* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download EXECUTIVE SUPPORT SYSTEMS (ESS)
Intelligence explosion wikipedia , lookup
Fuzzy logic wikipedia , lookup
Agent-based model wikipedia , lookup
Collaborative information seeking wikipedia , lookup
Philosophy of artificial intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Incomplete Nature wikipedia , lookup
Existential risk from artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Augmented reality wikipedia , lookup
Wizard of Oz experiment wikipedia , lookup
Ethics of artificial intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Ecological interface design wikipedia , lookup
Human–computer interaction wikipedia , lookup
Personal knowledge base wikipedia , lookup
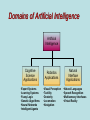
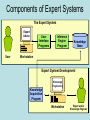
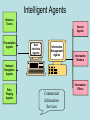
EXECUTIVE SUPPORT SYSTEMS (ESS) STRATEGIC INFORMATION SYSTEM DESIGNED FOR UNSTRUCTURED DECISION MAKING THROUGH ADVANCED GRAPHICS AND COMMUNICATIONS * EXECUTIVE SUPPORT SYSTEMS • DRILL DOWN: ability to move from summary to lower levels of detail • Designed for specific needs of CEO • Extensive support staff • Executive has 24 hour per day ability to examine, control progress throughout organization * EXECUTIVE SUPPORT SYSTEMS BENEFITS: • FLEXIBILITY • ABILITY TO ANALYZE, COMPARE, HIGHLIGHT TRENDS • GRAPHICS HELP EXPLORE SITUATION • MONITOR PERFORMANCE • TIMELINESS, AVAILABILITY OF DATA ALLOWS PROMPT ACTION * EXECUTIVE SUPPORT SYSTEMS USES IN A DIGITAL FIRM: • BUSINESS INTELLIGENCE: Info on salespeople, distributors, retailers • MONITORING BUSINESS PERFORMANCE: Balanced scorecard shows perspectives of customers, internal processes, learning, growth • ENTERPRISE WIDE REPORTING & ANALYSIS * Objectives: • Business uses of Artificial Intelligence – neural networks – Genetic algorithms – intelligence agents • Expert systems fuzzy logic virtual reality Case 2 Artificial Intelligence The Dawn of the Digital Brain • Numenta will translate the way the brain works into an algorithm that can run on a new type of computer • The human brain does not work like a computer • Intelligence, according to Hawkins, is pattern recognition Case Study Questions 1. What is the business value of AI technologies in business today? What value might exist if Jeff Hawkins can build a machine to think like humans? 2. Why has artificial intelligence become so important to business? 3. Why do you think banks & other financial institutions are leading users of AI technologies? What are the benefits & limitations of this technology? Intelligent Computers Remember Hal in the film 2001? Do computers think? Are they intelligent? Is Big Blue more intelligent than Gary Kasparov? • The Turing Machine! • • • • Intelligent Behavior Domains of Artificial Intelligence Artificial Intelligence Cognitive Science Applications •Expert Systems •Learning Systems •Fuzzy Logic •Genetic Algorithms •Neural Networks •Intelligent Agents Robotics Applications •Visual Perception •Tactility •Dexterity •Locomotion •Navigation Natural Interface Applications •Natural Languages •Speech Recognition •Multisensory Interfaces •Virtual Reality Natural Interfaces • Based in linguistics, psychology, computer science, etc. • Includes natural language & speech recognition • Development of multisensory devices that use a variety of body movements to operate computers • Virtual reality – Using multisensory human-computer interfaces that enable human users to experience computersimulated objects, spaces & “worlds” as if they actually exist Commercial Applications of AI Expert Systems • Expert System – A knowledge-based information system (KBIS) that uses its knowledge about a specific, complex application to act as an expert consultant to end users • KBIS – A system that adds a knowledge base to the other components on an IS Expert Systems • Developing expert systems • Expert system shell • Knowledge engineering Components of Expert Systems The Expert System Expert Advice User User Interface Programs Inference Engine Program Knowledge Base Workstation Expert System Development Knowledge Acquisition Program Knowledge Engineering Workstation Expert and/or Knowledge Engineer Development Tool • Expert System Shell – Software package consisting of an expert system without its knowledge base – Has inference engine and user interface programs Methods of Knowledge Representation • Case-Based – knowledge organized in form of cases – Cases: examples of past performance, occurrences and experiences • Frame-Based – knowledge organized in a hierarchy or network of frames – Frames: entities consisting of a complex package of data values Methods of Knowledge Representation • Object-Based – knowledge organized in network of objects – Objects: data elements and the methods or processes that act on those data • Rule-Based – knowledge represented in rules and statements of fact – Rules: statements that typically take the form of a premise & a conclusion – Such as, If (condition) then (conclusion) Expert System Benefits • Faster and more consistent than an expert • Can have the knowledge of several experts • Does not get tired or distracted by overwork or stress • Helps preserve and reproduce the knowledge of experts Expert System Limitations • • • • • Limited focus (DOMAIN) Inability to learn Maintenance problems Developmental costs Can only solve specific types of problems in a limited domain of knowledge Expert Systems Expert Systems IBM Network Management Neural Networks • Computing systems modeled after the brain’s mesh-like network of interconnected processing elements, called neurons • Interconnected processors operate in parallel and interact with each other • Allows network to learn from data it processes Neural Networks • Used to solve problems that people can’t … ??? • What happens? – Enormous number of cases (data) with representative I/O – Statistical inferencing to identify patterns – Use/reuse the pattern to predict future outcomes Neural Network Examples • BANK of AMERICA – NN evaluates commercial loan applications • AMERICAN EXPRESS: – NN reads handwriting on credit card slips • STATE OF WYOMING: – NN reads hand-printed numbers on tax forms • ARCO AND TEXACO: – NN helps pinpoint oil and gas deposits • SPIEGEL – NN prunes mailing list • DEERE & COMPANY – NN manages pension fund Fuzzy Logic Systems • Resembles human reasoning allowing approximations & inferences, use of ambiguous data • Fuzzy data • Fuzzy rules • Data is deliberately imprecise • Fuzzy logic can process this imprecise data Fuzzy Logic Systems Fuzzy Logic Rules Risk should be acceptable If debt-equity is very high then risk is positively increased If income is increasing then risk is somewhat decreased If cash reserves are low to very low then risk is very increased If PE ratio is good Then risk is generally decreased Fuzzy Logic SQL Query Select companies from financials where revenues are very large and pe_ratio is acceptable and profits are high to very high and (income/employee_tot) is reasonable Genetic Algorithms • Uses Darwinian, randomizing & other mathematical functions • Stimulates evolutionary process to yield better problem solutions • Mutations • Crossovers • Selections GE’s Engeneous • Page 304 (351) • Design of a Boeing 777 engine • Used genetic algorithm application • Used to develop more efficient fan blades • Estimated billions of years to evaluate the astronomical number of performance & cost combinations • Engenious expert system offered optimal solution in a week Virtual Reality (VR) • Computer-based systems to create a realistic environment, relying on multi-sensory I/O – a tracking headset with video goggles and stereo earphones, – a data glove or jumpsuit with fiber-optic sensors that track your body movements & – a walker that monitors the movement of your feet • 3D video games • Valuable for training, education, remote servicing, product design Virtual Reality (VR) Intelligent Agents • Use of software surrogates • Software robots “bots” • Many types of intelligent agents… Intelligent Agents Interface Tutors Presentation Agents Search Agents User Interface Agents Information Management Agents Information Brokers Network Navigation Agents RolePlaying Agents Commercial Information Services Information Filters User Interface Agents • Interface Tutors – observe user computer operations, correct user mistakes & provide hints & advice on efficient software use • Presentation – show information in a variety of forms & media based on user preferences • Network Navigation – discover paths to information & provide ways to view information based on user preferences • Role-Playing – play what-if games & other roles to help users understand information & make better decisions Intelligent Agents Dow Jones: Intelligent Web Agents • Page 309 (355) • Use to compare prices or other characteristics • 600,000 customers search stories from 6,000 publications • Dow uses intelligent agents and other AI technologies to manage the process • Results on web page or e-mailed to user