* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Classification of dietary supplement
Survey
Document related concepts
Epidemiology of metabolic syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Vegetarianism wikipedia , lookup
Saturated fat and cardiovascular disease wikipedia , lookup
Clinical trials on glucosamine and chondroitin wikipedia , lookup
Human nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Vitamin D deficiency wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
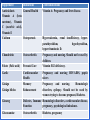
Dietary supplements A dietary supplement ( also known as food supplement or nutritional supplement ) It is a preparation intended to supplement the diet and provide nutrients, (such as vitamins, minerals, fiber, fatty acids, or amino acids) that may be missing or may not be consumed in sufficient quantities in a person's diet. They should not be considered a substitute for food Includes: Vitamins Minerals Herbs or other botanical (excluding tobacco) Amino acids Concentrate, metabolite, constituent, extract, or combination of any of the above Furthermore, it must also conform to the following criteria: Intended for ingestion in pill, capsule, tablet, powder or liquid form Not represented for use as a conventional food or as the sole item of a meal or diet People take supplements for all kinds of reasons, usually relating to their health. They hope these will limit the signs of ageing, extend life, cut the risk of chronic disease such as cancer and treat specific diseases such as arthritis women are more likely than men to take supplements older people and people in poorer health are also more likely to take them Classification of dietary supplement 1) Vitamin supplements 2) Weight-loss supplements 3) Supplements for colds 4) The ageing supplements 5) Fish oils 6) Body building 1) Vitamin supplements Who needs vitamin supplements? People at risk of vitamins deficiencies all pregnant and breastfeeding women should take vitamin D supplements women in the first 12 weeks of their pregnancy are recommended to take folic acid supplements, which reduce their child’s risk of neural tube defects. Pregnant are recommended to take Iron supplements. people aged 65 and over should take vitamin D. people who are not exposed to much sun should take vitamin D supplements all children aged six months to five years should be given a supplement containing vitamins A, C and D 2) Weight-loss supplements Are weight-loss pills safe? Company ? Ingredient ? Side effects ? Herbal???? 3) Supplements for colds Vitamin C and Zinc The recommended daily need of vitamin C is 80mg and most people will achieve this by eating. Regular vitamin C may slightly reduce the length of a cold in some people. vitamin C and Zinc reduces the duration of the cold and protects people against catching colds. 4) The ageing supplements Garlic Ginkgo biloba Ginseng Glucosamine GARLIC (ALLIUM SATIVUM) CARDIOVASCULAR EFFECTS reduce cholesterol biosynthesis antiplatelet effects antioxidant effects (e.g., increased resistance to lowdensity lipoprotein oxidation) and reductions in total cholesterol may be beneficial in patients with atherosclerosis. Garlic enhance blood vessel elasticity and decrease blood pressure (Proposed mechanisms include opening of potassium channels in vascular smooth muscle, and inhibition of angiotensin-converting enzyme). ANTIMICROBIAL EFFECTS activity against bacteria, fungi, protozoa and certain viruses. inhibition of thiol-containing enzymes needed by these microbes. ANTINEOPLASTIC EFFECTS high garlic consumption have a reduced incidence of stomach cancer. Adverse Effects nausea (6%), hypotension (1.3%). Breath odor (20–40%) at recommended doses using enteric-coated formulations. Drug Interactions & Precautions patients using anticlotting medications (e.g., warfarin) should use garlic cautiously. Dosage A daily dose of 600–900 mg/d of powdered garlic is most common. This is equivalent to one clove of raw garlic (2–4 g) per day. GINKGO BILOBA CARDIOVASCULAR EFFECTS Increase blood flow and reduce blood viscosity, enhancing tissue perfusion. Also Antioxidant effect. CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM EFFECTS Increased serum levels of acetylcholine. Reversible inhibition of monoamine (MAO) A and B, and enhanced GABA levels. Ginkgo is used to treat dementia of the Alzheimer type. Adverse Effects may include nausea, headache, stomach upset, diarrhea, Drug Interactions & Precautions Ginkgo may have antiplatelet properties. caution when used in combination with antiplatelet or anticoagulant medications. Dosage The daily dose ranges from 120–240 mg of the dried extract in two or three divided doses. Onset of effect may require 2–4 weeks. GINSENG modulation of immunity, energizing, mind-enhancing, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, antistress, analgesia, vasoregulatory, antiplatelet, improved glucose homeostasis, and anticancer properties. Clinical Trials improve physical and mental performance. Adverse Effects Weak estrogenic properties -- vaginal bleeding. Central nervous