* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download RT 255 C Cross Sectional Anatomy
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
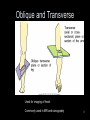
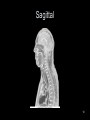
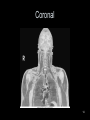
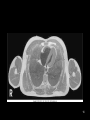
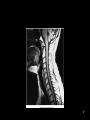
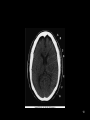
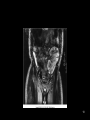
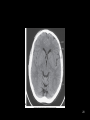
RT 255 C Cross Sectional Anatomy Week 1 FINAL 4-13-09 1 Name the Sectional Planes A B C D 2 Oblique and Transverse Used for imaging of heart. Commonly used in MR and sonography 3 Axial (Transverse) Planes –1 –2 –3 –4 –5 –6 4 Axial Scout 5 6 Axial (cross sectional) 7 Sagittal Plane • 1 • 2 • 3 8 Sagittal Scout 9 Sagittal 10 Coronal Plane • 1 • 2 • 3 • 4 • 5 11 Coronal 12 13 Coronal 14 Name the Imaging Plane 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 Both Radiation: Why CT vs. Radiography • Superimposition • Contrast Resolution – Less scatter • One exposure 26 Similar to Radiography • Radiopaque are white – Bone – Prosthesis • Lower density images are gray – Fat – Muscles – Organs • Very low density are black – Air 27 Hounsfield Units 28 Fundamentals of CT Cross sectional Tube rotates around patient Detectors measures primary data Primary data sent to computer Calculated according to algorithm Data assembled into a matrix Each sectional slice is displaced on cathode ray tube 29 Generations of Scanners • First generation – – – – 1 2 3 4 • Second generation – – – – 1 2 3 4 30 Third Generation • Rotate/ rotate • More than 750 detectors • 1-10 seconds 31 Fourth Generation • Rotate only • Fixed detectors • More detectors • Higher dose to PT 32 Technical Aspects • Remnant radiation is collected –1 –2 • Electrical signal digitized – Each signal assigned a number • Signals combined to form digital image – Field of View (FOV) determines amount of data to be displayed on monitor 33 Breakdown of the Digital Image • Array of numbers –1 • Pixel –1 –2 • Voxel –1 –2 –3 34 System Components • Computer – Operators console • Gantry • Table 35 Computer • Four basic functions – – – – 1. 2 3 4 36 Data Acquisition • Tech chooses various parameters –1 –2 –3 –4 37 Image Reconstruction • Digitizes raw data • Computer performs mathematical computations on a temporary storage system – Host computer has limited storage capacity • Reconstruction takes a few seconds 38 Long term Storage • After reconstruction it is transferred to another storage medium • Those temporary images on the host computer are archived separately as an independent study that can be retrieved later 39 Image display • Can be viewed on a video monitor • Tech and doctor can communicate with host computer to view images • Can manipulate images – 1 – 2 – Image resolution lost with reconstruction in other planes 40 Gantry • Circular • Aperture is the hole PT goes in • Houses – Detector, slip ring, generator and x-ray tube • Tube similar to x-ray tube – Must withstand higher amounts of heat • Can be tilted 30 degrees forward and back 41 Table • Automated device linked to gantry & computer • Moves in increments – According to protocol • Made of wood or low density carbon composite • Has a weight limit 42 Control Console • Where the tech controls the scanner • Has a keyboard, display monitor & mouse • Allows tech to control – – – – 1. 2 3 4 43 Image Manipulation • Windowing – 1. • Window width –1 –2 –3 • Window level –1 –2 44 Windowing Window width 400 Window width 2200 Window level 35 Window level 400 45 Factors Affecting Image Quality • • • • • • • Spatial resolution Contrast resolution Noise Artifacts Patient factors Scan times Scan diameter 46 Spatial Resolution • What happens to resolution with smaller phosphor crystals in standard film screen systems? • Is a function of pixel size – Smaller: better detail • Thinner slices: increased detail 47 Contrast Resolution and Noise • Appears as graininess • Ability to distinguish adjacent tissue • In CT it is better than in conventional x-ray – Less scatter • Low noise is smooth to the eye • High noise is blotchy and spotty • As noise increases contrast resolution decreases 48 Artifacts • Streak artifacts – Metallic objects, pacemakers, and prosthesis • High concentration barium 49 Patient Factors • Motion • Size of patient 50 Image Quality under Tech Control • Slice thickness • Scan time • Scan diameters 51 Diagnostic Applications • Most common anatomy examined is – Head, chest and abdomen • Exam of choice for: – Head trauma – CVA • Also useful for: – – – – – – – – – Infarctions Hemorrhage Disk herniations Craniofacial fractures and tumors Cancers Hydrocephalus Degenerative diseases Inflammatory infections Congenital disorders 52 Use of Contrast Media • Can be administered orally, rectally and intravenously • IV usually non-ionic contrast • BA and Hypaque used for abdomen and GI studies. – 2% concentration BA – Low concentration (hypaque) 53 Special Features • • • • • • Dynamic scanning CT angiography (CTA) Spiral/helical CT Multi-slice Spiral/helical CT 3 D imaging Radiation therapy treatment 54 Dynamic Scanning and CTA • After contrast administration • Sequential scanning times as different structures enhance • CTA: –1 –2 –3 55 CTA 56 CTA 57 Spiral / Helical CT and Multi-slice Spiral/ Helical CT • Single row of detectors • Gantry rotates around PT as table moves • Multiple rows of detector arrays • A four row scanner would scan 4 times faster • Scans a volume instead of slices • Better detail • Improced spatial resolution • Fast scan times • LG areas of body can be done with one breath hold – For peds and combative patients 58 Spiral and Multi-slice Spiral 59 3D Imaging • Postprocessing technique • Takes 2D raw data and constructs a 3D image 60 3D imaging 61 3D Imaging 62 Radiation Therapy Planning • Gives volumetric and depth calculation ability • Allows for one CT instead of the 3 they used to do • Flat board used instead of curved couch • Dose to normal tissue is minimized 63 RAD Therapy and CT 64 RAD Therapy and CT 65 CT and Radiation Dose • CT doses are higher than conventional radiography • A lower pitch results in a higher dose – More overlap • Thinner slices also result in a higher dose 66 CT vs. MRI • MRI exhibits better low contrast than CT • CT demonstrates bone better than MRI • Higher cost and takes longer • Faster, so preferred for some PT’s • Cannot do with metal – Small gantry – Wide aperture • Less costly 67 The Future of CT • Has significantly increased in the past 5 years • Higher quality images increase accuracy of diagnosis and treatment • Cost effective • Will continue to be a diagnostic tool 68