Mutualism Type of Species relationship harmed Commensalism Parasitism Mutualism = 1 species Species benefits Species neutral Symbiotic Relationships Commensalismone species benefits and the other is neither harmed nor helped Ex. orchids on a tree Epiphytes: A plant, such as a tropical orchid or a bromeliad, that grows on another plant upon which it depends for mechanical support but not for nutrients. Also called xerophyte, air plant. Symbiotic Relationships Commensalismone species benefits and the other is neither harmed nor helped Ex. polar bears and cyanobacteria Commensalism Whale & Barnacles Shark & Remora Symbiotic Relationships Parasitismone species benefits (parasite) and the other is harmed (host) • Parasite-Host relationship Symbiotic Relationships Parasitism- parasite-host Ex. lampreys, leeches, fleas, ticks, tapeworm, Not considered predator-prey because goal is not to KILL host Symbiotic Relationships Mutualism- beneficial to both species Cleaner Shrimp & Fish Bee & Flower Mutualism Egyptian Plover & Crocodile Symbiotic Relationships Mutualismbeneficial to both species Fungus + Bluegreen Algae Lichen