* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lab03: RAM, File types and Storage Devices
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
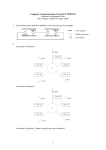
Lab 9 QMCS 200 Introduction to Computer and Information Technology (revised for R. Smith’s Section) Building a Local Area Network (LAN) Purpose This lab is designed to introduce you to how to build a local area network. Further, this lab will provide you with background knowledge on why a LAN would be useful, the hardware needed and will have you put a LAN together and experiment with its capabilities. Instructions Complete this lab with a partner and discuss each step with that person. You MUST use the 3 computers located in room OSS429 for this lab. You must set up a time to do this lab with either the instructor (R. Smith) or the course assistant (Tim Tursich). Check the instructor’s home page for contact information. The class home page (the one listing assignment due dates) has contact information for Tim Tursich. Together with your partner, write answers to those steps that require it (they are in boldface, underlined and surrounded by **) on a blank piece of paper. At the end of the lab, turn in your paper with your names on it or you may e-mail the answers. What is a Local Area Network (LAN) and why build one? 1. A LAN is a group of computers (typically, 2 – 50 computers) that are physically located near each other (on the same floor of a corporation or small business, across several floors of a house or within 1 room in a school lab). A small business or a home may want to connect 38 computers so that these people are able to share the internet, are able to share a printer or they might want to share some files between the computers. All computers in the LAN are connected to a box that can be a switch, hub or router AND this device is connected to the network/internet. The router, hub or switch and all computers in the LAN MUST be within 1 mile of each other, however, typically they are in the same room or within a few hundred feet. 2. Your first decision in building a LAN is to decide your purpose. File sharing and printer sharing is a separate issue from the internet connection. File sharing/printer sharing can be accomplished by connecting all your computers together into a LAN. You would not need to connect the LAN to the Internet. ©2005 QMCS Department – University of St Thomas 1 3. Do you want all computers to share the internet? Do you want to share files and/or a printer between the computers? Do you want to do both? We will create a LAN to do both. What hardware is needed? 1. Hardware needed to create a LAN includes the following: Switch (UST or a large company) OR Router/switch (your home or small business) that is 802.11g compatible. Wall connection to the corporate or university central computing facility where router/proxy server and gateway to the internet are located OR Broadband cable/DSL OR telephone Modem (if connecting to the internet from home or small business). Cat5 10/100 ethernet cable for each computer Network card for each computer Printer (if you desire to share it between all computers) 2. First, a brief discussion on where you might build this LAN. If you are building a LAN at UST or in a company, you will need a Switch and will not need a Router and Modem because a router and modem connection to the internet will be provided at a central location for the company or university. All computers will be connected together using either wireless or Ethernet methods and connected to a Switch box. The Switch may be located in the same room or down the hall. The Switch box will then be connected to the network connection (likely to a plug in the wall). In your company or university, this wall plug will then be connected to a central computer where a router and proxy server are located. Your information will go through the router and proxy server with the IP address of the router being sent through the internet. If you are building this LAN at your home, you WILL need a router, modem and switch AND will use one of the following hardware configurations: 1) - a Router with a separate (broadband) modem and a separate switch OR 2) - a Router with a built in switch and modem OR 3) - a Router with a built in switch and a separate modem. Each computer is connected to the Switch, then to the router and then to the modem although these features may be combined into one or two hardware devices. The modem is connected to the wall in your home where it leaves your home and travels to your ISP. 3. In this lab, we will connect three computers together in a LAN and then connect it to the internet. We will use UST as our ISP, therefore, we will use a Switch. Your choices are a switch that will accept a wireless connection from each computer or Ethernet cable. 