* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Congruent Triangles shortcuts SAS Notes
Euler angles wikipedia , lookup
Penrose tiling wikipedia , lookup
Golden ratio wikipedia , lookup
Multilateration wikipedia , lookup
Technical drawing wikipedia , lookup
Dessin d'enfant wikipedia , lookup
Apollonian network wikipedia , lookup
Rational trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Reuleaux triangle wikipedia , lookup
Trigonometric functions wikipedia , lookup
History of trigonometry wikipedia , lookup
Euclidean geometry wikipedia , lookup
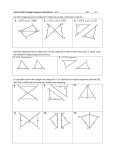
Congruent Triangles Triangles that have exactly the same size and shape are called congruent triangles. The symbol for congruent is ≅. Two triangles are congruent when the three sides and the three angles of one triangle have the same measurements as three sides and three angles of another triangle. The triangles in Figure 1 are congruent triangles. Figure 1 Congruent triangles. Corresponding parts The parts of the two triangles that have the same measurements (congruent) are referred to as corresponding parts. This means that Corresponding Parts of Congruent Triangles are Congruent (CPCTC). Congruent triangles are named by listing their vertices in corresponding orders. In Figure 1 , Δ BAT ≅ Δ ICE. Example 1: If Δ PQR ≅ Δ STU which parts must have equal measurements? These parts are equal because corresponding parts of congruent triangles are congruent. Tests for congruence To show that two triangles are congruent, it is not necessary to show that all six pairs of corresponding parts are equal. The following postulates and theorems are the most common methods for proving that triangles are congruent (or equal). (SSS Postulate): If each side of one triangle is congruent to the corresponding side of another triangle, then the triangles are congruent (Figure 2 ). Figure 2 The corresponding sides (SSS) of the two triangles are all congruent. (SAS Postulate): If two sides and the angle between them in one triangle are congruent to the corresponding parts in another triangle, then the triangles are congruent (Figure 3 ). Figure 3 Two sides and the included angle (SAS) of one triangle are congruent to the corresponding parts of the other triangle. (ASA Postulate): If two angles and the side between them in one triangle are congruent to the corresponding parts in another triangle, then the triangles are congruent (Figure 4 ). Figure 4 Two angles and their common side (ASA) in one triangle are congruent to the corresponding parts of the other triangle. (AAS Theorem): If two angles and a side not between them in one triangle are congruent to the corresponding parts in another triangle, then the triangles are congruent (Figure 5 ). Figure 5 Two angles and the side opposite one of these angles (AAS) in one triangle are congruent to the corresponding parts of the other triangle. (HL Postulate): If the hypotenuse and leg of one right triangle are congruent to the corresponding parts of another right triangle, then the triangles are congruent (Figure 6 ). Figure 6 The hypotenuse and one leg (HL) of the first right triangle are congruent to the corresponding parts of the second right triangle. (HA Theorem): If the hypotenuse and an acute angle of one right triangle are congruent to the corresponding parts of another right triangle, then the triangles are congruent (Figure 7 ). Figure 7 The hypotenuse and an acute angle (HA) of the first right triangle are congruent to the corresponding parts of the second right triangle. (LL Theorem): If the legs of one right triangle are congruent to the corresponding parts of another right triangle, then the triangles are congruent (Figure 8 ). Figure 8 The legs (LL) of the first right triangle are congruent to the corresponding parts of the second right triangle. (LA Theorem): If one leg and an acute angle of one right triangle are congruent to the corresponding parts of another right triangle, then the triangles are congruent (Figure 9 ). Figure 9 One leg and an acute angle (LA) of the first right triangle are congruent to the corresponding parts of the second right triangle. Example 2: Based on the markings in Figure 10 , complete the congruence statement Δ ABC ≅Δ . Figure 10 Congruent triangles. Δ YXZ, because A corresponds to Y, B corresponds to X, and C corresponds, to Z. Example 3: By what method would each of the triangles in Figures 11 (a) through 11 (i) be proven congruent? Figure 11 Methods of proving pairs of triangles congruent. (a) SAS. (b) None. There is no AAA method. (c) HL. (d) AAS. (e) SSS. The third pair of congruent sides is the side that is shared by the two triangles. (f) SAS or LL. (g) LL or SAS. (h) HA or AAS. (i) None. There is no SSA method. Example 4: Name the additional equal corresponding part(s) needed to prove the triangles in Figures 12 (a) through 12 (f) congruent by the indicated postulate or theorem. Figure 12 Additional information needed to prove pairs of triangles congruent. (a) BC = EF or AB = DE ( but notAC = DF because these two sides lie between the equal angles). (b) GI = JL. (c) MO = POandNO = RO. (d) TU = WXandSU = VX. (e) m ∠ T = m ∠ E andm ∠ TOW = m ∠ EON. (f) IX = EN or SX = TN (but not IS = ET because they are hypotenuses). Example 1 ABC XYZ Two sides and the included angle are congruent o AC = ZX (side) ACB = XZY (angle) CB = ZY (side) Therefore, by the Side Angle Side postulate, the triangles are congruent. o o Included Angle The included angle means the angle between two sides. In other words it is the angle 'included between' two sides. Identify Side Angle Side Relationships In which pair of triangles pictured below could you use the Side Angle Side postulate (SAS) to prove the triangles are congruent? Answer Pair four is the only true example of this method for proving triangles congruent. It is the only pair in which the angle is an included angle.