* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Eye - Introduction
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
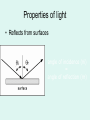
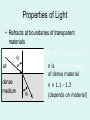
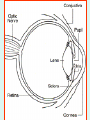
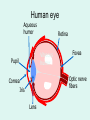
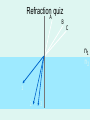
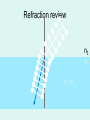
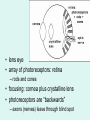
1 What is Vision ? VISION “A process that produces form images of the external world, a description which is useful to the viewer and not cluttered with the irrelevant information.” David Marr What is Light ? LIGHT Part of Electro Magnetic Spectrum to which the Eyes are sensitive What is Electromagnetic Spectrum ? TV 9 200nm 10,000nm Optical Radiations Radar 6 X-rays 1 UV Micro 3 IR Gamma -3 Cosmic -6 400nm Visible Light Radio 12 780nm Properties of light • Travels in straight lines Properties of light • Reflects from surfaces angle of incidence (qi) = angle of reflection (qr) Properties of Light • Refracts at boundaries of transparent materials sin (qi) = n sin (qr) qi n is refractive index of dense material air dense medium surf ace qr n ≈ 1.1 - 1.3 (depends on material) Frequency corresponds to colour OPTICAL MEDIA REFRACTION Human eye Aqueous humor Retina Vitreous humor Pupil Fovea Optic nerve fibers Cornea Iris Lens Refraction quiz A B C n1 n2 1 2 3 Refraction review n1 n2 n1<n2 The eyes receivers of information Shaping and transforming light into sensory perceptions The eye - receiver of information • Light sources: sun, light bulbs, candles, moon • Light reflects off of objects in environment sun obse rver The eye - receiver of information • Light sources: sun, light bulbs, candles, moon • Light reflects off of objects in environment objects effectively become light sources sun obse rver Photoreceptor “receptor of light [photons]” • photoreceptor cell transforms light into nerve impulses incoming light ray photoreceptor output of cell (signal along axon) Implications for vision • Does not matter if an object is a source or a reflector of light • Strength of reflection is a function of: – color of object – smoothness of object – relative orientation between light rays, surface normal, and observer Human Eye • lens eye • array of photoreceptors: retina – rods and cones • focusing: cornea plus crystalline lens • photoreceptors are “backwards” – axons (nerves) leave through blind spot Representing objects by edges • Very efficient compression • 100 million axons from photo receptors per eye • 1 million axons from ganglion cells per eye • Reduction by a factor of 100!! LIGHT Retina Receptors Brain Process Vision Sunset What will happen if Colors are not perceived ? RECEPTORS 100 Million Rods & Cones Billion Cells in Three Layers 10 Billion Calculations /Sec 1.2 Million Axons Optic Nerve > Dozen Vision Centers Three Dimensional World \FantasticTrip.pp s Global Facts BLIND VISION 3/60 OR LOW IN BEST SEEING EYE WHO ESTIMATES 42 – MILLION BLINDS IN THE WORLD HALF ARE DUE TO CATARACT CATARACT WITH VISION 3/60 OR LOW 20 M WILL INCREASE TO 40 M IN YEAR 2020 • Globally, at least 100 million eyes have visual acuity < 6 / 60 due to cataract. • Annually, at least 25 million eyes develop visual acuity < 6/60 due to cataract. ONE MILLION OPERATED EVERY YEAR BUT 1.5 M ADDED EVERY YEAR SO WORLD IS BECOMING MORE BLIND NUMBER OF EYE SURGEONS UK - 14 PER MILLION AFRICA – 1 PER MILLION CATARACT SURGURY RATE CSR UK – 4500 PER MILLION AUSTRALIA – 6500 PER MILLION AFRICA – 200-400 PER MILLION 95