* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download lecture20.3
Topology (electrical circuits) wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Flexible electronics wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Ground loop (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Network analysis (electrical circuits) wikipedia , lookup
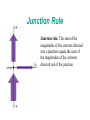
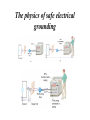
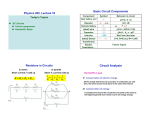
C H A P T E R 20 Electric Circuits 20.10 Kirchhoff's Rules There are two KIRCHHOFF'S RULES. 1. Junction rule 2. Loop rule These are useful in circuit analysis. Kirchhoff's Rules Junction rule. The sum of the magnitudes of the currents directed into a junction equals the sum of the magnitudes of the currents directed out of the junction. Loop rule. Around any closed circuit loop, the sum of the potential drops equals the sum of the potential rises. Junction Rule Junction rule. The sum of the magnitudes of the currents directed into a junction equals the sum of the magnitudes of the currents directed out of the junction. Application of Junction Rule Q: A galvanometer with a fullscale limit of 0.100 mA is to be used to measure a current of 60.0 mA. How much current will pass through the shunt resistance R? A: 60.0 – 0.1 = 59.9 mA Loop Rule Loop rule. Around any closed circuit loop, the sum of the potential drops equals the sum of the potential rises. Application of Loop Rule The circuit shown below contains two batteries and two resistors. Determine the current I in the circuit. Current Measurement Voltage Measurement Capacitors in Parallel Capacitors in Series RC CIRCUITS Charging RC Circuits Discharging The physics of heart pacemakers Heart pacemakers, for instance, incorporate RC circuits to control the timing of voltage pulses that are delivered to a malfunctioning heart to regulate its beating cycle. The physics of safe electrical grounding The physics of the physiological effects of current Serious and sometimes fatal injuries can result from electrical shock. The severity of the injury depends on the magnitude of the current and the parts of the body through which the moving charges pass. The amount of current that causes a mild tingling sensation is about 0.001 A. Currents on the order of 0.01−0.02 A can lead to muscle spasms, in which a person “can’t let go” of the object causing the shock. Currents of approximately 0.2 A are potentially fatal because they can make the heart fibrillate, or beat in an uncontrolled manner. Substantially larger currents stop the heart completely. However, since the heart often begins beating normally again after the current ceases, the larger currents can be less dangerous than the smaller currents that cause fibrillation.