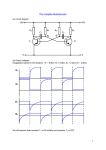
* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Negative mass wikipedia , lookup
Conservation of energy wikipedia , lookup
Electrical resistance and conductance wikipedia , lookup
Anti-gravity wikipedia , lookup
Electrical resistivity and conductivity wikipedia , lookup
Potential energy wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
QUIZ 1. Define electric force The amount of attraction or repulsion between two charged objects 2. What is charge measured in? C 3. If two charges are opposite, what happens to those charges? They will attract each other 4. The force between two charges can be calculated using the following equation F = k Q1Q2 r2 What two things affect the amount of Force between 2 charges? The size of the charge and the distance between them 5. Draw the electric fields of two negative charges and a positive and neutral charge When a battery is connected to a conductor; • One end of the conductor becomes positive, the other negative • Excess positive charge at one end, excess negative charge at other end • This causes an electric field to form, directed away from positive towards negative • Charges in the wire will experience a force due to this field • Free electrons in the wire will tend to move (in direction opposite to the field) • This movement of charge is called ELECTRIC CURRENT ELECTRIC CURRENT Electric Current is the flow of electric charge Magnitude of current is defined as the rate of transfer of charge Amount of charge that flows past any point in a conductor in one second A current of 1 A flows when 1 C flows past a point in 1 second 1 A = 1 C s-1 ELECTRIC CURRENT Electric Current is the rate of transfer of charge I=q t I = Current in Amps q = Charge in C t = Time in seconds 1 Ampere (A) = 1 C s-1 1C=1As Determine the charge that has flowed through a torch battery producing a current of 300mA if it has been left on for 20 minutes. I=q t q=Ixt 300 x 10-3 x 1200s = 360 C CURRENT FLOW • Electric charge can be positive or negative • The direction of an electric current is the direction of the flow of POSITIVE CHARGE • Positive charge can be transferred either by positive charges moving in the direction of the current or by negative charges moving in the opposite direction • In a metal wire, the current is carried by electrons moving in the direction opposite to that of the current • Two types of current, electron current and conventional current • CONVENTIONAL current is the one we use because it is the transfer of positive charge I t=0 I t = later --------------- -q ++++ ++++ ++++ +q EMF & ELECTRIC POTENTIAL In order to drive a current the charges must be given energy EMF stands for Electromotive Force, it is not a force but it is the energy given to charges EMF – concentration of charge Concentrated charges have potential energy, when the charges are allowed to move the electrical energy can be recovered EMF is electric potential given to charges by a device EMF & ELECTRIC POTENTIAL A battery uses chemical energy to give charges on its terminals potential energy A generator uses the kinetic energy of rotation to give charges potential energy A solar cell uses sunlight to give potential energy to charges ELECTRIC POTENTIAL SI unit for Potential is Joules per Coulomb 1J -1 C = 1 Volt The alternator of a car being driven at night with the headlights on is producing a 50 A current at an EMF of 12V How many coulombs of charge flow from the alternator each second? 1 A = 1 J s-1 50 A = 50 C per second How many joules of energy does each coulomb of charge obtain? 1 V = 1 J C-1 12V = 1C of charge is given 12J of energy How many joules of energy does the alternator produce each second? 1 C is given 12J of energy therefor 50 C x 12 J = 600J Where does this energy go? The energy goes to the headlights, the ignition and other electrical devices. Some may also go and recharge the battery ELECTRIC CIRCUITS AND POTENTIAL DIFFERENCE A electric circuit consists of at least one source of EMF, conductors and circuit elements (bulbs, switches) In these circuit elements is where electric potential energy is converted into heat, light, motion When a battery is connected to a circuit it creates a potential difference When switch is off all connected to positive terminal will have positive charge concentration, all those connected to negative side will have negative charge concentration When switch turned on, charges move through circuit using up their potential energy as they move through circuit elements. When charge moves through a circuit element it loses potential energy This is known as Potential Difference A charge q moving through a potential difference ∆V will lose energy E = qV E = energy in J q = charge in C V = voltage in V The potential difference across a torch bulb is found to be 2.7V. The current flowing through it is 0.2A How much charge flows through the torch in 1 minute? q = It q = 0.2A x 60 s q = 12C How much energy is lost by this charge? E = qV E = 12C x 2.7V E = 32.4 J Complete Q 7.3, page 289 in Heinemann Physics 1.What direction does current flow in a circuit? Current flows in the direction of the transfer of positive charge 2. A source of EMF does what to a charge? Gives electric potential energy to a charge 3. 1 V = ? 1 V = 1 J C-1