* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Circulatory System Chapters 17, 18, 19
History of invasive and interventional cardiology wikipedia , lookup
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Aortic stenosis wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Management of acute coronary syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
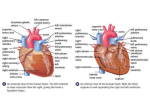
Circulatory System Chapters 17, 18, 19 • Plasma consists of : – 92% water, 8% solutes - mostly proteins (albumin, globulins (antibodies), fibrinogen), hormones, gasses (CO2, O2), nutrients (glucose), wastes (urea, ammonia). • Serum is fluid left after plasma clotting proteins are removed. • 45% Formed (cellular) elements. – all formed in the red marrow, short lived in circulation. • Consists of: – < 1% buffy coat (wbc and platelets) between plasma and rbcs. – Leukocytes - White Blood Cells - primarily function to defend against foreign bodies (bacteria, viruses, foreign proteins, etc). – Platelets (Thrombocytes) - cytoplasmic fragments. Help stop blood flow by forming a platelet plug. • 45% RBC (hematocrit- estimate of rbc mass). • Erythrocytes - Red Blood Cells 99%+ of formed elements of blood. Time to Draw! Lungs Pulmonary circuit Systemic circuit Body Tissues oxygen poor oxygen rich Lungs Pulmonary circuit Systemic circuit Body Tissues oxygen poor oxygen rich Lungs Right atrium Left atrium Right ventricle Left ventricle Pulmonary circuit Systemic circuit Body Tissues oxygen poor oxygen rich Pulmonary vein Lungs From RV Right atrium Left atrium Superior Vena Cava Inferior Vena Cava Atrioventricular valve - tricuspid Right ventricle Left ventricle To lungs Atrioventricular valve – bicuspid or mitral Aortic semilunar valve Aorta To body Pulmonary artery Pulmonary semilunar valve Body Tissues oxygen poor oxygen rich myocardium endocardium = endothelium Epicardium = visceral pericardium Interventricular septum CHORDAE TENDONAE - Tendon-like cords connect pointed ends and undersurfaces of AV flaps to papillary muscles attached to inner surface of ventricle. PAPILLARY MUSCLES - Contract as ventricles contract. Keeps AV flaps from everting back into atria, and stops backflow into atria. The Pacemaker and Conduction System of the Heart Intra-atrial path Sinoatrial node Right atrium Left atrium Atrioventricular bundle (of His) Atrioventricular node Right ventricle Left ventricle Left and Right bundle branches Conduction myofibers (purkinje) CORONARY ARTERIES - arise from small openings (aortic sinus) just above aortic semilunar valve. Arteries form an upside down crown around about the heart. CORONARY VEINS - Generally travel with arteries. Drain into right atrium by way of coronary sinus. CORONARY SINUS- When cardiac veins join together on posterior side of heart they form a sinus which drains into the right atrium.