4. You will need to insert a network card into the expansion slot of each computer. You will purchase a network card (NIC) that works with the switch(Ethernet or wireless). In this lab, you will insert (you will find it already installed) a 10/100 Ethernet network card. The CAT5 cable plugs into the card and plugs into the switch. In the computers in this lab, you will notice that there is NO NIC in the computer’s expansion slot. That is because the computers were purchased with the NIC and are built into the motherboard. On another computer, you may have to add a NIC. 5. To determine if there is a built in 10/100 NIC, select Start, Settings, Control Panel and double click on the System icon. Select the Hardware Tab and Device Manager. Select the + sign next to Network Adaptor. If a NIC is listed and you did not insert a card into the expansion slot, then your computer has a built in NIC. Do this on computer 04. **Use Alt printscreen to copy into Word and print the Device Manager window that shows the ©2005 QMCS Department – University of St Thomas 2 Network adaptor.** You will notice that there are two NIC’s. The one you will use to connect to the LAN is the Intel NIC. The Linksys NIC is an extra card that has been inserted into an expansion slot for the purpose of showing you where you will need to insert this in your own computer at home. You will not use the Linksys card in this lab. Shut computer 04 off and Open it up. Notice there is a Linksys NIC card in an expansion slot AND notice the metal piece inside the computer connected to the network port on the outside. This is the built-in NIC. 6. The printer will be connected to your choice of the computers and used by all. Go ahead and connect the printer to one of the computers. Connect it to computer 06. 7. Now, go ahead and check each computer for the Network card that has been installed. These computers have Intel NIC’s. It is on the motherboard (piece of metal connected to the network port and no additional NIC). Other brands in addition to Intel that are commonly purchased include: Linksys, Belkin, NetGear and 3Com. 8. Connect a CAT5 cable from each NIC to any of the ports 1X, 2X, 3X, … on the Allied Telesyn Switch. With the network cards in place and the cables attached between the NIC and the switch for EACH computer, your LAN is set up. 9. The hardware is now connected and you have a Local Area Network where you may share files and a printer between these computers. You are NOT connected to the internet. We will do that later. It is now ready to establish file sharing. 10. A little more explanation about what you have done and how it would be the same/similar at your home or place of business: A switch provides IP addresses to each computer in the LAN and will send incoming information to the correct computer based on its IP address. Setting up an Ethernet LAN off campus in your home would be identical except you will use a router/switch combination device instead of a switch. If you need to share a broadband Internet connection in your home or small business, you will need to use a router. A switch will not let you share a broadband cable/DSL Internet connection. There are a few exceptions to this rule. Call your ISP if you want to find out which to use without being charged for an extra IP address. A router is a component that connects your network to a Wide Area Network (WAN) like the internet. It can have an integrated 4 port or 8 port switch in it. A router is intelligent and is able to act as a firewall for protection against hackers from the outside. Again, this is not necessary in this lab because you are using UST as your ISP. In the central computing facility in Aquinas, there is a router and firewall. In packet-switched networks such as the Internet, a router is a device or, in some cases, software in a computer, that determines the next network point to which a packet of information should be forwarded toward its destination. The router is connected to at least two networks and decides which way to send each information packet based on its current understanding of the state of the networks it is connected to. A router is located at any gateway (where one network meets another), including each point-of-presence on the Internet. Most routers now are a hybrid of a router and switch. Instead of having multiple routers sitting around the house you have one box that is slightly larger. It has a place for your Internet connection and then places for all your computers CAT 5 cables. That box would have all the workings of a switch but also have a port for your high speed internet connection and something called a NAT. The NAT is what makes a router do what it does. The switch part sends all the data from the network to the NAT. The NAT helps determine where it goes and then sends it to its proper destination while masking its IP. ©2005 QMCS Department – University of St Thomas 3 If you desire wireless, you would purchase and install a wireless NIC and a wireless router/switch. You can have multiple NIC’s in a computer. Some people have a wireless NIC for traveling convenience and portability AND an Ethernet NIC for home or business use. The disadvantages of a wireless LAN include the following: interference by cell phones, cement in walls or simply distance can make the connection impossible, very slow or inconsistent speed and computer must be within 300 feet of the switch. The advantages of a wireless LAN are that there are no