* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Energy
Potential energy wikipedia , lookup
Efficient energy use wikipedia , lookup
William Flynn Martin wikipedia , lookup
Open energy system models wikipedia , lookup
Kinetic energy wikipedia , lookup
Energy subsidies wikipedia , lookup
Energy storage wikipedia , lookup
100% renewable energy wikipedia , lookup
Low-Income Home Energy Assistance Program wikipedia , lookup
Public schemes for energy efficient refurbishment wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative brake wikipedia , lookup
Zero-energy building wikipedia , lookup
World energy consumption wikipedia , lookup
Low-carbon economy wikipedia , lookup
Energy Charter Treaty wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Australia wikipedia , lookup
Alternative energy wikipedia , lookup
Internal energy wikipedia , lookup
International Energy Agency wikipedia , lookup
Life-cycle greenhouse-gas emissions of energy sources wikipedia , lookup
Distributed generation wikipedia , lookup
Energy returned on energy invested wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Energy harvesting wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in transport wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of Finland wikipedia , lookup
Energy in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Negawatt power wikipedia , lookup
Energy policy of the European Union wikipedia , lookup
Conservation of energy wikipedia , lookup
United States energy law wikipedia , lookup
Energy efficiency in British housing wikipedia , lookup
Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007 wikipedia , lookup
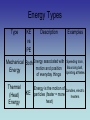
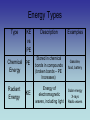
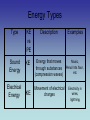
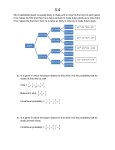
Energy Ch. 5 Energy I. Energy – the ability to do work (or cause change) Most energy can be classified into 2 general categories: Energy 1. Potential energy (PE) – stored energy or energy of position PE = mgh mass (kg) 9.8 m/s2 height (m) Energy 2. Kinetic Energy (KE) – energy of motion KE = ½ mass (kg) 2 mv velocity (m/s) Energy 3. The unit for energy is Joules (J). James Prescott Joule 1818-1889 Energy Types Type KE vs PE Description Mechanical Both Energy associated with motion and position Energy of everyday things Thermal (Heat) Energy KE Examples Speeding train, Bouncing ball, Sprinting athletes Energy is the motion of Candles, electric particles (faster = more heaters heat) Energy Types Type KE vs PE Description Chemical PE Energy Stored in chemical bonds in compounds (broken bonds – PE Increases) Radiant Energy Energy of electromagnetic waves, including light KE Examples Gasoline, food, battery Solar energy X-rays Radio waves Energy Types Type KE vs PE Sound Energy KE Electrical Energy KE Description Examples Music, Energy that moves through substances Pencil hits floor, etc (compression waves) Movement of electrical charges Electricity in wires, lightning Energy Types Type Nuclear Energy KE vs PE Description PE Energy that is stored+in the nucleus (holds p & neutrons together) Examples Sun (fusion), Powerplants (fission) Law of Conservation of Energy A. Energy may change forms but it cannot be created or destroyed B. If energy is conserved, then DPE = DKE (D is “change in”) C. Conservation of Mechanical Energy: (KE + PE)beginning = (KE + PE)end D. Energy flowchart shows how energy changes form. Law of Conservation of Energy a. The life of Stretchy the Rubber Band: Stretchy is pulled – KE PE Stretchy is released – PE KE Stretchy is broken – KE heat & sound Energy Problems Examples: What is the potential energy at points A through E? Energy Problems To demonstrate a cheerleading stunt, Miss Rokosik has to lift Miss Kalousek over her head (to a height of 2 m). Miss Kalousek has a mass of 50 kg. What is the potential energy of Miss Kalousek? Energy Problems What is Miss Kalousek’s kinetic energy while she is held above the ground? Energy Problems Miss Rokosik gets tired and drops Miss Kalousek from the 2 m height. What is her kinetic energy just before she hits the ground? How do you know?