system stimulation (e.g., insomnia, nervousness) and hypertension have been reported in patients using high doses. Drug Interactions & Precautions Irritability, sleeplessness, and manic behavior have been reported with (phenelzine, lithium, neuroleptics). Ginseng has antiplatelet properties and should not be used in combination with warfarin. Dosing 200 mg of ginseng extract is equivalent to 1 g of the crude root. GLUCOSAMINE found in human tissue, helps in production of articular cartilage. As a dietary supplement, is primarily used for osteoarthritis pain. Pharmacologic Effects & Clinical Uses In osteoarthritis, the rate of production of new cartilage is exceeded by the rate of degradation. glucosamine is thought to increase the supply of the necessary glycosaminoglycan building blocks, leading to better maintenance and strengthening of existing cartilage. Resulting in improvements of mobility and strength in patients joints. Adverse Effects well tolerated. mild diarrhea and nausea were occasionally reported. Drug Interactions & Precautions There are no known drug interactions with glucosamine. Dosage The dosage used is 500 mg three times daily or 1500 mg once daily. improvements observed after 1–2 months. 5) Fish oils Fish oils for adults and children Key points about fish oils The omega-3 fatty acids found in fish oils are important for good health and cannot be made by the body – they must be obtained from the diet (Eat two portions of fish a week). used by people who have already had a heart attack. For such people, consumption of two to four portions of oily fish per week is ideal, though omega-3 may be recommended as a supplement. There is no evidence that fish oils improve brainpower or memory in adults or children. 6) Body building Do the products work and are they safe? The risks of protein supplements Key points about body-building supplements The recommended daily protein intake is 55.5g for men and 45g for women and we can get this from our diet. In fact, most of us easily exceed this every day. Too much protein can carry some risks, and heavy metals in some supplements are of concern. Some body-building supplements contain illegal anabolic steroids not declared on the label. Nutrient Some Risks Associated supplementation Calcium Can cause constipation; increased risk of Dairy products, broccoli urinary stone formation in some people Can mask vitamin B12 deficiency Spinach, citrus fruits, beans Folic acid with Over Found in These Foods* Iron Accidental overdoses have caused poisoning in children Vitamin A Can cause birth defects, severe liver damage and diarrhea in high doses Vitamin D In very high doses, can result in anorexia, weight loss, polyuria, heart arrhythmias, and damage to the heart, blood vessels and kidneys Meats, beans, spinach, wholewheat bread Cheese, eggs, sweet potatoes, carrots, spinach Egg yolks; fortified foods such as milk and cereals Vitamin C Can cause diarrhea, nausea, cramps Citrus fruits, tomatoes, potatoes, red and green peppers, kiwi, broccoli, strawberries Zinc Can impair immune response and reduce red meat, beans, nuts, dairy copper absorption products Supplement Indications Antioxidants General Health Vitamin A (beta carotene), Vitamin C (ascorbic acid), Vitamin E Calcium Osteoporosis Chondroitin Osteoarthritis Folate (Folic acid) Prenatal Care Garlic Cardiovascular Health Memory Enhancement Ginkgo Ginkgo biloba Ginseng Glucosamine Contraindications Vitamin A: Pregnancy and liver disease. Hypercalcemia, renal insufficiency, hyperparathyroidism, hypothyroidism, hypervitaminosis D. Pregnancy and nursing. Should not be used by children. Vitamin B12 deficiency. Pregnancy and nursing HIV/AIDS, peptic ulcers Pregnancy and nursing. Hematologic disorders, epilepsy. Should not be used by women trying to become pregnant, Diabetes. Diabetes, Immune Hematologic disorders, cardiovascular disease, Function pregnancy, psychological imbalance. Osteoarthritis Diabetes, pregnancy Important Dietary Guidelines Tyramine-rich foods (important to avoid with MAO inhibitors, some antihypertensive) Aged cheese , Bananas ,Chocolate, Liver Potassium-rich foods (important to eat with potassiumwasting diuretics) Dried fruit , Sunflower seeds , Bananas , Grapefruit , Oranges , Tomatoes , Broccoli , Peaches , Nuts , Potatoes , Spinach Calcium-rich foods (important after menopause, in children, in hypocalcemic states) Broccoli , Dairy products , Spinach , Canned salmon Urine acidifiers (important in maintaining excretion of some drugs) Cheese , Eggs , Grains , Red meat , Fish Urine alkalinizes (important in maintaining excretion of some drugs) Apples , Citrus , fruit Milk , Vegetables Iron-rich foods (important in maintaining RBCs) Dried beans , Dried fruit , Organ meats (liver' heart, kidney) , Cereals, vegetables Low-sodium foods (important in CHF, hypertension, fluid overload) Egg yolks , Honey , Fresh fruit , Potatoes , Fresh vegetables , beans High sodium foods (important to avoid in CHF, hypertension, fluid overload) Canned soup , Butter , Tomato , ketchup , Buttermilk, Canned seafood , Sauces