* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Layers of the Earth
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
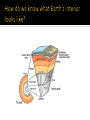
Inside the Earth At earth’s center is the inner core. The inner core is composed of nickel and iron in solid form. The depth from the surface is 6371 km Surrounding the inner core is an outer core. The outer core is composed of nickel and iron in a liquid state. The depth from the surface is 5150 km Around the core is the thickest of Earth’s layers, called the mantle. The mantle is composed mostly of compounds rich in iron, silicon, and magnesium. Although the mantle is solid, high pressure and temperature cause it to behave as a liquid in some ways. The depth from the surface is 2890 km Surrounding the mantle is the crust, a thin, rigid layer of lighter rocks that cover earth’s surface. The depth from the surface is 0-65 km The crust covers earth’s entire surface; there is oceanic crust and continental crust. Continental crust: composed of granite at thicknesses of 35 km (60 km over mountain ranges) Oceanic crust: composed of basalt at thicknesses of about 5 km Suppose you could drive a car at 100 km/hr (62 mi/hr) from Earth’s surface to the center of the core. At that speed, the car would take about half an hour to drive through most continental crust, about another 29 hours to drive through the mantle, and about an additional 35 hours to drive to the center of the core. Earth’s near surface layers are further classified by their material properties. Lithosphere: The crust and the upper most portion of the mantle together. The thin, slush like layer of the mantle to which the lithosphere floats upon. YouTube - The Solid Earth - Environmental Science Wells drilled into Earth are mostly in the upper 7 km of the crust. Deepest well is in Russia- took 20 years to drill a 12 km hole, cost more then $100 million. Drilling stopped in 1989 after getting stuck at 12 km. Materials from earth’s interior are brought to the surface during volcanic activity. Only useful to depths of about 200 km below the surface. Seismic earthquake waves travel time depends on properties of rock material that they pass through. Certain waves cannot travel through liquid states. Seismic waves allow travel faster in denser rock material. Earthquakes for Kids