* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Jelly Fish Anaphylaxis
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
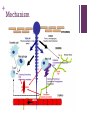
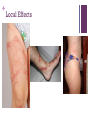
+ The Anaphylaxis Blues Jellyfish strikes back Dr Daniel Khamoudes Toxicology Service Prince Of Wales Hospital + Outline Case History Facts + Case 38M Otherwise well Hx of anaphylaxis to bee stings Blue Bottle Sting at Maroubra 1730 First aid with water to remove Presented POW ED 1800 with pain Primary sting L lateral ankle Pain locally and L groin 8/10 + Case In ambulance bay, hot water submersion 1830 sudden onset tongue angioedema Moved to resus Nil respiratory or haemodynamic compromise Adrenaline 0.5mg IM at 1855 Rapid resolution within 5 minutes Hydrocortisone 200mg IV Ranitidine 50mg IV Fexofenadine 180mg po Fentanyl 150mcg, in 50mcg aliquots + Case Return of angioedema 2000 Nil respiratory or haemodynamic compromise Second dose Adrenaline 0.5mg IM 2010 Resolution of symptoms over 10 minutes Further boluses of Fentanyl as groin pain an issue Creatine kinase and UEC NAD HDU admission for observation re angioedema Nil further episodes Pain settled overnight + History Discovered 19031 Richet and Portier Dogs vs Jellyfish toxin Second exposure lower dose lethal 1913 Nobel Prize Origin Greek –ana (against) –phylaxis (protection) Originally aphylaxis (publicist) 1. Wikipedia + Mechanism Nematoblasts->Nematocysts Spring loaded syring Discharge within 700ns of contact 18m/s 5.4x106g Pressure 7.7GPa Local and systemic injury + Mechanism + Mechanism Toxin2 Local and systemic Tubule Collagens, glycoproteins and polysaccharides Innate and adaptive cellular and humoral responses 2. J Tibballs, A Yanagihara, H Turner, K Winkel. Immunological and Toxinological Responses to Jellyfish Stings. Inflammation & Allergy - Drug Targets, 2011, 10, 438-446. + Mechanism + Physalia Utriculus Physalia physalis vs Physalia utriculus Float and Tail Nematocysts remain active + Local effects Immediate pain and erythema Progressive pain to draining lymph nodes Long term scarring unlikely but occurs + Local Effects + Systemic Effects Venom Pore forming in plasma membrane, Ca influx/swelling/lysis2,3 Neuro/cardio toxicity2,4 Potential deaths with Physalia physalis 5,6 Immune Response – immediate and delayed Hypersensitivity reaction Previous exposure Cross reactivity 3. Edwards, L.P.; Whitter, E.; Hessinger, D.A. Apparent membrane pore-formation by Portuguese Man-of-war (Physalia physalis). Toxicon, 2002, 40(9), 1299-1305. 4. Burnett, J.W. Treatment of Atlantic cnidarian envenomations. Toxicon, 2009, 54(8), 1201-1205.5. 5. Tibballs, J. Australian venomous jellyfish, envenomation syndromes, toxins and therapy. Toxicon, 2006, 48(7), 830-859. 6. L Cegolon, W Heymann, G Mastrangelo. Jellyfish Stings and Their Management: A Review. Marine Drugs, Feb 2013. 11(2):523-550 + Treatment Supportive Analgesia Consider regional Hot water submersion3 Anaphylaxis APP ALS IgG production noted8 7. C Loten, B Stokes, D Worsley, J Seymour, S Jiang, G Isbister. A randomised controlled trial of hot water (45°C) immersion versus ice packs for pain relief in bluebottle stings. MJA April 2006. 184(7):329-333. 8. Russo, A.J.; Calton, G.J.; Burnett, J.W. The relationship of the possible allergic response to jellyfish envenomation and serum antibody titers. Toxicon, 1983, 21(4), 475-480. + Summary Local and systemic symptoms Treatment supportive +/- specific ?Steroid topical ?Sun exposure + References Wikipaedia 2. J Tibballs, A Yanagihara, H Turner, K Winkel. Immunological and Toxinological Responses to Jellyfish Stings. Inflammation & Allergy - Drug Targets, 2011, 10, 438-446. 3. Edwards, L.P.; Whitter, E.; Hessinger, D.A. Apparent membrane pore-formation by Portuguese Man-of-war (Physalia physalis). Toxicon, 2002, 40(9), 1299-1305. 4. Burnett, J.W. Treatment of Atlantic cnidarian envenomations. Toxicon, 2009, 54(8), 1201-1205.5. 5. Tibballs, J. Australian venomous jellyfish, envenomation syndromes, toxins and therapy. Toxicon, 2006, 48(7), 830-859. 6. L Cegolon, W Heymann, G Mastrangelo. Jellyfish Stings and Their Management: A Review. Marine Drugs, Feb 2013. 11(2):523-550 7. C Loten, B Stokes, D Worsley, J Seymour, S Jiang, G Isbister. A randomised controlled trial of hot water (45°C) immersion versus ice packs for pain relief in bluebottle stings. MJA April 2006. 184(7):329-333. 8. Russo, A.J.; Calton, G.J.; Burnett, J.W. The relationship of the possible allergic response to jellyfish envenomation and serum antibody titers. Toxicon, 1983, 21(4), 475-480.