* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The ECG in clinical practice: making the diagnosis at a glance
Quantium Medical Cardiac Output wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
Atrial fibrillation wikipedia , lookup
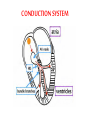
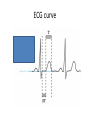
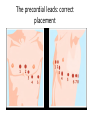
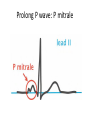
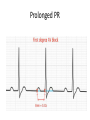
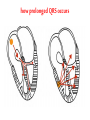
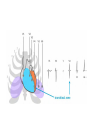
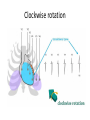
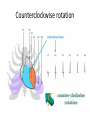
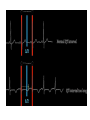
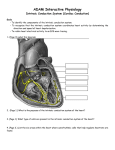
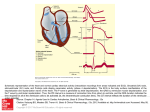
The ECG in clinical practice: making the diagnosis at a glance Prepared and presented by Dr Lukoji Specialist Physician DEFINITION: • Graphic recording of the electrical activity (potential) of the heart on a standard paper grid. CONDUCTION SYSTEM (FLIP CHART) • Sinus node (initiate the electrical impulse): 6080/minutes: fires the impulse to the atria • AV node (CS in RA): only electrical connection between atria and ventricles: transmit the impulse from the atria to the ventricle: slows down the impulse (filter and regulator) • Bundle of His: made out of 2 branches: LBB and RBB • Purkinje network: within the ventricle CONDUCTION SYSTEM How ECG is generated: • Impulse depolarizes successively the atria then the ventricles follow by repolarization for each . • Depolarization and repolarization are then recorder graphically as an ECG in form of a curve by means of electrodes attached to the patient’s body surface at conventional spots. • Depolarization and repolarization generate waves on the tracing. ECG curve Deconstructing the ECG curve: • • • • • • • P wave: atrial depolarization QRS complex: ventricular depolarization (varies) T wave: ventricular repolarization Isoelectric line Calibration signal (rectang=10mm=1mv) ECG generally prints at a speed of 25mm/sec Leads: standards (I,II,III), augmented (aVF, aVL, aVR) &precordial (V1 to V6) • Leads#electrodes Electrodes placement • Proper placement is key to accurate tracing hence accurate diagnosis. • Ensure proper skin preparation • Ensure patient is calm (explain) • Connect electrodes at appropriate spots (chest electrodes!) The precordial leads: correct placement ECG stepwise analysis • • • • • Check calibration Check paper speed Check patient identity If needed have a caliper and lens I take a minimum of 5 minutes to analyze each ECG (you do not need to hurry, details are key for accurate diagnosis) • Get senior colleague opinion if doubt (overdiagnosis or underdiagnosis) • Automated interpretation from ECG machine is often misleading: beware!!! What to look for: general impression and rhythm analysis • • • • • • • • • • • What is the rhythm: NSR or not? What is the heart rate? P wave duration Intervals measurement: P, PR, QRS, QT QRS axis QRS duration QRS amplitude: low voltage, sokolow, RSS QRS infarction signs Rotation and transition zone ST and T segment T-U wave 1 • • • • • Sinus rythm P positive in lead I and II Every P wave is followed by QRS complex PR interval is constant QRS interval is constant 2. Heart rate: 300/large square between R-R interval P wave duration Prolong P wave: P mitrale Right atrial hypertrophy: P pulmonale PR interval Prolonged PR Short PR duration (pre-excitation syndrome) Short PR duration Prolong QRS duration how prolonged QRS occurs Bundle branch block Bundle branch block Clockwise rotation Counterclockwise rotation Illustration of LVH ST depression and T inversion T wave inversion ST SEGMENT AND ACS