* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download pbis study guide KEY
Cell theory wikipedia , lookup
Developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Homeostasis wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic resistance to malaria wikipedia , lookup
Microbial cooperation wikipedia , lookup
Human embryogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
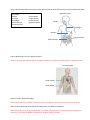
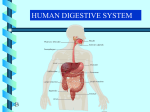
Name: ___________________________ Date: ___________________ Period: _____________ PBIS Study Guide Complete this study guide to help prepare for the PBIS Assessment. You will also need to review all labs, handouts, and notes. Explain the difference between cells, tissues, organs and organ systems. Cells are the basic units of life. Tissues are a group of cells with the same structure and function. Organs are a combination of different types of cells that work together to perform a common function. Organ systems include multiple organs with related functions that work together. Use this word bank to label each organ system diagrams below. Write the function for each part below the label. Word Bank: Heart Trachea Artery Bronchioles Circulatory system Lung Vein Nose Diaphragm Respiratory system Respiratory System Nose Trachea Lung Bronchioles Diaphragm How do diseases get into your respiratory system? Diseases enter the respiratory system through our nose or mouth. Circulatory System Heart Veins Artery How do diseases get into your circulatory system? Diseases can enter the circulatory system through a cut. Infections that begin in other systems can travel through the blood throughout the body. Use this word bank to label each organ system diagrams below. Write the function for each part below the label. Word Bank: Mouth Stomach Esophagus Small intestine Immune system Digestive System Lymph Nodes Large intestine Lymph vessels Digestive system Mouth Eosphagus Stomach Large Intestine Small Intestine How do diseases get into your digestive system? Diseases can enter the digestive system through the mouth or nose due to something we’ve touched or eaten. Immune System Lymph Vessels Lymph Nodes Where are white blood cells made? Most white blood cells are made in the bone marrow, though they can also reproduce in the lymph nodes. What are three ways that white blood cells help protect your body from disease? White blood cells can (1) engulf infected cells or microbes, (2) poke holes in cells causing their cytoplasms to drain out, or (3) create antibodies to indentify or disable invading microbes. Respiratory System: Its purpose is to take in the required oxygen needed for cellular respiration and to release the carbon dioxide that is produced as waste. Organ Nose Trachea Lung Diaphragm Function Warm, filter, and add moisture to air A passageway between the mouth/nose and the bronchi/lungs; it also helps filter the air. Allow oxygen to enter our bloodstream and carbon dioxide to escape Contracts to draw air into our lungs by making space inside the rib cage bigger. This makes us inhale. When it relaxes the ribcage gets smaller again and we exhale. Circulatory System: Its purpose is to deliver oxygen, carbon dioxide, nutrients, and waste around the body in the blood. Organ Heart Veins Artery Function Pumps blood to the body and lungs. Carries blood toward the heart Carries blood away from the heart. Digestive System: its purpose is to break down food into small enough pieces for it to be absorbed into the body Organ Mouth Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine Function To tear and chew food. Saliva adds enzymes and moisture. Pushes food from the mouth to the stomach. Churns and adds enzymes/acid to food. Adds more enzymes to food and allows nutrients to be absorbed. Absorbs liquids and water from waste food that we do not absorb. Immune System: its purpose is to defend the body from disease Organ Lymph vessels Lymph nodes Function Pathways that take in fluids from the body and return them to circulatory system. Houses many white blood cells and filters bacteria and viruses out of the lymphatic system.