* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Exploration – short accounts
Portuguese India Armadas wikipedia , lookup
Portuguese India wikipedia , lookup
Nanban trade wikipedia , lookup
Conquistador wikipedia , lookup
Treaty of Tordesillas wikipedia , lookup
Portuguese discoveries wikipedia , lookup
Age of Discovery wikipedia , lookup
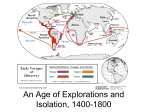
Exploration – short accounts Causes of the Age of Exploration Demand for spices – a new route to Asia and the spice world had to be found. A growing Turkish Muslim Empire blocked the regular trade route across land from Asia to Europe. Merchants needed to find a way to get cinnamon, nutmeg, cloves, pepper and silk to Europe where there was a huge demand for them and massive profits to be made. Spices were used to preserve food, to add flavour to bland food and to cure disease. Wealth and fame for explorers – the leaders of the expeditions hoped that they would gain riches and titles for themselves Wealth and power for European countries – European leaders wanted to gain control of the spice trade. Many rulers wanted gold and jewels from undiscovered lands, they saw an opportunity to conquer new lands and create huge empires. Spread of Christianity – Explorers and Rulers wanted to convert people of the new lands to Christianity. The explorers often took priests with them to convert the native people. The Renaissance spirit – the renaissance was creating a questioning spirit in Europe. Many people wanted to discover more about the world. This spirit of curiosity and hunger for knowledge led Europeans to explore other parts of the world. Improvements in ships and navigation – new ships called caravels (triangular sails and overlapping planks) were developed. These ships were faster and stronger than any ships previously built. Compasses were used to tell sailors what direction they were heading. An astrolabe was used to calculate latitude (distance north or south of the equator). Portolan charts were made giving accurate maps of the coastlines, as time went on maps got more accurate. Speed was measured using a log and line. Life on board a ship Life on board a ship was difficult. Officers and captains came from better off classes while sailors were from poorer backgrounds. More sailors were taken on board than were needed as the captain had to factor in those that would die. The captain was in charge of the ship. He was assisted by the first mate. Food was not good – dry and heavily salted. Food and water often ran out on long voyages. Ships biscuits became infested with maggots. Scurvy was common due to a lack of Vitamin C (fresh fruit and vegetables in the diet). This disease was the biggest killer of sailors on long journeys. Discipline was strict and punishment was severe. Sailors could be flogged or put in chains, and some were executed. Sailors face many dangers on board a ship. Storms could lead to shipwreck and drowning. Sailors often found themselves attacked by hostile natives. Crews could suffer from starvation and dehydration. Many sailors also were afraid of sailing off the edge of the world or attacks by sea monsters. Portuguese exploration The Portuguese led the way in the Age of Exploration, which began in the 15th Century. During the middle ages many Portuguese sailors had explored the North coast of Africa. The leader of the Portuguese explorations was Prince Henry the Navigator, third son of the King of Portugal. He realised that his country could become very rich if its sailors could sail to the bottom of Africa and onwards to India. Henry set up a school for sailors at Sagres. Here shipmakers, sailors, mapmakers and astronomers came to plan voyages along the African coast. In 1487 Bartholomeu Dias reached the Southern tip of Africa. In 1498 another Portuguese sailor Vasco Da Gama was the first sailor to reach India by sailing around Africa. Very soon the Portuguese sailed all the way to the Spice Islands. The Portuguese had discovered a new and very profitable trade route between Europe and Asia. Armed Portuguese ships began to guard the new route. They set up trading posts and forts in Africa, India and the Spice Islands. Portugal established a large empire and grew very rich and powerful. Their expeditions greatly improved the knowledge of the African coast. The Portuguese language and culture spread to parts of Africa. The Portuguese managed to break the Muslim control of the spice trade and helped to reduce the price of spices in Europe. They inspired the Spanish to launch expeditions to find trade routes to the East. Consequences of the Age of Exploration Wealth - Europe, particularly Spain and Portugal, became very wealthy. Both countries established great empires. They were soon followed by Holland, Britain and France. Rivalry over land often led to wars between these great powers. New goods became common in Europe. Among those introduced from the Americas were the potato, tobacco, chocolate and the tomato. Spices became widely available in Europe. Migration – millions of people were attracted to the colonies in the New World because of the promise of cheap lands and an easier life. Spread of Christianity – Spain, Portugal and France spread the Catholic religion wherever they went. England and Holland spread the Protestant religion. Christianity took root among the native peoples the Americas. Slavery – Europeans began the mass transportation of African slaves to the Americas to work on sugar and tobacco plantations. Disease – millions of natives died from European diseases carried by the European settlers. These diseases included measles and the common cold. This made it easier for the Europeans to conquer their lands. Language and culture – European languages replaced the traditional languages of the native people. Today Brazilians speak Portuguese and Argentineans speak Spanish. Europeans imposed their new culture on the new lands – laws, art and architecture. Decline of great civilisations – the great empires of Aztecs in Mexico and the Incas in Peru were destroyed. Europeans used native Americans as slaves on their estates. Knowledge – all the main areas of the world were explored. Better maps, showing all the new lands were produced. The old ideas Europeans had about the world were proved wrong. Theft – native peoples were robbed of all their gold and other precious raw materials. Native peoples everywhere were robbed of their land.