* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Tracing Phylogeny
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
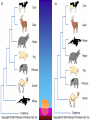
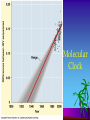
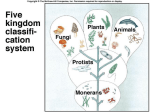
Systematics The study of biological diversity in an evolutionary context Systematic Tools Molecular Comparisons – usually (rRNA or mtDNA) DNA-DNA Hybridization Restriction maps DNA Sequence analysis Taxonomy The science concerned with naming and classifying the diverse forms of life Taxonomic Groups Domain Kingdom Phylum (Division) Class Order Family Genus Species Domains (Table 27.2) Bacteria Archaea Eukarya Cell type Prokaryote Prokaryote Eukaryote Introns Absent Present Present RNA Poly One Several Several P. S. Formylmethionine Methionine Methionine Binomial Nomenclature Panthera leo (African Lion) Binomial Nomenclature Ardea herodias (Great Blue Heron) Classification and Phylogeny Phylogenetic Groupings Monophyletic – ancestor and all its descendants Phylogenetic Groupings Paraphyletic – ancestor with some but not all its descendants Phylogenetic Groupings Polyphyletic – two different ancestors Phylogenetic Groupings Similarities Homology – likeness attributed to shared ancestry Similarities Analogy – likeness due to similar ecological roles and natural selection due to convergent evolution Molecular Homoplasy Analogous species that have similar DNA sequences that evolved independently in two species Ontogeny Recapitulates Phylogeny (Ernst Haeckel) Ontogeny – individual development Recapitulates – repeats Phylogeny – evolutionary descent The Science of Systematics Phenetics – based on a number of similarities and differences – does not take into account homology or analogy – all groupings Classical Evolutionary Systematics George Gaylord Simpson The Science of Phylogenetic Systematics Classical Evolutionary Systematics – most commonly used up until recently – based on shared homologous structures – takes into account the amount of adaptive evolutionary change (novelties) – Monophyletic and paraphyletic groupings The Science of Systematics Cladistics (Phylogenetic Systematics) – based on shared homologous structures – only monophyletic groupings Will Hennig The Science of Phylogenetic Systematics Cladistic Assumptions 1. Monophyletic 2. Descent follows a bifurcating pattern 3. Changes in characteristics occur in lineages over time Cladistics Shared primitive characters – Outgroupings – Plesiomorphies Ancestral characteristics Shared derived characters – Synapomorphies Phylograms Ultrametric Trees Cladistics Cladistics Cladistics Pitfalls Reptiles????? Molecular Clock Tree of Life Phylogenetic Fuse