* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download organ systems - Peoria Public Schools
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
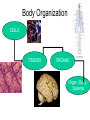
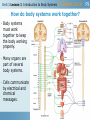
Big Idea The human body is made up of systems that have different functions, an these systems work together to maintain the body. Unit 1 Lesson 1 Introduction to Body Systems How do the body systems work together to maintain homeostasis? Key Terms: homeostasis (will be combined with lesson 2) Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Body Organization CELLS TISSUES ORGANS Organ (Body) Systems Unit 1 Lesson 1 Introduction to Body Systems P6-8 Inside Out What do the body systems do? • Body systems (organ systems) help organisms coordinate and complete the necessary functions for life. • Groups of organs that work together form body systems. • Coordinate all the functions of the body Unit 1 Lesson 1 Introduction to Body Systems P6-8 What do the body systems do? • The muscular system allows movement of body parts. • The skeletal system supports the body, protects important organs, and makes blood cells. • The respiratory system gathers oxygen from the environment and gets rid of carbon dioxide. • The male reproductive system produces sperm and delivers it to the female reproductive system. • The female reproductive system produces eggs and nourishes a developing fetus. • he cardiovascular system moves blood through the body. Unit 1 Lesson 1 Introduction to Body Systems P6-8 What do the body systems do? • The lymphatic system returns leaked fluids back to the blood and is a part of the immune system. • The endocrine system makes chemical messages that regulate conditions in the body. • The integumentary system is the protective covering of the body that acts as a barrier. • The excretory system gets rid of the body’s waste. • The digestive system breaks down food into nutrients that can be used by the body. • The nervous system collects information and responds to it by sending messages. - Body Organization and P6-8Homeostasis Organs and Organ Systems Each organ in your body is part of an organ system, which is a group of organs that work together to perform a major function. Working Together Activity Which organ system(s) is involved in these activities? Activity Organ Systems Involved in activity Snoring 3 Sweating 2 Jumping at a loud sound 5 Drinking Water 5 Running 5 Eating an apple 4 Maintaining a heartbeat 3 P6-8 Working Together Activity Which organ system(s) is involved in these activities? Activity Organ Systems Snoring (3) Sweating (2) Jumping at a loud sound (5) Drinking Water (5) Running (5) Eating an apple (4) Maintaining a heartbeat (3) Organ System Major Organs in the System Digestive Stomach, intestines Breaks down food Respiratory Lungs, diaphragm Provide oxygen to the cells and remove carbon dioxide from body Simile The ____(organ system) is like a/an _____(object) because it_______. Main Function of the Organ System The digestive system is like a blender because it breaks down food. The respiratory system is like an oxygen tank because it contains gas. Muscular The ____________________________is like a ______________________because it _______________________________________. Skeletal The ____________________________is like a ______________________because it _______________________________________. Excretory The ____________________________is like a ______________________because it _______________________________________. Nervous . Circulatory Endocrine Simile Organ System Organs in the System Digestive Stomach, intestines Respiratory Muscular Provides support Bladder, kidney Removes wastes The excretory system is like a trash can because it is used to remove wastes. Brain, spinal cord Relays messages between the brain and body through electrical impulses Excretory Endocrine Breaks down food The digestive system is like a blender because it breaks down food. The skeletal system is like a clothes hanger because it provides support. Skeletal Circulatory The ____(organ system) is like a/an _____(object) because it_______. Provide oxygen to the The respiratory system is like an oxygen Lungs, cells and remove tank because it contains gas. carbon dioxide from diaphragm body The muscular system is like a rubber band because it can allow something to Bicep, Provides movement move. abdominals Femur, ribs, skull Nervous Main Function of the Organ System Heart, aorta Thyroid, adrenals The nervous system is like an electrical cord because it relays messages through electrical impulses. The circulatory system is like a semi-truck because it transports materials to different Transports materials places. to cells Produces chemicals needed by body The endocrine system is like a chemical factory because it produces chemicals for specific purposes. Unit 1 Lesson 1 Introduction to Body Systems A Closer Look P8 How are structure and function linked? • Different organisms can have organs with similar structures, functions, shapes, and sizes. • The shapes and sizes of cells are related to their function. 7) The movement ability of muscle cells allows muscle tissue to contract and relax, which moves the body. Unit 1 Lesson 1 Introduction to Body Systems A Closer Look How do body systems work together? • Body systems must work together to keep the body working properly. • Many organs are part of several body systems. • Cells communicate by electrical and chemical messages. P9 P9 8) Underline the following – examples of systems working together: The endocrine system releases hormones to prepare the body for action. The eyes, part of the nervous system, see the ball coming. They send electrical messages to the brain. The brain sends electrical messages to the muscles. The bones and muscles grip the bat tightly. The muscles and bones help the legs move quickly. The heart pumps quickly to move blood from the lungs to the body. Muscles use oxygen from the blood to keep moving. 9) The nervous system and the integumentary system are interacting. The integumentary system is producing the sweat, which causes water to be lost from the body. The brain, which is part of the nervous system, detects that the body needs more water and is making the person thirsty. Unit 1 Lesson 1 Introduction to Body Systems P10 Keeping the Balance What is homeostasis? Basic Needs of ALL cells: • Food, oxygen and have their wastes takes away. • If body conditions were to change cells would not be able to do their jobs. • Homeostasis is the body maintaining a constant internal environment when outside conditions change. • Body systems can respond (quickly and in the right way) to changes in the external environment. Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Unit 1 Lesson 1 Introduction to Body Systems P10 Keeping the Balance What is homeostasis? 10) The body temperature increases, the person feels hot, and he or she sweats Copyright © Houghton Mifflin Harcourt Publishing Company Unit 1 Lesson 1 Introduction to Body Systems P11 What can go wrong with homeostasis? • A problem in one body system may cause problems in other body systems. • Body cells cannot work properly may cause disease or death. • Lack of food and the presence of toxins (prevent cells from carrying out life processes) or pathogens (break down cells)may disrupt the proper functioning of body systems. • Problems with the structure or function of cells, tissues, or organs can cause problems in the body. • If cells cannot get energy or necessities, they cannot work properly. – disrupt homeostasis • When the body cannot maintain homeostasis, it is easier for pathogens to invade the body. Body System Affected What are the effects? Nervous System Disrupts proper functioning of the brain. The brain cannot respond properly to internal or external messages Digestive System Liver and other organs can be harmed by alcohol, which will affect the ability of the system to digest food and remove toxins from the body. Reproductive System P11 Could harm the ability to produce healthy sex cells, or in the case of a woman, develop and nourish a healthy baby. P12 13) Respiratory 14) Nervous, Blood 15) Nervous; Muscular (either order) 16) Brain or nervous system 17) The amount of oxygen getting into the body will be reduced, so every cell and every system would be starved of oxygen. The body’s tissues and organs would not be able to work properly pg 13 & WS due Monday