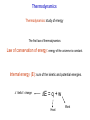* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 10 - Bakersfield College
Relativistic mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Eigenstate thermalization hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Adiabatic process wikipedia , lookup
Thermodynamic system wikipedia , lookup
Thermodynamic temperature wikipedia , lookup
Internal energy wikipedia , lookup
Heat transfer physics wikipedia , lookup
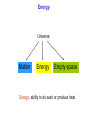
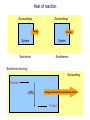
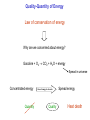
Chemistry B2A Chapter 10 Energy Energy Universe Matter Energy Empty space Energy: ability to do work or produce heat. Energy Kinetic energy (KE): energy of motion KE = ½ mV2 V: velocity Potential energy (PE): stored energy (Position & Composition) Law of conservation of energy Kinetic and Potential Energy Kinetic energy Potential energy A B A Change in potential energy for ball A (change in level) T of hill increases B Work: change the position of ball B Heat: friction between surface & ball Frictional heating (heat is a form of energy). Heat and Temperature Temperature: measure of random motions of the components of substance. T↑ move faster Kinetic energy ↑ Heat and Temperature Cold Water Hot Water Energy is transferred from high T to low T. Heat: Flow of energy due to a T difference. Tfinal = Thot initial + Tcold initial 2 Heat units of heat: calorie (cal) joule (J) English system SI system Joule: Energy (heat) required to raise T of one gram of water by 1C. 1 cal = 4.184 J Heat Amount of heat = specific heat × mass × change in temperature Amount of heat = SH × m × (T2 – T1) SH = Specific heat capacity (cal/g °C) T2 = final temperature T1 = initial temperature Heat of reaction 2HgO(s) + heat (energy) 2Hg(l) + O2(g) Endothermic reaction C3H8(s) + 5O2(g) 3CO2(g)+ 4H2O(l) + heat (energy) Exothermic reaction All combustion reactions are exothermic. Heat of reaction Surroundings Surroundings Energy Energy System System Exothermic Endothermic Exothermic (burning) Surrounding Reactant (PE) Energy released to the surroundings as heat Product Thermodynamics Thermodynamics: study of energy The first law of thermodynamics: Law of conservation of energy: energy of the universe is constant. Internal energy (E): sum of the kinetic and potential energies. “delta”: change E = q + w Heat Work Thermodynamics E = q + w Energy flows into system via heat (endothermic): q = +x Energy flows out of system via heat (exothermic): q = -x Surroundings Surroundings Energy Energy System System E 0 E 0 Endothermic Exothermic Enthalpy Enthalpy (Thermochemistry): heat of chemical reactions. For a reaction in constant pressure, the change of enthalpy is equal to energy that flows as heat. Hp = heat Constant pressure “-” heat or Hp: exothermic: heat flows out of the system. “+” heat or Hp: endothermic: heat flows into the system. Calorimetry Calorimeter: A device to measure the heat energy released or absorbed by a reaction. T H Hess’s Law State function: a property of system that changes independently of its pathways. Enthalpy is a state function. In a chemical reaction, change of enthalpy is the same whether the reaction takes place in one step or in a series of steps. 1 Step N2(g) + 2O2(g) 2NO2(g) H1 = 68 kJ 2 Steps N2(g) + O2(g) 2NO(g) 2NO(g) + O2(g) 2NO2(g) H2 = 180 kJ H3 = -112 kJ N2(g) + 2O2(g) 2NO2(g) H2 + H3 = 68 kJ Two rules about enthalpy 1. If a reaction is reversed, the sign of H is also reversed. N2(g) + 2O2(g) 2NO2(g) H1 = 68 kJ 2NO2(g) N2(g) + 2O2(g) H1 = -68 kJ 2. If the coefficients in a balanced reaction are multiplied by an integer, the value of H is also multiplied by the same integer. 2 N2(g) + 2O2(g) 2NO2(g) H1 = 68 kJ 2N2(g) + 4O2(g) 4NO2(g) H1 = 2 68 kJ = 136 kJ Quality-Quantity of Energy Law of conservation of energy Why are we concerned about energy? Gasoline + O2 CO2 + H2O + energy Spread in universe Concentrated energy Quantity Use of energy to do work Quality Spread energy Heat death Energy and Our World Woody plants Photosynthesis Sun Source of energy Coal Natural gas Petroleum 6CO2 + 6H2O + energy of sun Photosynthesis C6H12O6 + 6O2 glucose Energy and Our World Fossil Fuels: formed from the decomposition of marine plants and animals. 1. Natural gas – 90 to 95 percent methane. – 5 to 10 percent ethane, and a mixture of other low-boiling alkanes. 2. Petroleum – A thick liquid mixture of thousands of compounds, most of them hydrocarbons. (C1-C4) (C5-C10) (C10-C18) (C15-C25) (C25) Energy and Our World 3. Coal – Was formed from the remains of plants that were buried (under high P and T). – 20% of our energy. – Expensive, dangerous, and produces pollution (CO & SO2). Greenhouse Effect Driving forces Energy spread: concentrated energy is dispersed widely. (Exothermic process) heat Matter spread: molecules of a substance are spread out and occupy a larger volume. Dissolving is endothermic process, but because of matter spread, it occurs. Entropy (S) A measure of disorder or randomness. Energy spread Faster random motions of the molecules in surroundings. Matter spread Components of matter are dispersed (occupy a larger volume). The second law of thermodynamics: The entropy (S) of the universe is always increasing. We run towards a disorder (heat death of universe). A Spontaneous process is one that happens in nature on its own. (because of increasing entropy) Dissolving