cables necessary between the computer and the router/switch and the computer can be moved anywhere within wireless reach of the signal from the router/switch. Some LAN’s will use an Access Point hardware device that is connected to an Ethernet Router/switch. The Access Point accepts a wireless connection from each of the computer’s NICs. 11. More than one switch or router/switch CAN be connected together. At UST, there are many LANs such as room 431. These computers in 431 connect into a switch located down the hall. The computers in room 432 also connect into another switch, 428 into another switch and 434 into another switch. Other floors in OSS also have LANs. All of these switches are connected together and then into a Network connection that travels to Aquinas and connect to a piece of hardware called a bridge that is connected to the e-mail server, admin. server, web server and then connected to the router and proxy server and then out to the internet. 12. If you have a home with 10 computers, you would use two routers and connect 5 computers to each. One router cable would connect to the other and ultimately be connected to the ISP. You could also use 2 switches connected together with one switch connected to a router and the router connected to the cable modem and then to the internet. Setting up the LAN for file and print sharing among computers in the LAN File Sharing 1. Now, go to one of the computers and begin setting it up for sharing among the computers. First, we will establish file sharing and Second, we will enable each computer to be able to use the printer. 2. Many companies and homes desire to share some files (but not all) between computers. Many companies will have a public folder that can be shared and is stored on a server. We will create a public folder on each of the computers and make it visible to each of the other computers so they may read the files in the folder but will not be able to change them. 3. We will first establish file sharing on the each computer. 4. On computer station01, create a folder on the desktop and name it Shared folder-station 01. 5. Right mouse click on the folder and select properties. Click on the Sharing tab. 6. Click on share this folder. 7. Now create a brief Word processing document and save it in this folder. 8. Go to each of the other computers on the LAN and complete steps 4, 5, 6 and 7 naming the folder Shared folder-station 04 or Shared folder-station06. 9. Now, we will check it out to see if we can indeed look at the files in each shared folder. ©2005 QMCS Department – University of St Thomas 4 10. Go to computer station 01, Double click on My Network Places. 11. You will see a panel on the left where Entire Network is listed. If you do not see this panel, select Tools and Folder Options from the menu. Select the General tab and click on Show Common Tasks in Folders. Now, the panel will appear. 12. Click on Entire Network. 13. You will see all three of the following OR you may only see Microsoft Windows Network: Microsoft Terminal services Microsoft Windows Network Web Client Network 14. Double click on Microsoft Windows Network 15. UST (the LAN in this room) should appear in the right panel. If you set this up at home, it will be called MSHOME or some other similar name. If you were connected to the internet (if you connected the switch to the wall), you will see other LAN’s (in addition to UST) on the UST network. If you were in a company, this would also be the case. Double click on UST. 16. As long as you are not connected to the internet and have only connected the 3 computers into a LAN, you will see 3 computers that are connected to your LAN. ©2005 QMCS Department – University of St Thomas 5 17. These are the names given to the computers when Windows was initially installed. The computers in our LAN that you just assembled are : QM110 -01 QMCS110-04 QM110-06 You might not like these names, but they are the default names when you installed your OS. If you want to see the name of your (or each of many) computer here in the lab OR at home and you want to change the name if you like, go to the control panel and double click on System. Click on the Computer Name tab. PLEASE Don’t change the names in this lab. **Use Alt Print Screen to print the window that displays the computer name for one of the computers used in this lab.** 18. Double click on the computer station where you want to locate files, so select either computer station 04 or 06. You MAY be asked to provide a username and password to access this folder. You would need to provide the Username and Password for the computer you are accessing. If it asks you for this, use localadmin and Qmcs110class as this is the username and password for each of the computer stations. 