* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plant Notes12
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Venus flytrap wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
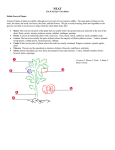
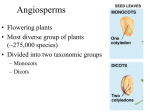
Plant Notes General Characteristics: Multicellular Eukaryotic __________________ Cell walls made of _____________ Vascular plants contain xylem (takes water up plant) and phloem (takes food down the plant) Plant Organs: ___________ ___________ ___________ ___________ Simple Plants- The Bryophytes “______________________” plants Live in ______areas like swamps, marshes, and streams to help in reproduction. They lack true roots but have ____________ instead. Examples- __________, liverworts, and hornworts Sporophyte- produces ____________ Gametophyte- produces _______________ Ferns- The first vascular plants Most important adaptation: o ______ allows movement of _____ up from the roots to all parts of the plant o ____________ transports ______________ and the products of photosynthesis throughout the plant. Have underground stems called _______________ o Rhizome adaptations: The rhizomes act as a ____________when the fern is unable to photosynthesize during ______or otherwise unsuitable conditions Have large leaves called ___________ Contain haploid ____________ under the fronds which are produced in tiny clusters called ___________ Roots, Stems, and Leaves in Plants: Roots-Functions: Absorbs ____________ and ____________ from the soil _________________ the plant into the ground Stores extra ___________ for later use if needed Label: 1. Where photsynthic products are stored 2. Where water flows to the stem 3. Where nutrients flow to the plant Types of Roots : Tap- large primary root with tiny hair-like roots for more absorption o Example: ________________ o Adaptation of taproot in Savanna: Umbrella thorn Acacias grow in the African savannas. One of the Umbrella Thorn's adaptions to ____________ conditions is a deep ____________which can reach 115 feet under the ground. If it did not have taproots, then it would not get the ___________ during the dry spells. Fibrous- roots are all similar in size o Example: ___________ o Adaptation of fibrous roots in the desert: Many _____________ have very long, fibrous roots which absorb moisture from the soil. Some, like ball cacti, have shorter, more compact roots that absorb dew water that falls off the cactus. How do roots play a role in the nitrogen cycle? Nitrogen is an essential nutrient needed to make ____________ and other important organic compounds, but most organisms cannot use free nitrogen. Gaseous nitrogen is broken apart in the process of ____________ f______________. The bacteria in the soil convert the ammonia to nitrites and nitrates. The nitrates are easily absorbed by plant roots. In this way, nitrogen is passed into the food chain and ultimately returned to the soil, water, and atmosphere. Roots and Symbiosis: Roots often form symbiotic associations with soil ________. In this association, the plant ___________ from phosphorus that is taken up and supplied by the fungus, and the fungus ____________ from carbohydrates produced by the plant. This is an example of __________________. Stem-Functions: Transport _______________ and ____________ up and ______ down through the plant Support the ____________ Store extra food for the plant Most stems connect the leaves to the roots, like a highway connects cities. Highlight terms that stems have in common with roots. Do they perform the same function? Leaves-Function: To ____________________ or make food (______________) for the plant Internal Leaf Structure : ___________- waxy covering that prevents water loss; adaptation to land for plants Upper & lower _______________- first cell layer; produces cuticle for protection _______________ layer- long, slender cells with many chloroplasts where most ____________________ takes place ____________- contains xylem & phloem _______________ layer- in the center of the leaf; irregularly shaped cells that are loosely packed with lots of air space between them to resemble a sponge; some photosynthesis takes place here Air spaces- embedded in spongy layer; allows for quick exchange of _______ (O2) and carbon dioxide (CO2) _____________- hot dog shaped cells that surround and monitor stomata openings ______________- openings in leaves & some stems that allow oxygen to escape and CO2 to enter leaf The interaction between roots, stems, and leaves: The __________ travels throughout the entire plant transporting ___________ solutes (food). Depending on the plant’s needs, phloem can change its flow direction. ____________ involves the movement of water and minerals starting at the roots, running through the stems, and ends at small pores (stoma) in the leaves. Stomata can open and close, not only at a certain time of day, but also upon the osmotic condition of the plant. Photosynthesis— Photosynthesis Formula: In the presence of light, plants transform carbon dioxide and water into carbohydrates (glucose) and release oxygen. __________________= carbon dioxide & water __________________= sugar (glucose) & oxygen Structures involved in photosynthesis: Organ- _________ (occasionally in stems) Layer- __________________ Cell organelle- _________________ Molecule- _________________ o __________ pigment o Absorbs light energy from the sun & stores it in __________ bonds in glucose o Only pigment that can transform light energy into chemical energy Seeded Plants-Two categories of seed plants: 1. Gymnosperms- “__________________” - Male cones produce ___________ for reproduction 2. Angiosperms- “_____________________” – Reproduction takes place in the ________________ – Divided into two sub groups: ____________________________________ Parts of the Flower 1. ___________- modified leaves surrounding the base of the flower for protection of the developing bud 2. ____________- all of the sepals collectively 3. ___________- colorful, often fragrant modified leaf to attract insects 4. __________- all of the petals 5. ___________- male reproductive structures collectively; look like upside down golf clubs; consists of two parts: anther and filament 6. ________- top part of stamen (head of golf club); produces pollen (male gamete) 7. ____________- long, thin structure (shaft of golf club) that supports the anther and holds it up high 8. ___________- female reproductive structures; consists of stigma, style, ovary, ovules, and ova 9. ___________- sticky tip of pistil; produces nectar and traps pollen 10. __________- long, thin tube that leads to the ovary 11. _____________- enlarged, pear-shaped structure on the bottom of the pistil; contains the ovules and ova; becomes the fruit 12. ____________- individual “room” inside the ovary that produces ova 13. __________- the female gametes (eggs) Fruit Function To continue the species of a plant A ripened ovary that contains seeds is called a __________. Seed Dispersal ____________—transport of burred seeds in animal’s fur or feathers; fleshy fruit eaten, digested, and excreted at another location; bury seeds to come back to eat later (squirrels burying acorns). __________________-- smaller seeds that have wings or other hair-like or feather-like structures (dandelion or sycamore seeds) _____________________-- Plants living along streams and rivers have seeds that float downstream, which germinate at new sites Regulating Growth and Development in Plants _________________ Control Plant Growth and Development: A _________________ is a chemical that is produced in one part of an organism and then _________________ to another part of the organism, where it brings about a __________________. A _________________ is a growth response in which the direction of growth is determined by the direction from which the _____________ comes. Auxins are responsible for producing tropisms. If the response is toward a stimulus, it is called a ______________ tropism. If the response is away from a stimulus, it is a __________________ tropism. Tropism: Phototropism Definition: Growth response to __________ positive negative Gravitropism Thigmotropism Phototropism growth toward light growth away from light Growth responses to ______________ Growth responses to _____________ Gravitropism Thigmotropism