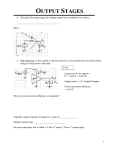
* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Review II
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Electronic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Flexible electronics wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Integrated circuit wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Rectiverter wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
ECE 1250 Midterm I – Exam Topics: Op Amps You may also need to use the following concepts to solve the op amp problems: voltage /current dividers, KVL/KCL, Node-Voltage, resistors in series/parallel, Ohm’s Law. 1) Identify common Op Amp Circuits. Be able to identify common op amp circuits. These are the op amp used as a switch (no feedback), inverting and non-inverting amplifiers, inverting and non-inverting summers, voltage follower, difference amplifier. Example: See Op Amp Cookbook on Recognizing Inverting & Non-Inverting Amplifiers (see links online). More Examples: See all of the Op Amp HW & Similar Problems, and be able to tell what kind of circuit each is dealing with. 2) Design common Op Amp Circuits. Be able to design (specify the resistors for) the common op amp circuits above. Understand voltage rails and the linear region of the circuit. For example: Design a circuit where Vo = 3Vin Examples: See Op Amp Cookbook, and Problems 4.9, 4.15, 4.26 3) Compute the output voltage or current for a general op amp circuit. Use the ideal op amp assumptions (In = Ip = 0, Vp=Vn, Vo = A(Vp-Vn) where A is very large) to simplify the circuit. Then solve the circuit using voltage /current dividers, KVL/KCL, Node-Voltage, resistors in series/parallel, Ohm’s Law, etc. I will suggest a method for solving the problem, but you may use any method that works. Example: Use Node-Voltage to : 4) Design an electrical system using Op Amps. Be able to design a block diagram of an electrical system, be able to design the individual blocks of that system (as in 3 above), and be able to determine if any of the op amp(s) in your system will saturate for a given set of input voltages. Be prepared to EXPLAIN your system (tell how it works, what all of the interim voltages and currents are between the blocks of your block diagram). Example2: Design a system where Vo = 3 ( V1 + V2) – 4 V3 Example3: Design a system where Vo = 15V IF V1>V2 and V3>5V.