* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nebular Theory
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Dark matter wikipedia , lookup
Space Interferometry Mission wikipedia , lookup
Non-standard cosmology wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Rare Earth hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Cygnus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Perseus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Late Heavy Bombardment wikipedia , lookup
Beta Pictoris wikipedia , lookup
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Andromeda Galaxy wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
Structure formation wikipedia , lookup
Lambda-CDM model wikipedia , lookup
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
History of Solar System formation and evolution hypotheses wikipedia , lookup
Directed panspermia wikipedia , lookup
Future of an expanding universe wikipedia , lookup
Spitzer Space Telescope wikipedia , lookup
Stellar kinematics wikipedia , lookup
Orion Nebula wikipedia , lookup
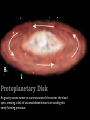
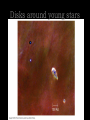
Nebular Theory E5.3A Explain how the solar system formed from a nebula of dust and gas in a spiral arm of the Milky Way Galaxy about 4.6 Ga (billion years ago). Milky Way Galaxy As viewed from Earth. Appears to be a milky band of stars across the sky. Milky Way Galaxy (Artist’s Interpretation) Observations suggest that it is a spiral galaxy. It is made up of a central bulge with spiral density arms radiating outward. The arms are areas with a concentration of matter, usually in the form of hydrogen gas, contained in clouds called nebulae. The Sun is located about ½ way out from the center to the edge on the Orion (local) Arm. Nebula Cloud of gas and dust. Sight of new star formation. Protostars • Gravity causes contraction of matter in clouds. Gravitational energy is converted into heat energy causing them to glow red. Protostars Protoplanetary Disk As gravity causes matter to contract toward the center, the cloud spins, creating a disk of unconsolidated matter surrounding this newly forming protostar. Protoplanetary disk Star blocked out to make protoplanetary disk visible Infrared allows astronomers to see dust surrounding stars. Accretion Matter not collected in the center is swept up in the protoplanetary disk forming early planets (protoplanets) through a process called accretion. Disks around young stars Meteorite evidence for accretion Evidence for the Nebular Theory 1. Observations of star forming regions (nebulae) and protoplanetary disks. 2. Age of rocks 3. Meteorite samples 4. Meteor craters throughout solar system 5. Asteroid belt