19. Shared folder-station 06 (or other station) will appear and if you double click on it, all files will appear. You may open any of them (if there are multiple files) but will not be able to Save them back on the other computer. You COULD save it on your computer. ©2005 QMCS Department – University of St Thomas 6 20. You may go to any of the computers on the LAN and be able to view files on any of these computers as well. 21. If you were not on the UST system but instead built this network at home or at a small business, steps 12 through 17 would look slightly different. You might see step 12, but instead of UST in step 15, you might see mshome and in step 16, you would see the list of your computers on your home LAN. If you were in a company, you would see the network established within the company and would have the name ABCLan01 or something similar. 22. AT UST, at your home or on any LAN, a shortcut to doing this that will always give you a list of the folders on the computer for which you have allowed sharing : Click on Start and Run Enter: \\QM110-01 or the name of any computer on the LAN (QM110-06 or QMCS110-04). If you don’t know the names of the computers, you will have to sit at each computer, go to the Control panel, System and Computer Name tab and read the computer name. ** Use Alt Print Screen and print the window where you have entered \\QM110-01 or other computer station number.** Printer Sharing If you have trouble with file sharing, you may copy files you need to print to the computer that has the printer – just use file sharing. 1. Now we will set up printer sharing and try it out. 2. Go to the computer where the printer is attached. This lab assumes it is station 06. 3. If you just attached the printer to the computer, you may have to install it (lab 8) and may have to insert the CDROM that contains the printer driver. Often, printers are automatically recognized and a formal installation is not necessary. Your printer in this lab should automatically be recognized and Windows XP will find the printer driver. NOTE: You should not have to install the printer in this lab!! ©2005 QMCS Department – University of St Thomas 7 4. Select Start, Settings and Printers and Faxes. 5. Select the printer and right mouse click. Select properties. 6. Select the Sharing tab and click on Share this printer. 7. Reboot station 06. 8. Now, go to another computer on the LAN and go into Word processing and open up a file from another computer on the LAN. Select File Print and click the drop down arrow next to Name and select the printer that is connected to another computer on the LAN. **You will print to this printer.** 9. If the printer does not show up, reboot the computer and try again. If it still does not show up, select Network Places from the Desktop and select the computer where the printer is located (QM110-06) Printers and Faxes. Then, right mouse click on the Canon Printer and select: Connect. Setting up the ISP connection to share the internet 1. Before these computers can share the internet, you must have an Internet Service provider (ISP). There are numerous choices including: AOL, Comcast, Earthlink, Qwest and many others. The ISP may provide you with web space to store a web site, an email address and space to store your e-mail messages that you receive and send AND other storage space (similar to the U drive at UST). You may elect NOT to use the web or email space they provide, but to use another e-Mail address (www.yahoo.com, for example). The main purpose for obtaining an ISP is to gain ACCESS known as a GATEWAY to the internet. It is your connection to the internet highway. Your instructor will provide information about ISP’s. You may already be connected to an ISP at home with one computer. If not, you must first subscribe to an ISP and have them come to your home or business and install the connection so you have a wall plug. During this lab, you will use the University of St Thomas as your ISP access to the internet. 2. When you connect your computers (your LAN) to the ISP to access the internet, you will need to connect to the ISP using your choice of communications methods. You may choose a 56k telephone dial up connection, cable, DSL, Satellite, T1/T3 line. Wireless is not available at this time to connect from your home or place of business to your ISP. The University of St Thomas as an ISP uses a T1 or T3 line. At home or a small business, you would likely use a DSL or cable connection. If you were connecting to an ISP using a Cable, DSL, phone line or Satellite, you would need a modem specific for that communication method. Broadband or Cable/DSL modems will all work for Cable or DSL. The modem is connected to the wall plug in and leaves your house or place of business and is connected to your ISP. Wireless connections to the internet are not available at this time as there would need to be wireless towers in the community similar to cell phone towers. With a T1 line such as at UST, you will connect a CAT5 ethernet cable directly into the wall plug in a lab on campus, or dorm room, therefore, you do not need a modem. 3. If you desire to connect several computers to the ISP using the same communication line, you must first connect all computers together into a LAN (which you have done) and then connect the LAN (the switch) (connect CAT5 cable from 8MDI port on the switch) to the modem or to the wall plug in (when using UST as your ISP). If you were at home, you would have a router/switch and a modem. 