* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download COMPLICATED CATARACT
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
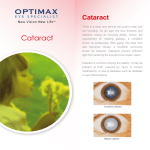
Prepared by Aizuddin Hidrus Mohd Zakariyya Bin Kamil It means opacification of the lens secondary to local(ocular) or systemic disease Ocular disease- disturbance of the nutrition of the lens and accumulation of toxins in the aqueous. The opacity usually starts in the posterior part of the cortex in the axial region(posterior cortical) as the capsule here is very thin and the subcapsular epithelium is absent allowing easy passage of toxins inside the lens. Examples: 1)perforated central corneal ulcer 2)chronic glaucoma 3)iridocyclitis 4)chorio-retinitis 5)retinal –deatchment 6)intraocular tumors 7)high myopia 8)Retinitis pigmentosa 9)Subluxation or dislocation of the lens 1)Diabetic cataract a)Snow flakes cataract(true diabetic cataract): -It occurs typically in young type 1 diabetics(insulin dependent) -It starts as “fluid vacuoles” then a cloud of opacities resembling “snow-flakes” appear all over the lens and finally becomes totally milky white. b)Pre-Senile cataract: -It stimulates senile cataract but it develops at an earlier age 2)Hypo-paratyrodism 3)Severe anemia 4)Toxic(Naphthalene,didnitrophenol,ergot,thalium, and systemic cortisone) 5)Radiation(infra red in glass blowr cataract,x ray ,electric cataract and ultrasonic radiation) 6)Other systemic diseases:atopic dermatitis,myotonia dystrophica,sclerodermia,mongolism, and cretinism.) -Positive history of ocular or systemic diseases. -The age may be suggestive (young age). -The opacity starts in the posterior subcapsular area,shows polychromatic luster )characteristic rainbow display of colors) seen on slit lamp examination . -The opacity may progress to total opacity with chalky white appearance (excessive calcium deposition). -The eye shows sign of the original disease e.gKPs of iridocyclitis,High intraocular pressure or bad projection of light in retinal detachment. -retinal function should be good -If the opacity is total,retina cannot be seen ,so Ultrasonography is mandatory -Cataract extraction is done by extra capsular cataract extraction .