* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 1.0.KEYSTONE PREDATOR copy
Habitat conservation wikipedia , lookup
Ecological fitting wikipedia , lookup
Unified neutral theory of biodiversity wikipedia , lookup
Biodiversity action plan wikipedia , lookup
Occupancy–abundance relationship wikipedia , lookup
Latitudinal gradients in species diversity wikipedia , lookup
Introduced species wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical ecology wikipedia , lookup
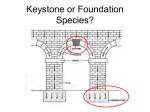
KEYSTONE PREDATOR Pacific Northwest http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=P8FlmTlmdzc Location of Robert Paine’s 25year investigation on how the loss of a top predator affects the rest of the intertidal community. WHAT IS A COMMUNITY? a group of populations of different species living close enough together to interact WHAT DETERMINES STRUCTURE OF AN ECOLOGICAL COMMUNITY? •! Is it just environmental factors or do the species themselves have a role to play? •! If they do, are all species equal or are some more important than others? INTERTIDAL SPECIES •! Producers – produce their own food •! Consumers – rely on other species for food •! stationary filter-feeders •! mobile predators PRODUCERS: ALL RED ALGAE (RHODOPHYTA) •!Nori Seaweed - Porphyra •!Black Pine - Neorhodomela •!Coral Weed - Corallina Black Pine: Neorhodomela Nori: Porphyra Coral Weed - Corallina CONSUMERS: FILTER-FEEDERS •!Acorn Barnacle - Balanus •!Goose Neck Barnacle - Mitella •!Mussel - Mytilus Acorn Barnacle: Balanus Mussel: Mytilus Goose Neck Barnacle: Mitella CONSUMERS: PREDATORS •! Whelk - Nucella •! Chiton - Katharina •! Starfish - Pisaster Whelk: Nucella Chiton: Katharina Sea Star: Pisaster Exercise One: Flexing Your Mussels •! Goal: Determine dominance hierarchy among three sessile consumers •! How do species interact with each other? •! Which species are competitively dominant over others? •! Paint a patch of one stationary competitor (e.g., Acorn Barnacle) over about third to half of the intertidal area •! Observe at least 10 weeks •! Did either of the other two stationary competitors displace Acorn Barnacle? Note: Do not count empty squares that get occupied by other species. Competitive Dominance Hierarchy •!Applies to stationary species – producers and sessile consumers •!Looks at a species’ ability to out-compete and ultimately displace other species •!In constructing dominance hierarchy diagram, arrows point to stronger competitors •!E.g., black pine starts growing on and ultimately takes over all space occupied by Nori seaweed •!Black pine is competitively dominant over Nori seaweed •!Represented in diagram as: Nori seaweed Black pine Competitive Dominance Hierarchy Exercise Two: You Are What You Eat •! Examine gut contents of 10 consumer predators and record information in table •! Run simulation for 100 weeks •! Click on microscope and examine gut contents of 10 predators •! Determine percentages of each species consumed by each predator •! Construct food web diagram FOOD WEB DIAGRAM •! Summarizes information about interconnected sets of food chains in the same ecosystem •! Uses arrows to connect species to various species that they eat •! Like in a dominance hierarchy diagram, the arrows point from species consumed to species that consumes them •! Usually predators at top, herbivores in middle, and producers at bottom Note: Do not count organisms with empty guts. Food Web Diagram Do not include information from dominance hierarchy. EXERCISE Three: Who Rules The Rock? •!Determine which predator’s removal has the biggest impact on the intertidal community •!Before starting: Make prediction about the impact of removing each predator from the community. •! Exercise: •! Record starting population size of each species •! Remove one of the consumer predators •! Run simulation by clicking Step 200 button •! Record new population sizes •! Repeat for the other predators; be sure to reset for each trial Abundance Data – Removal Experiment SPECIES BEFORE REMOVALS AFTER WHELK REMOVAL AFTER CHITON REMOVAL AFTER STARFISH REMOVAL Nori Green Algae Coral Weed Mussel Acorn Barnacle Goose Neck Barnacle Whelk Chiton Starfish 0 0 0 Who Rules the Rock? •! Not all species in ecosystem are equal •! Which one is the dominant species? •! Dominant species - the ones that comprise the greatest biomass or highest abundance •! Which one is keystone species? •! Keystone species - the one which, when removed, causes the community structure to change dramatically http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Ng6CNn6XnBg Starfish – Keystone Species Starfish •! the keystone species •! governs biological diversity in the entire intertidal zone Tatoosh Island, Washington: What Happened When the Keystone Species Was Removed? Mussel bed kept in check by Pisaster When Pisaster was regularly removed the mussel bed migrated one meter further down the intertidal zone. Yellow line indicates boundary of mussel bed before Pisater was removed. Salmon, Keystone Species in Pacific Northwest Salmon are dying in record numbers because of: •! Harvesting •! Hatcheries •! Habitat changes •! Hydropower Salmon support wildlife from birds to bears to orcas Without keystone species what will happen to the rest of the ecological http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hgXHvxon3_g community? http://www.wdfw.wa.gov/hab/salmonwild/salmonwild2.pdf Species Reintroduction Take the on-line quiz before beginning this part. + Species Reintroduction + Invasion – Carcinus meanus + Biocontrol – Sacculina carcini Important Dates 11/17, Wednesday: + Stream ecology lab report + Notebooks 11/19, Friday: + Pick up notebooks – 1PM-4PM Walker6213 (if graded) 11/22, Tuesday – last date to submit all outstanding assignments Power point presentations will be posted in a folder on RPI-LMS before Thanksgiving 11/30, Tuesday @ 9AM - LAB EXAM