4. Connect a CAT5 cable from the switch (from the LAN) to the University of St. Thomas ©2005 QMCS Department – University of St Thomas 8 network (the UST ISP) by connecting the cable to the network wall plug. As soon as you have connected the cable from the switch to the wall here in the lab, you are connected to the ISP. **Open Internet Explorer or another browser and enter a web site. Use Alt Print Screen to print a page.** 5. Off campus, you would need to connect the router/switch to a cable or DSL modem using a CAT5 ethernet cable and the modem to your ISP outlet as you would not be using the UST Internet Service provider. 6. Now, a refresher on the difference between a router and a switch. Routers are one of several types of devices that make up the "plumbing" of a computer network. Switches and routers all take signals from computers or networks and pass them along to other computers and networks, but a router is a “gateway” to the internet in that it is the only one of these devices that examines each bundle of data (packets) as it passes and makes a decision about exactly where it should go. Because we are using UST as an internet service provider, we would not need a router in this lab. A switch would do the job as UST has a router in Aquinas that all internet access at UST travels through on its way out into the internet highway. A switch decides which of the computers on the LAN to send the information coming in. A hub (older technology) does not decide which computer to send information to and sends all information to ALL computers on the LAN. At home and in small businesses, you would typically purchase a router/switch combination and connect all computers to it. The router/switch combination would be connected to the modem and to the wall connection to your ISP. 7. For some of you who want to know more, here you are. The functions that a router performs are necessary for communication between the computers on your network and computers on other networks on the Internet at the network layer (TCP/IP). Probably the most important thing that a router does is perform NAT, which stands for Network Address Translation. NAT is a technology that allows computers on a network behind an Internet connection to communicate with computers outside the network; to the rest of the Internet the network is a single IP address (the one your ISP gave you), and NAT allows for incoming and outgoing connections between the computers on the network who have their own "internal" IP addresses and the computers outside the network who see only the ISPassigned IP address. 8. Another possibility for connecting a LAN at home to the internet would be the following. You could use one of your computers in your home as a "gateway" to the internet using Internet connection sharing software like the kind that Windows comes with. All computers in your home would need to be connected to this computer and it would perform the same functions as a hardware router, but there are some disadvantages that come with using that setup, like how all of the computers on the network lose Internet access if the gateway computer is offline. If you want to share an Internet connection between two or more computers in your home or small business, a hardware router is the best thing to get for it. Now that you are connected to an ISP (through UST), you have access to other LAN’s at St. Thomas and other computers on those LANs. You would have to know the username and password to access folders those computers have decided to share with others or printers that are shared. **Click on My Network Places, Entire Network and Microsoft Windows Network. You will see a list of LAN’s at UST from which you will select UST**. ©2005 QMCS Department – University of St Thomas 9 9. Again, because you are connected to the UST network, you will see all computers at St Thomas listed. The computers in your LAN are included. QM110-01, QMCS110-04, QM110-06. 10. At your home or small business where you have connected to an ISP where you have purchased a subscription, you will see only your LAN and the computers you connect. Only in a large company or university will you see many LAN’s and many computers. YOU are DONE 1. OPTIONAL STEP------ If you would like to see what a router will do when you use it instead of a switch, you may do the following. Disconnect all cables from the switch and reconnect them to the combination Ethernet/wireless router/switch. You may need to reboot each of the computers or will need to wait 5 minutes or so while the router recognizes each computer. When you access My Network Places, you will see only your LAN (UST) and ©2005 QMCS Department – University of St Thomas 10 only the 3 computers in the LAN. This is what it will look like if you created this at your home or small business. 2. BEFORE YOU LEAVE THIS ROOM, YOU MUST DO THE FOLLOWING to prepare for the next group. Delete the Shared folder from each desktop and disconnect all hardware from the computers and the switch or router so that others in this class who set up the LAN, will be able to learn by completing each step. 3. Shut down each computer. ©2005 QMCS Department – University of St Thomas 11