* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PPT File
Survey
Document related concepts
Electromagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Electrical resistivity and conductivity wikipedia , lookup
History of electromagnetic theory wikipedia , lookup
Superconductivity wikipedia , lookup
Lorentz force wikipedia , lookup
Electrical resistance and conductance wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
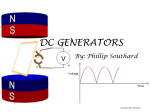
An alternating current generator, or AC generator, produces an alternating current, which means the voltage produced alternately reverses from positive to negative polarity, producing a corresponding change in the direction of current flow. Much like a DC generator, an AC generator requires a coil to cut across the force lines of a magnetic field. This coil is attached to two slip rings, which deliver the current to and from the load destination, thus completing the circuit. Alternating current generators are often called alternators. During the first half turn, the coil cuts across the field near the magnet's north pole. Electrons travel up the wire, and the lower slip ring becomes positively charged. When the coil cuts near the South Pole of the wire during the second half turn, the lower slip ring becomes negatively charged, and electrons move down the wire. The faster the coil turns, the faster the electrons move, increasing the frequency (in Hertz) of the current produced by the generator.