* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Communicable Diseases
Onchocerciasis wikipedia , lookup
Leptospirosis wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Cross-species transmission wikipedia , lookup
African trypanosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Visceral leishmaniasis wikipedia , lookup
Sexually transmitted infection wikipedia , lookup
Eradication of infectious diseases wikipedia , lookup
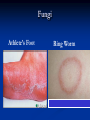
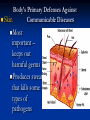
Communicable and Noncommunicable Diseases After this lesson you will be able to: Compare and contrast between noncommunicable and communicable diseases Define the common pathogens that cause communicable diseases Distinguish between communicable and non-communicable diseases Non-Communicable disease Also called non-infectious diseases For example: Heart disease Communicable diseases Also called infectious diseases. Passed through direct/indirect contact Non-communicable diseases Diseases that CANNOT be spread from one person/thing to another Diseases that are not caused by pathogens (bad germs) Can affect any system in the body (circulatory, nervous, respiratory) Can be treated but not usually cured Causes of non-communicable diseases 1. Hereditary- passed from parent to child 2. Environmental Where you live –or work For example: Nuclear power plant 3. Lifestyle Poor health habits – tanning, smoking, drinking, poor diet, lack of exercise and emotional stress. Preventing non-communicable disease Have a balanced diet Get regular exercise Avoid tobacco, alcohol, and other drugs Regular check-ups can identify early warning signs Common Non-Communicable Diseases Cancer Cardiovascular Heart Attack Stroke disease Communicable Diseases Definition Caused by direct or indirect spread of pathogens (bad germs) from a person or thing to another. Pathogens and Vectors Pathogens are disease causing agents (bad germs) Vectors are disease-causing organisms that carry pathogens from one host to another For example: Mosquitoes transmit malaria Ticks transmit Lyme disease How diseases are spread Direct contact - touching infected area of person Indirect - sneezing, coughing, sharing personal items Contact with vectors (animals and insects) - bites Other contact - eating contaminated foods Where Diseases Enter The Body Mouth Eyes Nose A break in skin (cuts) Genitals Prevention for communicable diseases Wash hands Cover mouth when sneezing or coughing Proper care of food, don’t share food Eat healthy and exercise to improve immune system Shower daily Common Types of Pathogens Bacteria Virus Fungi Protozoan Bacteria (100 million will fit in a grain of sand.) Most common of all pathogens. Most DO NOT cause disease. Reproduces through cell division. Examples:Strep throat , Lyme disease Bacteria Video http://webcast.mediaondemand.com/library_video/20000901/27_bacteria_300.asx Virus All viruses are considered Parasites Smallest and simplest of microorganisms. Can only live on living cells It tricks human cells to reproduce more viruses. Examples- chicken pox, cold, flu, measles, rabies, HIV/AIDS Protozoa Most are harmless One celled organism Grows in water Multiples quickly in moist places For example: Malaria Fungi Live off non-living things. Include molds, yeast, and mushrooms Live in warm moist places such as locker room floors Examples: Ring worm / athletes foot Fungi Athlete’s Foot Ring Worm The Body’s Primary Defenses Against Diseases Skin Mucus Cilia Membrane Body’s Primary Defenses Against Skin Communicable Diseases Most important – keeps out harmful germs Produces sweat that kills some types of pathogens Body’s Defense Against Communicable Disease Mucus Membrane Cells that line nose, mouth and throat produce mucus to trap germs Body’s Defense Against Communicable Disease Cilia Wavelike hairs that sweep out germs from throat, nose, etc Body’s Secondary Defenses •Fever – the temperature of the body increases to slow multiplication of pathogens •White Blood Cells – special cells that kill pathogens •Chemical Barriers – tears and saliva •Reflexes – blinking, coughing and sneezing Take the quiz Click on this link: www.masteryconnect.com/bubblesheet Enter the Test ID (given to you by your teacher) Enter your Student ID Complete the quiz