* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Management of Occupational Exposures to HBV, HCV, and HIV
Middle East respiratory syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Oesophagostomum wikipedia , lookup
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
Human cytomegalovirus wikipedia , lookup
Herpes simplex virus wikipedia , lookup
West Nile fever wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Henipavirus wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Epidemiology of HIV/AIDS wikipedia , lookup
Sexually transmitted infection wikipedia , lookup
Antiviral drug wikipedia , lookup
Diagnosis of HIV/AIDS wikipedia , lookup
Microbicides for sexually transmitted diseases wikipedia , lookup
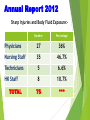
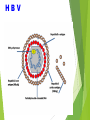
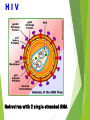
Management of Occupational Exposures to HBV, HCV, & HIV Annual Report 2012 Sharp Injuries and Body Fluid Exposure:Number Percentage Physicians 27 36% Nursing Staff 35 46.7% Technicians 5 6.6% HK Staff 8 10.7% 75 *** TOTAL HBV Hapedna Virus double stranded DNA Risk for Occupational Transmission of HBV ► HBsAg& HBeAg-positive blood : The risk of developing clinical hepatitis is 22%– 31%; The risk of developing serologic evidence of HBV infection is 37%–62%. ►HBsAg-positive, HBeAg-negative blood The risk of developing clinical hepatitis is 1%–6%; The risk of developing serologic evidence of HBV infection is 23%–37% HCV Flavi virus. It is a single stranded RNA Risk for Occupational transmission of HCV HCV-positive source is 1.8% (range: 0%–7%) rarely occurs from mucous membrane. HIV Retrovirus with 2 single stranded RNA Risk for Occupational Transmission of HIV The risks for occupational transmission of HIV vary with the type and severity of exposure: ♦ In percutaneous exposure 0.3% ( 0.2%–0.5%) ♦ In mucous membrane exposure, approximately 0.09% ( 0.006%–0.5%) A percutaneous injury or contact of mucous membrane or nonintact skin WITH Blood ,tissue and body fluids Semen and vaginal secretions , CSF, synovial , pleural , peritoneal , pericardial& amniotic fluid Feces, nasal secretions, saliva, sputum, sweat, tears, urine, and vomitus are not considered potentially infectious unless they contain blood. Contact without barrier protection to concentrated virus in lab Human bites: evaluation of HCP + Patient . Treatment of an Exposure Site Wash needle stick and cuts with soap and water Flush splashes to the nose, mouth, or skin with water Irrigate eyes with clean water, saline THEN Report the incident to your supervisor Immediately seek medical treatment Evaluation of the Source HEPATITIS B MARKERS ANTI- HCV ANTI - HIV Evaluation of the HCW HEPATITIS B MARKERS ANTI- HCV ANTI – HIV LFT in HCV Source A. HBs Ag +ve source. a. Unvaccinated HCW Hepatitis B immunoglobulin (HBIG) 10-12 IU/Kg(500 IU) + Hepatitis B vaccine series PEP should be administered as soon as possible after exposure(preferably within 24 hours). The effectiveness of HBIG when administered >7 days after is unknown. ≈ b. In previously vaccinated HCW i. Known responder (HBs Ab > 10 ml U/ml); no treatment. ii. If non-responder HBIG within 24 hours + Hepatitis B vaccination at the same time. OR Second dose of HBIG can be given 1month later. HCV Positive Source A short course of interferon started early in the course of acute hepatitis C is associated with a higher rate of resolution. ≈ Perform baseline testing for anti-HCV and ALT ≈ Earlier diagnosis of HCV infection is desired, testing for HCV RNA (R-T PCR QUALITATIVE AND QUANTITAVE ) ≈ Perform follow-up testing (e.g., at 4 & 6 months) for anti-HCV and ALT . ≈ Confirm all anti-HCV positive results. HIV Positive Source Several Factors may increase the risk of transmission:a. If HCW is exposed to a large quantity of blood. b. A procedure that involved a needle is placed directly in a vein or artery or a deep injury. c. If the source patient is in the terminal illness. d. If the injury is deep with hollow-bore needles or penetrating sharps-related event. PEP in Percutaneous Exposure Class 1 asymptomatic HIV infection or known low viral load (e.g., (<1,500 RNA copies.ml). Class 2 symptomatic HIV infection, AIDS, acute zero conversion, or known high viral load. PEP in Mucous Membrane Exposure Class 1 Class 2 asymptomatic HIV infection or known low viral load (e.g., (<1,500 RNA copies.ml). symptomatic HIV infection, AIDS, acute sero conversion, or known high viral load. Antiretroviral Agents for PEP ≈ Nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NRTIs). ≈ Nucleotide reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NtRTIs). ≈ Nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors (NNRTIs), ≈ Protease inhibitors(PIs), and a single fusion inhibitor. HIV PEP should regimen (zidovudine (AZT) + lamivudine (3TC) complete a full 4-week ) HCP Follow-up ≈ Anti- HIV test at 6 weeks, 3 months, 6 months Extending follow-up to 12 months ≈ EIA standard test ≈ direct virus assays not recommended